Extended Description of the Vector Map
Printable PDF Exact Detailed Map Zambia Admin, Roads, Cities, Towns, Railroads, Water objects Adobe PDF, 66 mb ZIP
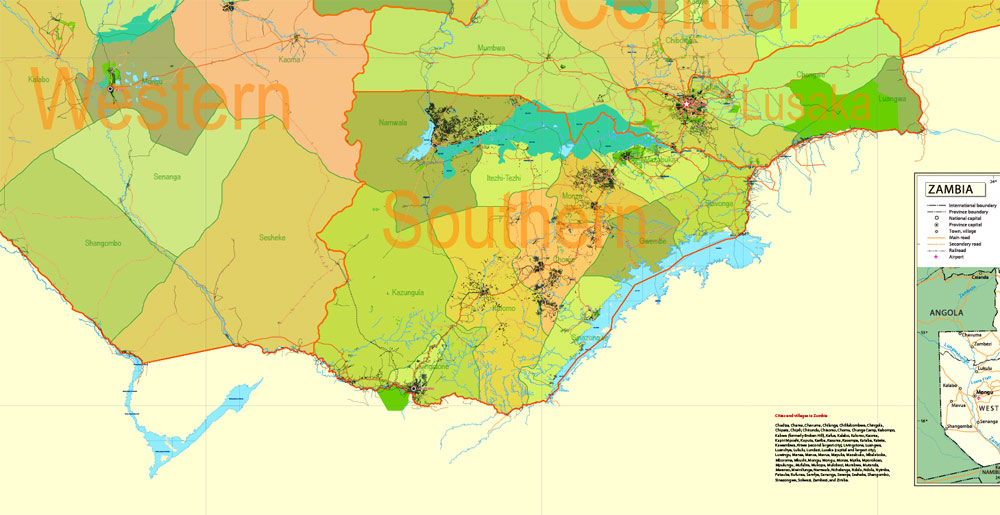
Map for publishing, design, printing, publications, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers and builders, business, logistics. The most exact and detailed map of the country.
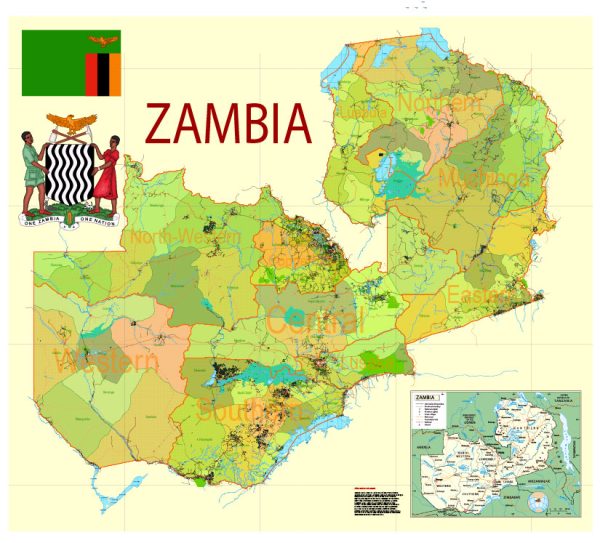
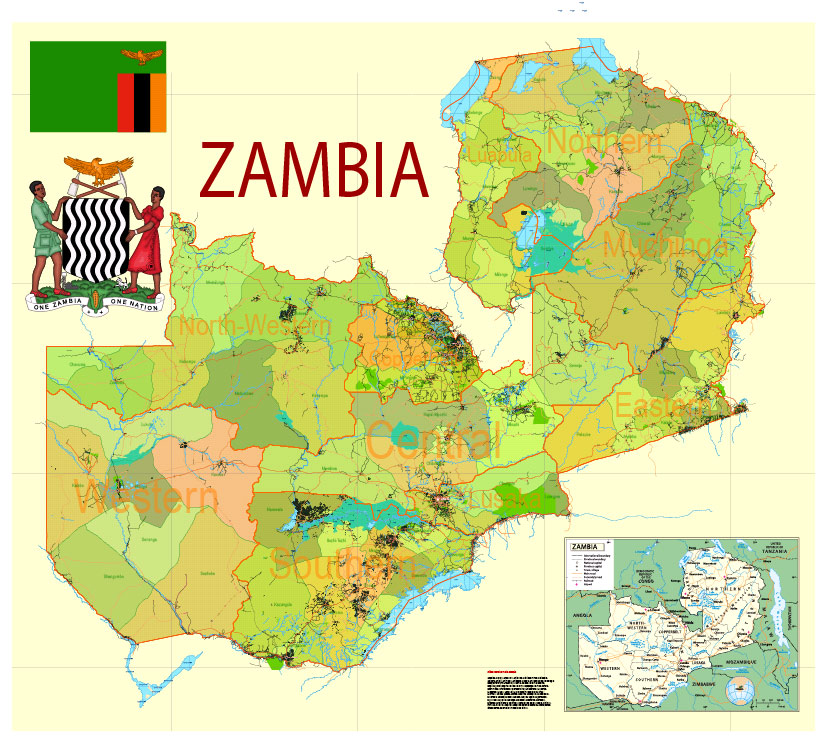
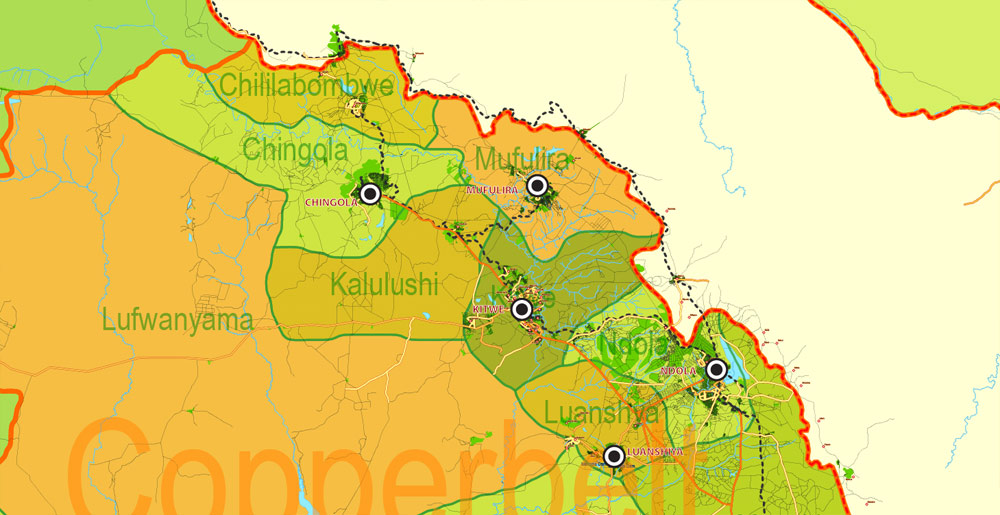
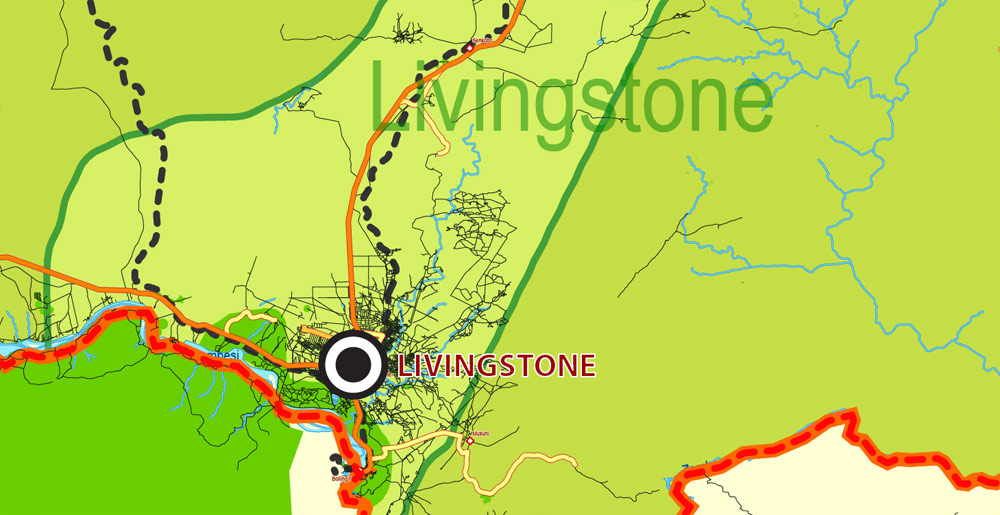
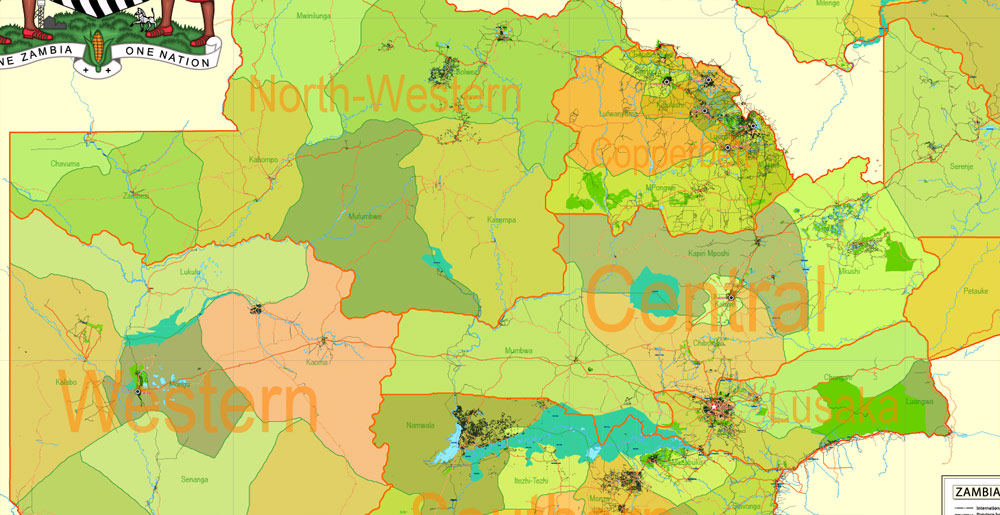
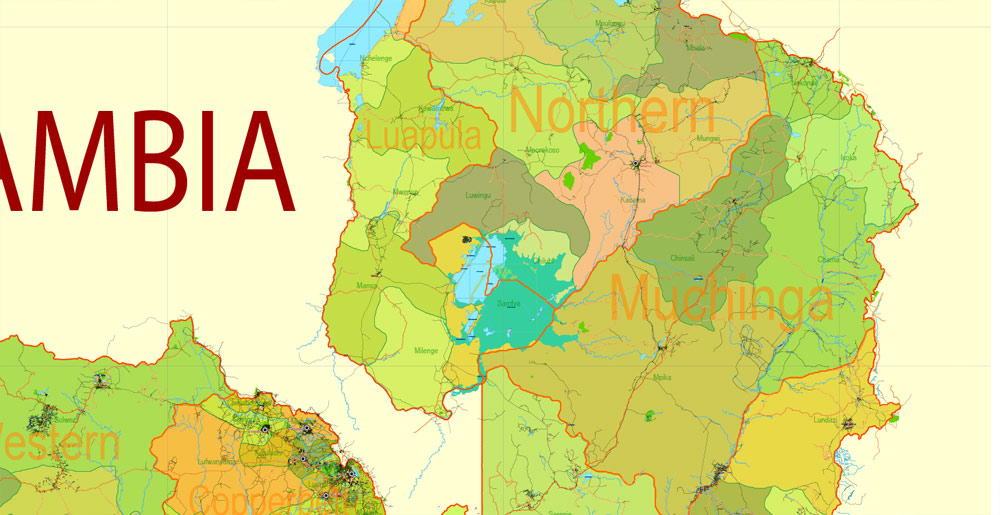
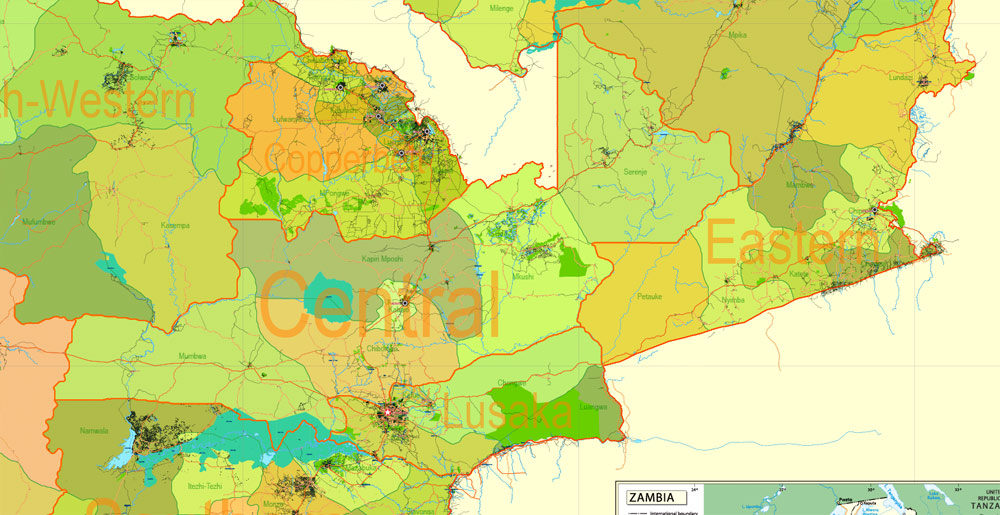
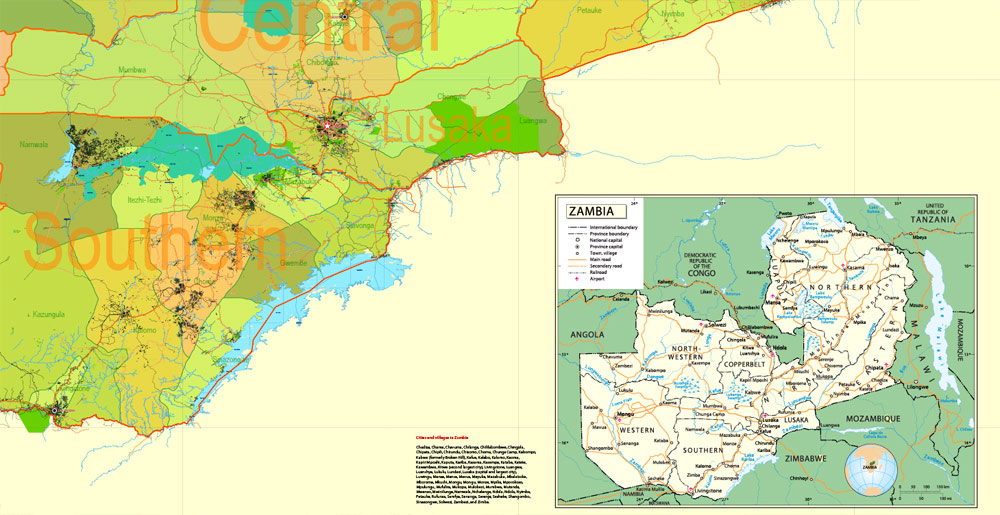
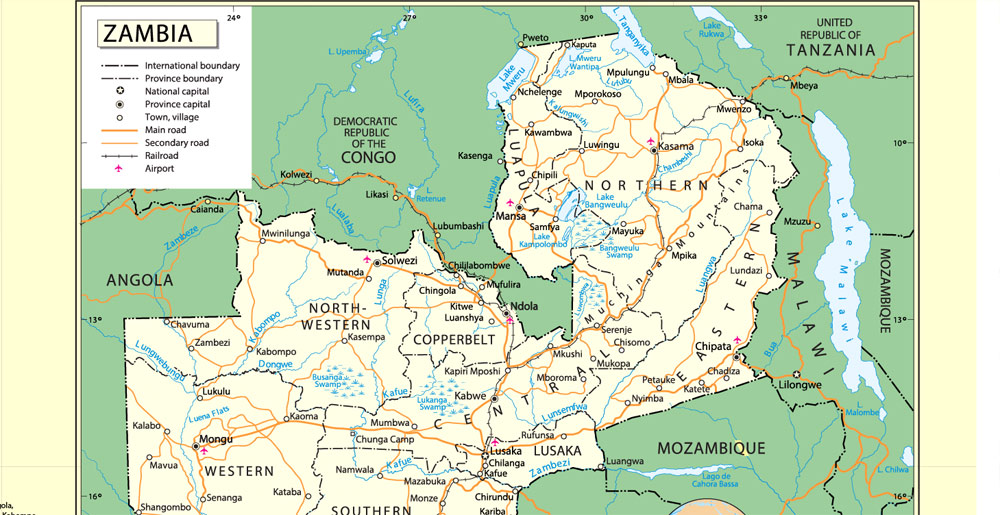
Layers: legend + coat of arms + simple map (UN) + flag, grids, waterways and water objects, names_water, districts and names_districts, provinces and names provinces, main_roads, civil_roads, main_cities with names and icons, towns and villages, names towns and villages, etc.
Text format names
DWG, DXF, ESRI Shapes, and other formats – by request, same price, please contact.
Zambia, Africa.
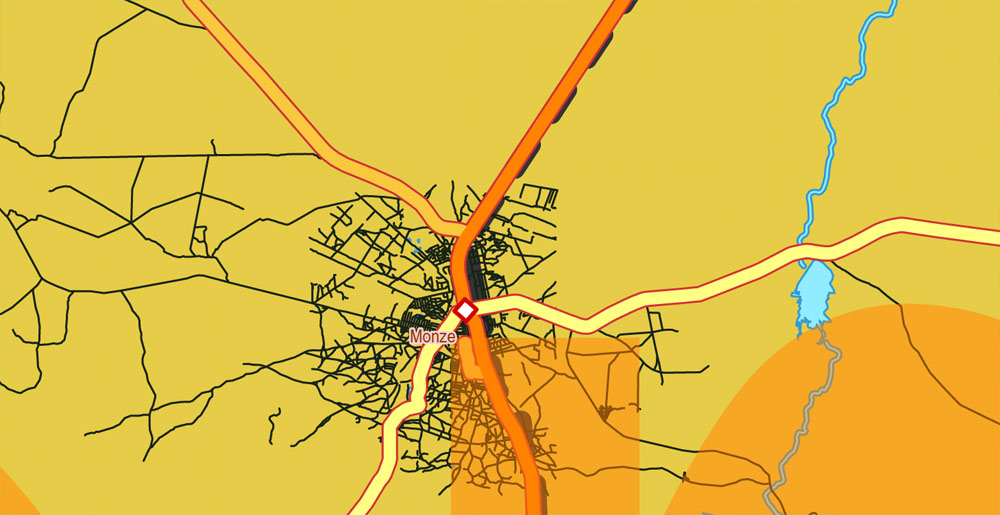
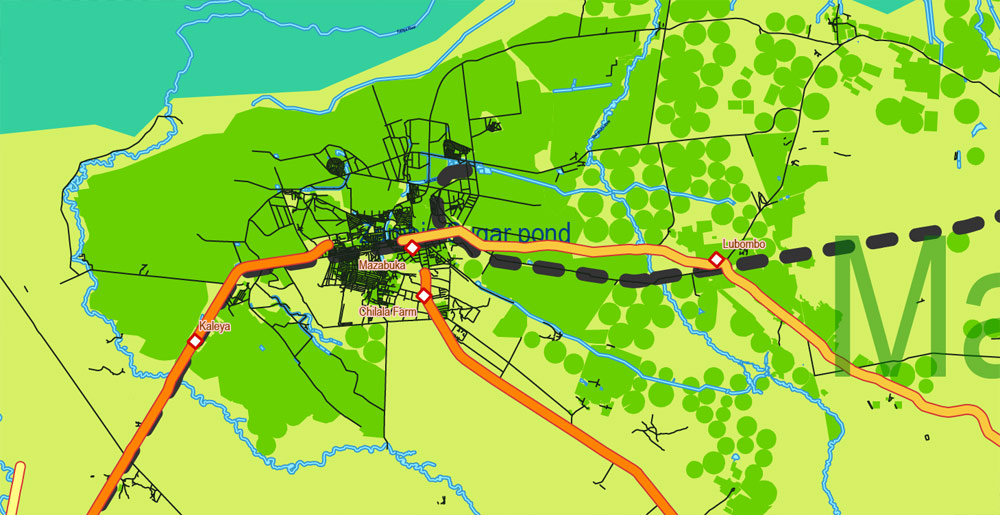
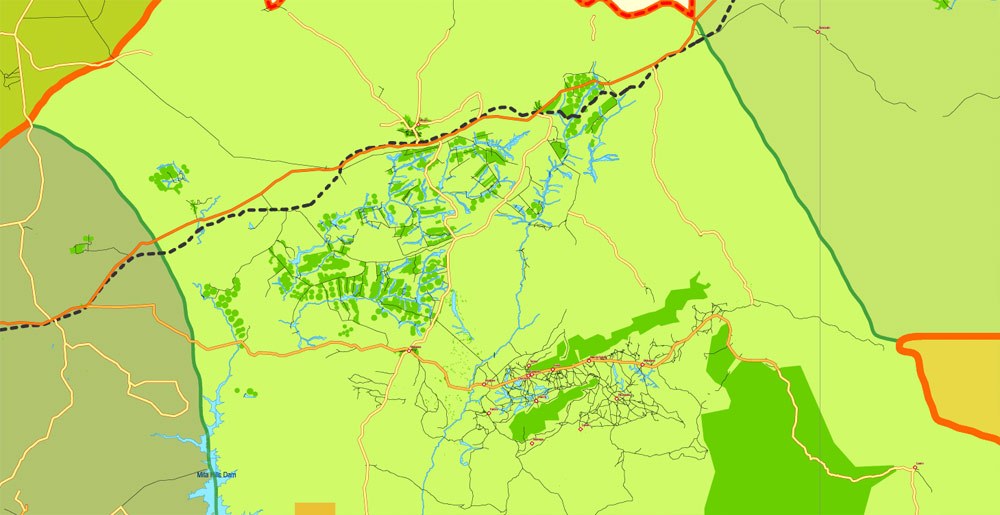
This vector map of Zambia is used as a basis for design, editing, and further printing.
This is the most detailed, exact map of Zambia for high-quality printing and polygraphy. You can always clarify the map development date by contacting us.
For your convenience, all objects on Zambia vector map are divided into layers. And the editing is very easy – colors, lines, etc.
You can easily add any objects needed (e.g. shops, salons, sale points, gas station or attraction) on any layer of Zambia vector map.
Zambia is a landlocked country in south-central Africa (although some sources consider it part of east Africa), neighbouring the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city is Lusaka, in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the northwest, the core economic hubs of the country.
The southernmost headstream of the Congo River rises in Zambia and flows west through its northern area firstly as the Chambeshi and then, after the Bangweulu Swamps as the Luapula, which forms part of the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Luapula flows south then west before it turns north until it enters Lake Mweru. The lake’s other major tributary is the Kalungwishi River, which flows into it from the east. The Luvua River drains Lake Mweru, flowing out of the northern end to the Lualaba River (Upper Congo River).
Lake Tanganyika is the other major hydrographic feature that belongs to the Congo basin. Its south-eastern end receives water from the Kalambo River, which forms part of Zambia’s border with Tanzania. This river has Africa’s second highest uninterrupted waterfall, the Kalambo Falls.
Zambia, in southern Africa, is a landlocked country of rugged terrain and diverse wildlife, with many parks and safari areas. On its border with Zimbabwe is famed Victoria Falls – indigenously called Mosi-oa-Tunya, or “Smoke That Thunders” – plunging a misty 108m into narrow Batoka Gorge. Spanning the Zambezi River just below the falls is Victoria Falls Bridge, a spectacular viewpoint.
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, neighbouring the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west. The capital city is Lusaka, in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the northwest, the core economic hubs of the country.
Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. After visits by European explorers in the eighteenth century, the region became the British protectorates of Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia and North-Eastern Rhodesia towards the end of the nineteenth century. These were merged in 1911 to form Northern Rhodesia. For most of the colonial period, Zambia was governed by an administration appointed from London with the advice of the British South Africa Company.
On 24 October 1964, Zambia became independent of the United Kingdom and prime minister Kenneth Kaunda became the inaugural president. Kaunda’s socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP) maintained power from 1964 until 1991. Kaunda played a key role in regional diplomacy, cooperating closely with the United States in search of solutions to conflicts in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. From 1972 to 1991 Zambia was a one-party state with the UNIP as the sole legal political party under the motto “One Zambia, One Nation”. Kaunda was succeeded by Frederick Chiluba of the social-democratic Movement for Multi-Party Democracy in 1991, beginning a period of social-economic growth and government decentralisation. Levy Mwanawasa, Chiluba’s chosen successor, presided over Zambia from January 2002 until his death in August 2008, and is credited with campaigns to reduce corruption and increase the standard of living. After Mwanawasa’s death, Rupiah Banda presided as Acting President before being elected President in 2008. Holding office for only three years, Banda stepped down after his defeat in the 2011 elections by Patriotic Front party leader Michael Sata. Sata died on 28 October 2014, the second Zambian president to die in office. Guy Scott served briefly as interim president until new elections were held on 20 January 2015, in which Edgar Lungu was elected as the sixth President.
In 2010, the World Bank named Zambia one of the world’s fastest economically reformed countries. The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is headquartered in Lusaka.
Area
• Total
752,618 km2 (290,587 sq mi) (38th)
• Water (%) 1
Population
• 2016 estimate 16,591,390 (68th)
• 2010 census 13,092,666
• Density 17.2/km2 (44.5/sq mi) (191st)
Author Rating
Aggregate Rating
no rating based on 0 votes
Zambia Administrative Map
Product Name Zambia Printable PDF Map Admin, Roads, Cities, Towns, Railroads, Water objects Adobe PDF
Price
USD 39
Product Availability
Available in Stock





 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS