The history of cartography, the art and science of mapmaking, spans thousands of years and has evolved significantly over time. Here’s a brief overview of key developments in the history of cartography, with a focus on the world map:
- Ancient Maps:
- The earliest known maps date back to ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians, who created clay tablets with basic representations of land and city layouts.
- The Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks also produced early maps.
- Ptolemy’s Geographia:
- In the 2nd century CE, the Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy created “Geographia,” a significant work that introduced the concepts of longitude and latitude and provided a framework for mapmaking.
- Ptolemy’s world maps were based on a grid system, and they influenced mapmaking for centuries.
- Medieval European Maps:
- During the Middle Ages, European maps were influenced by religious beliefs and lacked geographical accuracy.
- Mappa mundi, or world maps, from this era often depicted the world with Jerusalem at the center.
- Age of Exploration:
- The Renaissance and the Age of Exploration (15th to 17th centuries) spurred significant advancements in cartography.
- Navigational maps, known as portolan charts, became important for European explorers.
- Maps improved in terms of accuracy and detail as explorers charted new lands.
- Mercator Projection:
- In the 16th century, Gerardus Mercator developed a cylindrical projection that became the basis for modern world maps.
- The Mercator projection was particularly useful for navigation but led to distortions in the size of land masses at higher latitudes.
- 18th and 19th Centuries:
- Advances in surveying and the use of triangulation allowed for more accurate maps.
- Explorers like James Cook mapped the Pacific, while Lewis and Clark explored the western United States.
- 20th Century:
- The 20th century saw the development of topographic maps, which provided detailed information about the Earth’s surface.
- Aerial photography, satellites, and geographic information systems (GIS) revolutionized mapmaking.
- Digital Cartography:
- The digital revolution in the late 20th century led to the development of computer-based mapping and geographic information systems (GIS).
- Online mapping services like Google Maps and GPS navigation systems became ubiquitous.
- Modern Mapping:
- Today, cartography continues to evolve with the use of satellite imagery, remote sensing, and advanced GIS technologies.
- Maps are created for various purposes, including navigation, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and more.
The history of cartography is a rich and complex journey, marked by cultural, technological, and scientific advancements. It has played a crucial role in our understanding of the world and continues to be a vital tool for various fields and industries.


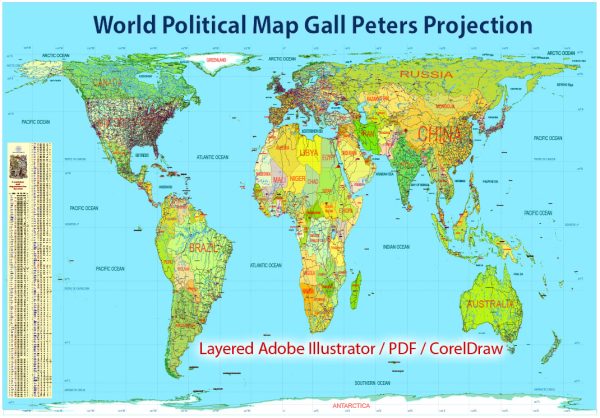
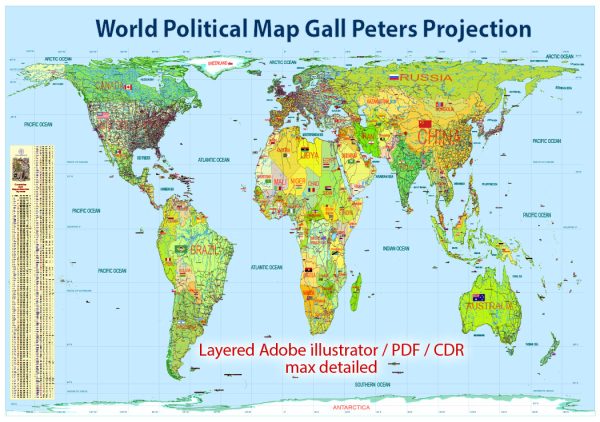
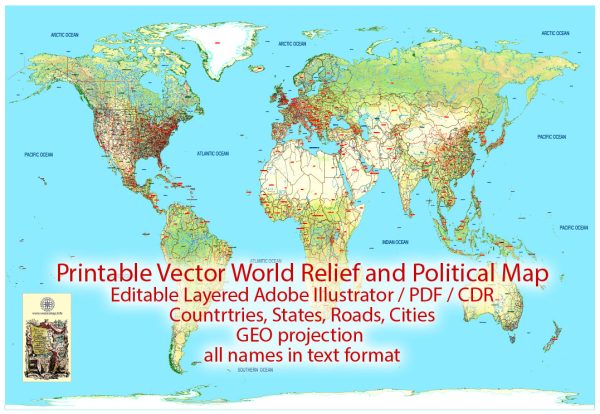
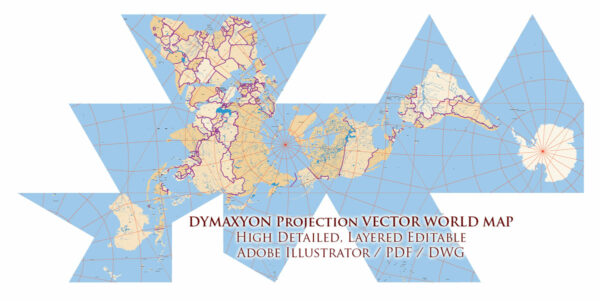
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS