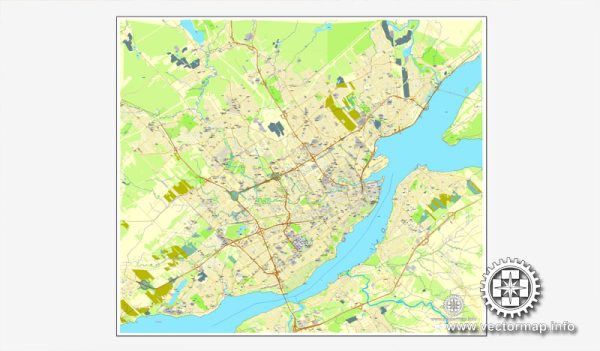
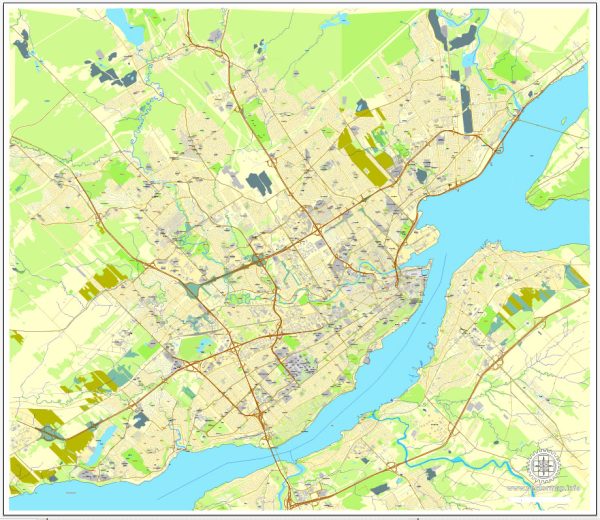
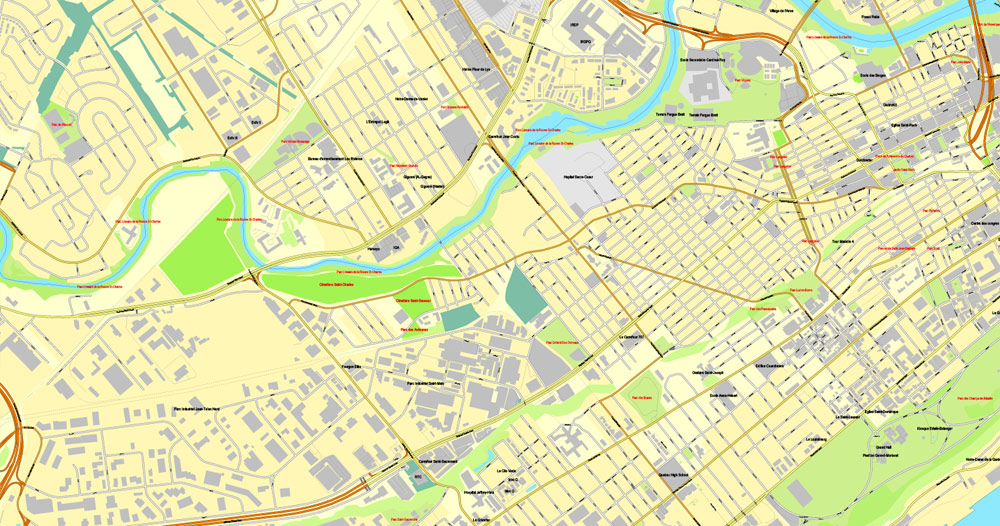
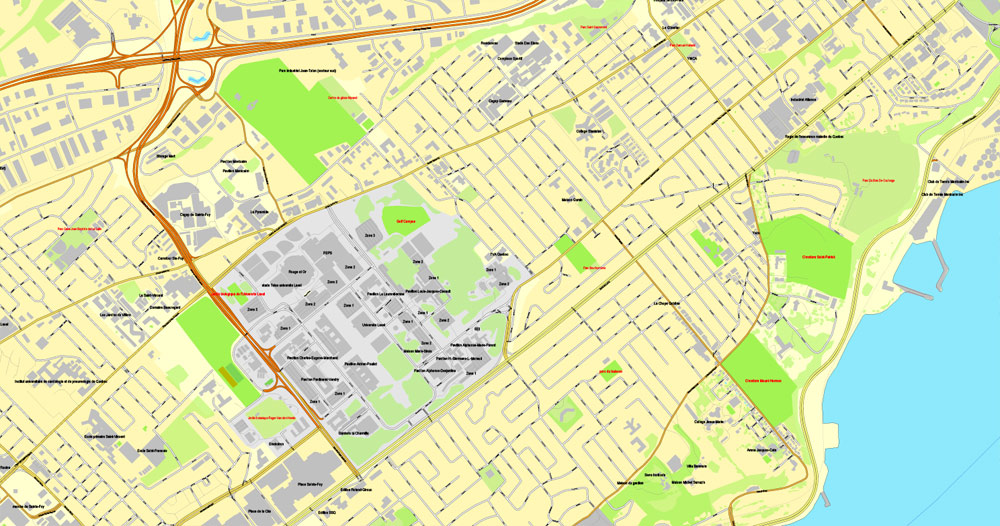
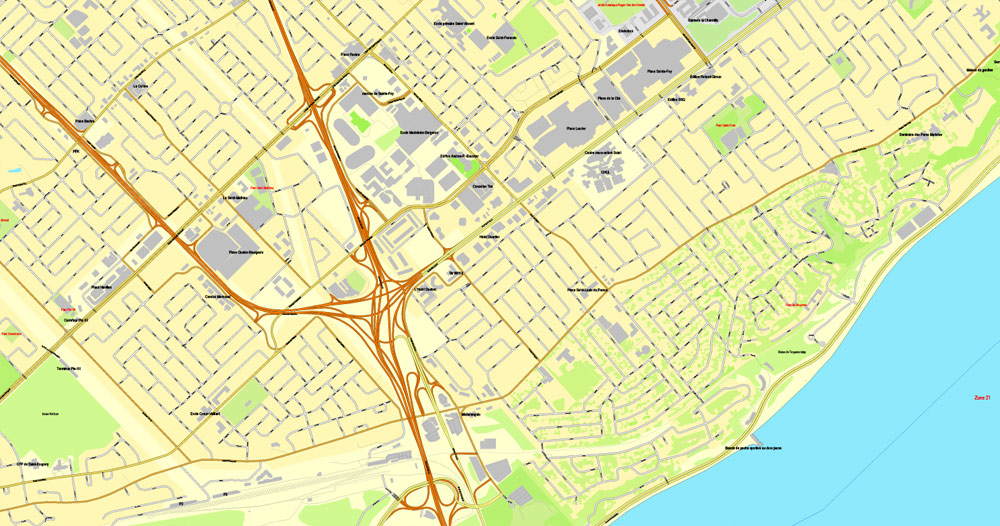
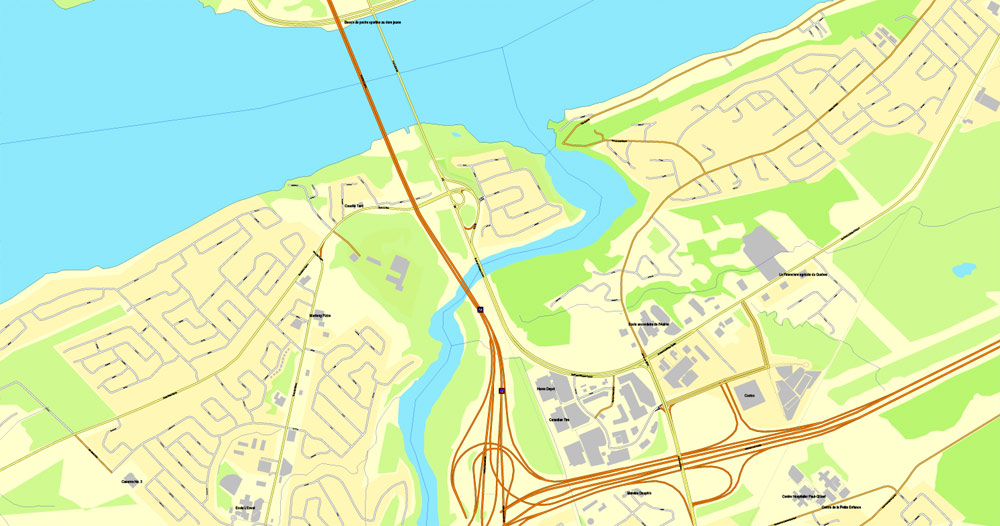
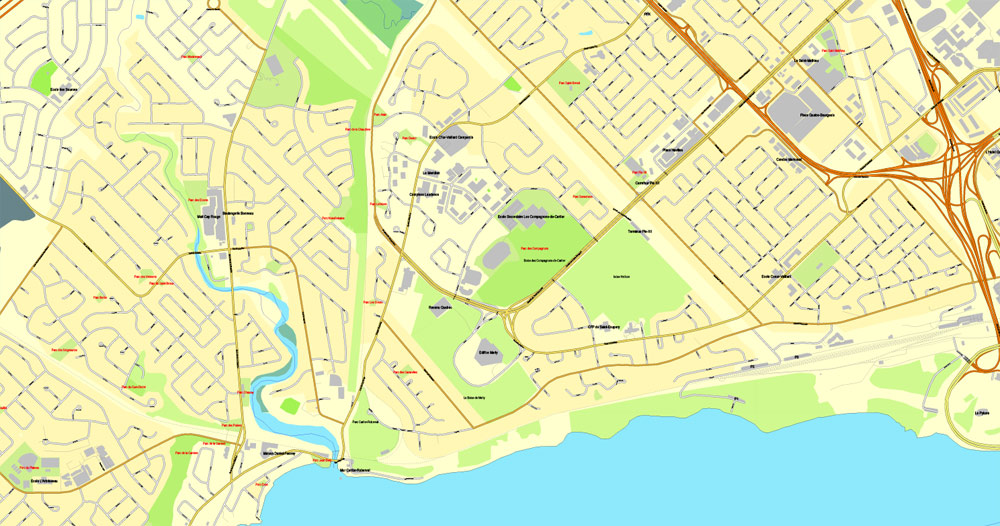
Quebec City Map, Canada, Printable City Plan V.3.09 Adobe PDF, full vector, Map V3.09, scalable, editable, separated text layer street names, 15 mb ZIP
All streets, some more buildings. Map for publishing, design, printing, arts, projects, presentations.
You can edit this file by Adobe Illustrator, Adobe Acrobat, Corel Draw.
CDR, DWG, DXF and other formats – on demand, same price, please, contact
Quebec, Canada.
This vector map of Quebec is used as a basis for design, editing, and further printing.
This is the most detailed, exact map of Quebec for high-quality printing and polygraphy. You can always clarify the map development date by contacting us.
For your convenience, all objects on Quebec vector map are divided into layers. And the editing is very easy – colors, lines, etc.
You can easily add any objects needed (e.g. shops, salons, sale points, gas station or attraction) on any layer of Quebec vector map.
Quebec is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is bordered to the west by the province of Ontario and the bodies of water James Bay and Hudson Bay; to the north by Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay; to the east by the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the province of Newfoundland and Labrador; and to the south by the province of New Brunswick and the U.S. states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York. It also shares maritime borders with Nunavut, Prince Edward Island, and Nova Scotia. Quebec is Canada’s largest province by area and its second-largest administrative division; only the territory of Nunavut is larger. It is historically and politically considered to be part of Central Canada (with Ontario).
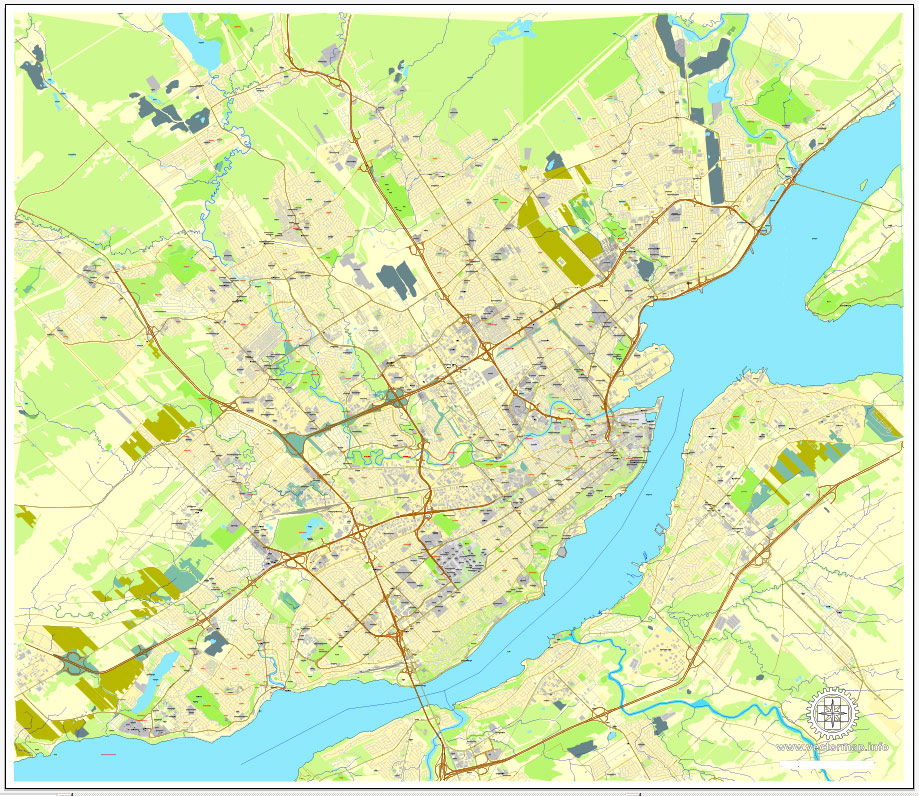
One of the advantages of Quebec vector maps of our production is the relevance of cartographic data, we constantly update all our products.
This vector map of Quebec is used by:
designers, layout designers, printers, advertisers and architects. Our product – vector maps – is designed for further editing and printing in large formats – from @Wall format (a few meters) to A-0 and A-1, A-2, A-3.
Quebec map in vector format is used for design, urban planning, presentations and media visualizations.
Advertising and presentation map of Quebec (usually the final designer marks the routes, and puts the client’s objects (shops, saloons, gas stations etc.)
The undoubted advantage is that people will NEVER throw out this advertising product – the map. In fact, as an advertising medium, a map is the most “long-playing” of the well-known polygraphic advertising media, with the longest lifespan, and the maximum number of interactions with the customer.
For travelers, maps are sold at the airports and gas stations around the world. Often the source is our vector maps.
Take a look, who purchases our vector maps of Quebec in “Our Clients and Friends” page – these are large and small companies, from super-brands like Volvo and Starbucks, to small design studios and printing houses.
It’s very easy to work with vector maps of Quebec, even for a not very experienced designer who can turn on and off the map layers, add new objects, change the colors of fill and lines according to customer requirements.
The undoubted advantage of Quebec vector maps in printing is an excellent and detailed visualization, when customer can expand a large paper map and instantly define his location, find a landmark, an object or address on map, unlike using the popular electronic formats of Google and Yandex maps for example.
Printable vector maps of Quebec are much more convenient and efficient than any electronic maps on your smartphone, because ALL DETAILS are displayed in the entire space of Quebec map.
Useful tips on working with vector maps of cities and countries in Adobe Illustrator.
«V» – launches the Selection tool (cursor, black arrow), which makes active any vector line.
«А» – launches the Direct Selection tool (white cursor), allows you to select curve elements and drag them to the desired place.
«R» – activates the Rotate tool, which helps you rotating selected objects around the center point by 360 degrees.
«E» – gives you the opportunity to use the Eraser tool and erase unnecessary parts.
«X» – switches between Fill and Stroke in the Tools section. Try to get used to this hot key and
you will quickly understand that you can’t live and work without it.
Guides are not limited to vertical and horizontal in Adobe Illustrator. You can also create a diagonal guide for example. Moreover, you can turn any contours into guides. Select the outline and go to View > Guides > Make Guides (Create Guides), or simply press Cmd/Ctrl + 5. You can also turn the guides back into an editable object. Go to menu, View > Guides > Unlock Guides (Release Guides), select the guide you want to edit and select View > Guides > Release Guides (Reset Guides), or just press Cmd/Ctrl + Option / Alt + 5).
Quebec is the second-most populous province of Canada, after Ontario. It is the only one to have a predominantly French-speaking population, with French as the sole provincial official language. Most inhabitants live in urban areas near the Saint Lawrence River between Montreal and Quebec City, the capital. Approximately half of Quebec residents live in the Greater Montreal Area, including the Island of Montreal. English-speaking communities and English-language institutions are concentrated in the west of the island of Montreal but are also significantly present in the Outaouais, Eastern Townships, and Gaspé regions. The Nord-du-Québec region, occupying the northern half of the province, is sparsely populated and inhabited primarily by Aboriginal peoples. The climate around the major cities is four-season continental with cold and snowy winters combined with warm to hot humid summers, but farther north long winter seasons dominate and as a result the northern areas of the province are marked by tundra conditions. Even in central Quebec, at comparatively southerly latitudes, winters are severe in inland areas.
You will probably want to change the color scheme used on our Quebec vector map.
To quickly and effectively play with colors.
Of course, you can do it manually, all objects in our Quebec vector map are divided according to types and layers, and you can easily change the color gamma of vector objects in groups and layers.
But there is more effective way of working with the whole VECTOR MAP of Quebec and all layers:
The overview dialog «Edit colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» (this dialog box name can change depending on the context):
If you have selected a part or a layer of Quebec vector map and open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or the Color Catalog, or if you choose Edit > Edit Colors> Repaint Graphic Object, then the «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box appears, and you get access to «Assign» and «Edit» tabs.
If a picture or a map fragment is not selected, and you open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or in the Color Catalog, the «Edit Colors» dialog box appears and you can only access the «Edit» tab.
Regardless of the name at the top of the dialog box, the right-hand side always displays the color group of the current document, as well as two default color groups: Print Color and Grayscale. These color groups can be selected and used any time.
Quebec independence debates have played a large role in the politics of the province. Parti Québécois governments held referendums on sovereignty in 1980 and 1995; both were rejected by voters, the latter defeated by a very narrow margin. In 2006, the House of Commons of Canada passed a symbolic motion recognizing the “Québécois as a nation within a united Canada”.
While the province’s substantial natural resources have long been the mainstay of its economy, sectors of the knowledge economy such as aerospace, information and communication technologies, biotechnology, and the pharmaceutical industry also play leading roles. These many industries have all contributed to helping Quebec become an economically influential province within Canada, second only to Ontario in economic output.
Create and edit color groups of Quebec vector map, and also assign colors using the «Edit Colors»/ а «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
A. Creating and editing of a color group on the «Edit» tab
B. Assigning colors on the «Assign» tab
C. Select a group of colors from the «Color groups» list
The option «Repaint a graphic object» in the lower part of the dialog box allows you to preview the colors on a selected layer of Vector map, or a group of elements, and specify whether its colors will be redefined when the dialog box is closed.
The main areas of the dialog box are:
«Edit»
The «Edit» tab is designed to create a new or edit the existing color groups.
The harmony rules Menu and the Color Wheel are used to conduct experiments with color harmonies. The color wheel shows how colors are related in color harmony, and the color bars allow you to view and manipulate an individual color values. In addition, you can adjust the brightness, add and remove colors, save color groups and view colors on the selected Vector Map of Quebec or a separated layers.
«Assign»
The «Assign» tab is used to view and control on how the original colors are replaced with colors from the color group like your corporate colors in the Vector Map of Quebec.
The assign color ability is provided only if the entire map, layer or fragment is selected in the document. You can specify which of new colors replace the current colors, whether the spot colors should be preserved and how colors are replaced (for example, you can replace colors completely or changing the color tone while maintaining the brightness). The «Assign» tab allows you to redefine colors in the Vector Map of Quebec, or in separate layers and fragments using the current color group or reducing the number of colors in the current Vector Map.
Color groups
Is a list of all saved color groups for current document (the same groups appear in the «Samples» palette). You can edit and delete the existing color groups, as well as creating a new ones using the list of “Color Groups” in the dialog box. All changes appear in the «Samples» palette.
The highlighted color group shows, which color group is currently edited.
Any color group can be selected and edited, or used to redefine the colors in the selected vector map of Quebec , its fragments or elements.
Saving a color group adds this group to the specified list.
Opening the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
Open the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box using one of the following methods:
«Edit»> «Edit Colors»> «Repaint Graphic object» or «Repaint With Style».
Use these commands if you need to edit the colors in the selected vector map of Quebec city.
«Repaint Graphic object» button on the «Control» panel.
Use this button if you need to adjust colors of Quebec vector map using the а «Repaint graphic object» dialog box.
The specified button is available if the selected vector map or its fragment contains two or more colors.
Note. This color editing method is convenient for global color adjustment in a vector map, if global colors were not used when creating a Map of Quebec.
The «Edit colors» button or «Edit or apply colors» on the «Color Catalog» palette
Click this button if you need to edit colors on the «Color Catalog» palette or edit and then apply them to the selected Vector Map of Quebec or its fragment.
The «Edit color group» button or «Edit or apply color group» on the «Samples» palette.
Click this button if you need to edit the colors in the specific color group or edit and apply them to the selected Vector Map of Quebec or a group of its elements, for example, the whole layer “Streets and lines”. You can also double-click the color group in the Samples panel to open the dialog box.
If the map file is too large and your computer freezes or even can’t open it quickly:
1. Try to reduce the color resolution of the video card (display) to 256 colors while working with a large map.
2. Using Windows Task Manager, select all the application you don’t need, while working with map, just turn them off.
3. Launch Adobe Illustrator. (DO NOT OPEN the vector map file)
4. Start the Windows Task Manager using administrator rights > Find the “Illustrator” process > set the «real time» priority,
5. Open the file. When you see the LEGACY FONT popup window – click “OK” (do not update). You can restore the TEXT later.
6. Can also be useful: When file is opened – Edit > Settings > Basic Settings > disable smoothing. /// It looks scary, but works quickly)))
We recommend saving the file in Adobe Illustrator 10 version. It’s much more stable when working with VERY BIG size files.
Quebec is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is bordered to the west by the province of Ontario and the bodies of water James Bay and Hudson Bay; to the north by Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay; to the east by the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the province of Newfoundland and Labrador; and to the south by the province of New Brunswick and the U.S. states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York. It also shares maritime borders with Nunavut, Prince Edward Island, and Nova Scotia. Quebec is Canada’s largest province by area and its second-largest administrative division; only the territory of Nunavut is larger. It is historically and politically considered to be part of Central Canada (with Ontario).
Quebec is the second-most populous province of Canada, after Ontario. It is the only one to have a predominantly French-speaking population, with French as the sole provincial official language. Most inhabitants live in urban areas near the Saint Lawrence River between Montreal and Quebec City, the capital. Approximately half of Quebec residents live in the Greater Montreal Area, including the Island of Montreal. English-speaking communities and English-language institutions are concentrated in the west of the island of Montreal but are also significantly present in the Outaouais, Eastern Townships, and Gaspé regions. The Nord-du-Québec region, occupying the northern half of the province, is sparsely populated and inhabited primarily by Aboriginal peoples. The climate around the major cities is four-season continental with cold and snowy winters combined with warm to hot humid summers, but farther north long winter seasons dominate and as a result the northern areas of the province are marked by tundra conditions. Even in central Quebec, at comparatively southerly latitudes, winters are severe in inland areas.
Quebec independence debates have played a large role in the politics of the province. Parti Québécois governments held referendums on sovereignty in 1980 and 1995; both were rejected by voters, the latter defeated by a very narrow margin. In 2006, the House of Commons of Canada passed a symbolic motion recognizing the “Québécois as a nation within a united Canada”.
While the province’s substantial natural resources have long been the mainstay of its economy, sectors of the knowledge economy such as aerospace, information and communication technologies, biotechnology, and the pharmaceutical industry also play leading roles. These many industries have all contributed to helping Quebec become an economically influential province within Canada, second only to Ontario in economic output.
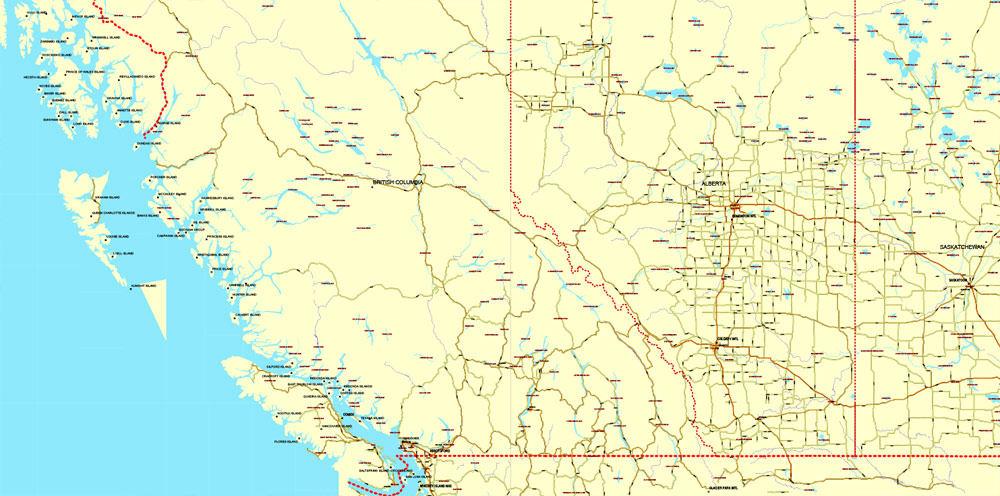
Quebec, Canada’s largest province, occupies a vast territory (nearly three times the size of France), most of which is very sparsely populated. With an area of 1,542,056 square kilometres (595,391 square miles), it is the second largest of Canada’s provinces and territories and the tenth largest country subdivision in the world. More than 90 percent of Quebec’s area lies within the Canadian Shield, and includes the greater part of the Labrador Peninsula. Quebec’s highest mountain is Mont D’Iberville, which is located on the border with Newfoundland and Labrador in the northeastern part of the province in the Torngat Mountains. The addition of parts of the vast and scarcely populated District of Ungava of the Northwest Territories between 1898 and 1912 gave the province its current form.
Quebec is bordered by the province of Ontario, James Bay and Hudson Bay (including the circular Nastapoka arc) to the west, the provinces of New Brunswick and Newfoundland and Labrador to the east, the United States (Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont and New York) to the south, and Hudson Strait and Ungava Bay to the north. Its northernmost point is Cape Wolstenholme.
Quebec includes several islands. These include Island of Montreal and Îles Laval, which are parts of the major cities of Montreal and Laval, respectively, Anticosti Island, a sparsely populated island in the outlet of the Saint Lawrence River, and the Magdalen Islands, an archipelago in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
In 1927, the border between the Province of Quebec and the Dominion of Newfoundland was delineated by the British Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. The government of Quebec does not officially recognize this boundary. See The Labrador boundary dispute.
The territory of Quebec is extremely rich in resources in its coniferous forests, lakes, and rivers—pulp and paper, lumber, and hydroelectricity are still some of the province’s most important industries. The far north of the province, Nunavik, is subarctic or arctic and is mostly inhabited by Inuit.
The most populous region is the Saint Lawrence River valley in the south, where the capital, Quebec City, and the largest city, Montreal, are situated. North of Montreal are the Laurentians, a range of ancient mountains, and to the east are the Appalachian Mountains which extends into the Eastern Townships and Gaspésie regions. The Gaspé Peninsula juts into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the East. The Saint Lawrence River Valley is a fertile agricultural region, producing dairy products, fruit, vegetables, maple sugar (Quebec is the world’s largest producer), and livestock.
In 1899, the United States claimed Fox Island under the Guano Islands Act of 1856.
Hydrography
Quebec has one of the world’s largest reserves of fresh water, occupying 12% of its surface. It has 3% of the world’s renewable fresh water, whereas it has only 0.1% of its population. More than half a million lakes, including 30 with an area greater than 250 square kilometres (97 sq mi), and 4,500 rivers pour their torrents into the Atlantic Ocean, through the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the Arctic Ocean, by James, Hudson, and Ungava bays. The largest inland body of water is the Caniapiscau Reservoir, created in the realization of the James Bay Project to produce hydroelectric power. Lake Mistassini is the largest natural lake in Quebec.
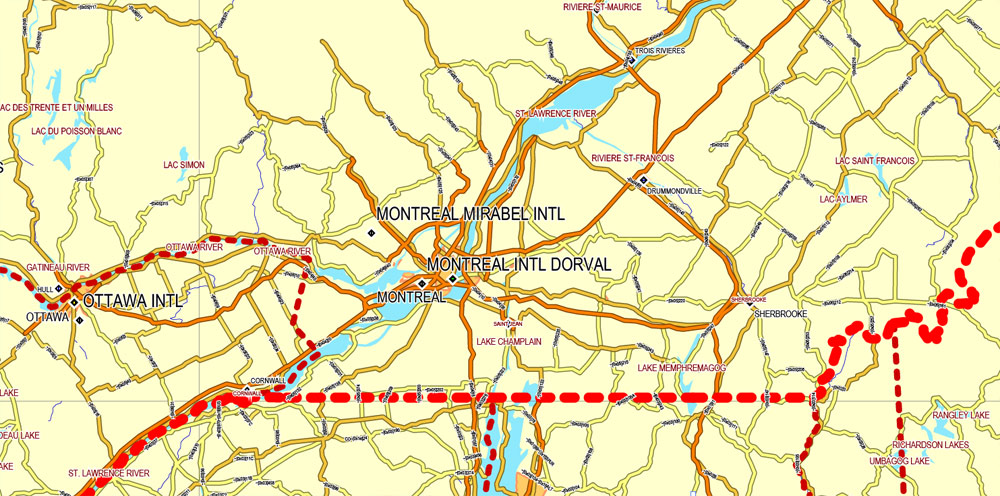
The Saint Lawrence River has some of the world’s largest sustaining inland Atlantic ports at Montreal (the province’s largest city), Trois-Rivières, and Quebec City (the capital). Its access to the Atlantic Ocean and the interior of North America made it the base of early French exploration and settlement in the 17th and 18th centuries. Since 1959, the Saint Lawrence Seaway has provided a navigable link between the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes. Northeast of Quebec City, the river broadens into the world’s largest estuary, the feeding site of numerous species of whales, fish, and seabirds. The river empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. This marine environment sustains fisheries and smaller ports in the Lower Saint Lawrence (Bas-Saint-Laurent), Lower North Shore (Côte-Nord), and Gaspé (Gaspésie) regions of the province. The Saint Lawrence River with its estuary forms the basis of Quebec’s development through the centuries. Other notable rivers include the Ashuapmushuan, Chaudière, Gatineau, Manicouagan, Ottawa, Richelieu, Rupert, Saguenay, Saint-François, and Saint-Maurice.
Topography
Quebec’s highest point at 1,652 metres is Mont d’Iberville, known in English as Mount Caubvick, located on the border with Newfoundland and Labrador in the northeastern part of the province, in the Torngat Mountains. The most populous physiographic region is the Saint Lawrence Lowland. It extends northeastward from the southwestern portion of the province along the shores of the Saint Lawrence River to the Quebec City region, limited to the North by the Laurentian Mountains and to the South by the Appalachians. It mainly covers the areas of the Centre-du-Québec, Laval, Montérégie and Montreal, the southern regions of the Capitale-Nationale, Lanaudière, Laurentides, Mauricie and includes Anticosti Island, the Mingan Archipelago, and other small islands of the Gulf of St. Lawrence lowland forests ecoregion. Its landscape is low-lying and flat, except for isolated igneous outcrops near Montreal called the Monteregian Hills, formerly covered by the waters of Lake Champlain. The Oka hills also rise from the plain. Geologically, the lowlands formed as a rift valley about 100 million years ago and are prone to infrequent but significant earthquakes. The most recent layers of sedimentary rock were formed as the seabed of the ancient Champlain Sea at the end of the last ice age about 14,000 years ago. The combination of rich and easily arable soils and Quebec’s relatively warm climate makes this valley the most prolific agricultural area of Quebec province. Mixed forests provide most of Canada’s springtime maple syrup crop. The rural part of the landscape is divided into narrow rectangular tracts of land that extend from the river and date back to settlement patterns in 17th century New France.
Autumn landscape of Haute-Gaspésie
More than 95% of Quebec’s territory lies within the Canadian Shield. It is generally a quite flat and exposed mountainous terrain interspersed with higher points such as the Laurentian Mountains in southern Quebec, the Otish Mountains in central Quebec and the Torngat Mountains near Ungava Bay. The topography of the Shield has been shaped by glaciers from the successive ice ages, which explains the glacial deposits of boulders, gravel and sand, and by sea water and post-glacial lakes that left behind thick deposits of clay in parts of the Shield. The Canadian Shield also has a complex hydrological network of perhaps a million lakes, bogs, streams and rivers. It is rich in the forestry, mineral and hydro-electric resources that are a mainstay of the Quebec economy. Primary industries sustain small cities in regions of Abitibi-Témiscamingue, Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean, and Côte-Nord.
Mont Tremblant Resort, Laurentian Mountains
The Labrador Peninsula is covered by the Laurentian Plateau (or Canadian Shield), dotted with mountains such as Otish Mountains. The Ungava Peninsula is notably composed of D’Youville mountains, Puvirnituq mountains and Pingualuit crater. While low and medium altitude peak from western Quebec to the far north, high altitudes mountains emerge in the Capitale-Nationale region to the extreme east, along its longitude. In the Labrador Peninsula portion of the Shield, the far northern region of Nunavik includes the Ungava Peninsula and consists of flat Arctic tundra inhabited mostly by the Inuit. Further south lie the subarctic taiga of the Eastern Canadian Shield taiga ecoregion and the boreal forest of the Central Canadian Shield forests, where spruce, fir, and poplar trees provide raw materials for Quebec’s pulp and paper and lumber industries. Although the area is inhabited principally by the Cree, Naskapi, and Innu First Nations, thousands of temporary workers reside at Radisson to service the massive James Bay Hydroelectric Project on the La Grande and Eastmain rivers. The southern portion of the shield extends to the Laurentians, a mountain range just north of the Saint Lawrence Lowland, that attracts local and international tourists to ski hills and lakeside resorts.
The Appalachian region of Quebec has a narrow strip of ancient mountains along the southeastern border of Quebec. The Appalachians are actually a huge chain that extends from Alabama to Newfoundland. In between, it covers in Quebec near 800 km (497 mi), from the Montérégie hills to the Gaspé Peninsula. In western Quebec, the average altitude is about 500 metres, while in the Gaspé Peninsula, the Appalachian peaks (especially the Chic-Choc) are among the highest in Quebec, exceeding 1000 metres.
Québec is a predominantly French-speaking province in eastern Canada with 2 vibrant cities in its south, connected by the Chemin du Roy highway along the Saint Lawrence River. The metropolis Montréal is named after Mt. Royal, the triple-peaked hill at its heart. Dating to 1608, Québec City retains its old colonial core, Place Royale, and historic harbor, Vieux Port, now known for nightlife.
Area: 1.667 million km²
Founded: July 3, 1608
Population: 8.215 million (Jul 1, 2014)
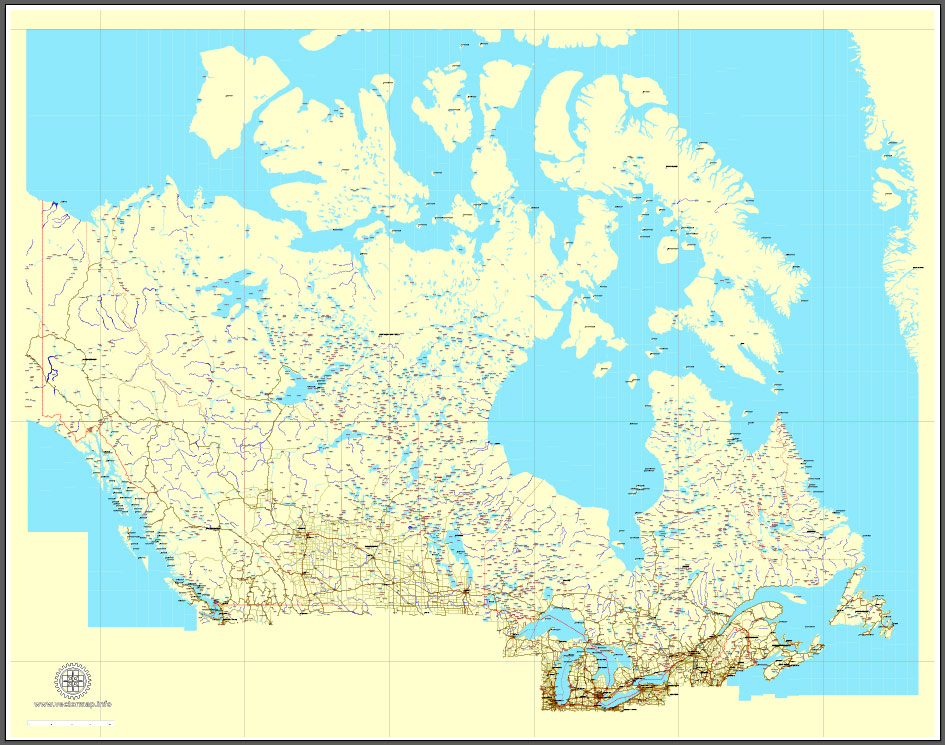
Download Free vector Map Canada, mainroads, cities, borders, province borders, Adobe Illustrator Text format street names, full editable, Layers: grownd, nombres, borders, symbols, halo
vector_map_canada_mainroads_mercator_projection_ai-ai
Download Free PDF Map Canada, mainroads, cities, borders, province borders, Adobe PDF Text format street names, full editable, Layers: grownd, nombres, borders, symbols, halo
vector_map_canada_mainroads_mercator_projection_pdf-pdf

















 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS