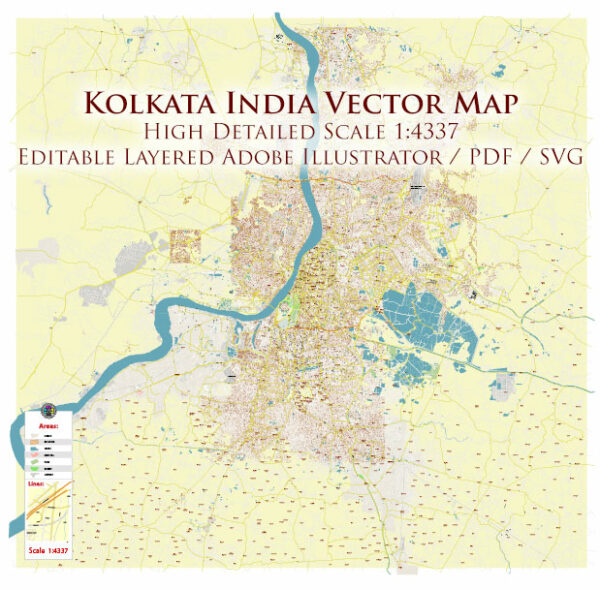
Extended Description of the Vector Map
Printable SVG Vector Map of Kolkata India high detailed scale 1:4337 full editable Street Map in layers, scalable, text format all names, 33 MB ZIP
All street names, Main Objects, Buildings. Map for design, printing, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers, and builders, business, logistics.

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers
Layers list:
- Legend
- Grids
- Labels of roads
- Names of places (city, hamlet, etc.)
- Names of objects (hospitals, parks, water)
- Names of main streets
- Names of secondary streets
- Arrows of streets
- Main Streets, roads,
- Railroads
- Secondary streets
- Railroads
- Buildings
- Airports and heliports
- Water objects (rivers, lakes, ponds)
- Color fills (parks, hospital areas, land use, etc.)
- Background
The most exact and detailed map of the city in scale.
For Editing and High-Quality Printing
Kolkata, India: Historical Description
Early Origins and Foundation (Pre-17th Century)
- Ancient and Medieval Roots : The area around Kolkata was part of the ancient kingdom of Gangaridai , mentioned by Greek and Roman historians. Medieval Bengal saw the rise of Hindu and Muslim dynasties, but the region remained a cluster of villages like Kalikata , Sutanuti , and Govindapur .
- Portuguese and Mughal Influence : The Portuguese established a trading post near Kolkata in the 16th century. By the late 17th century, the Mughal Empire controlled the region, leasing land to the British East India Company.
British Colonial Era (1690–1947)
- Founding by the British : In 1690, Job Charnock , an agent of the East India Company, acquired the villages of Kalikata, Sutanuti, and Govindapur. Though Charnock is traditionally credited as the founder, modern scholarship suggests Kolkata emerged organically through trade and settlement.
- Capital of British India : Kolkata became the capital of British India in 1772 under Warren Hastings , the first Governor-General. The construction of Fort William (1756–1773) solidified British control.
- Growth as a Colonial Hub : The city flourished as a center of trade, education, and administration. Landmarks like St. John’s Church (1787), Government House (now Raj Bhavan, 1803), and the Victoria Memorial (1921) symbolized colonial power.
- Cultural Renaissance : Kolkata became the birthplace of the Bengal Renaissance in the 19th century, driven by reformers like Raja Ram Mohan Roy (founder of the Brahmo Samaj), Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar , and later, Rabindranath Tagore (Nobel laureate in Literature, 1913). Institutions like Hindu College (1817) and University of Calcutta (1857) fostered intellectual growth.
- Political Turmoil : The city was a hotspot for resistance:
- Partition of Bengal (1905) : Triggered widespread protests during the Swadeshi Movement .
- Revolutionary Movements : Figures like Aurobindo Ghosh and Subhas Chandra Bose mobilized anti-British sentiment.
- Indian National Congress : Played a key role in the independence struggle, hosting sessions in Kolkata.
Post-Independence Era (1947–Present)
- Partition and Refugee Crisis : The 1947 partition of India displaced millions, with Kolkata absorbing a massive influx of refugees from East Pakistan (now Bangladesh).
- Capital Shift : In 1911, the British shifted India’s capital to New Delhi , diminishing Kolkata’s political prominence but not its cultural and economic influence.
- Naxalite Movement : The 1970s saw violent leftist uprisings (Naxalite movement), reflecting socio-economic tensions.
- Economic Decline and Resilience : Kolkata faced industrial decline post-independence but remained a hub for education, arts, and literature. The Howrah Bridge (1943) and Metro Railway (1984) symbolized infrastructure resilience.
- Name Change : In 2001, the city’s name officially reverted to Kolkata (closer to its Bengali pronunciation).
Cultural Legacy
- Diverse Communities : Armenians, Jews, Chinese, and Anglo-Indians contributed to Kolkata’s cosmopolitan identity.
- Literary and Artistic Heritage : Home to luminaries like Tagore, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay (author of Vande Mataram ), and filmmakers like Satyajit Ray.
- Festivals : Kolkata’s Durga Puja is a UNESCO-recognized cultural spectacle.
Modern Kolkata
Today, Kolkata balances its colonial legacy with contemporary challenges. It remains a center for education (e.g., IIT Kharagpur, Jadavpur University), literature, and cinema, while grappling with urbanization and political dynamics. Its history is etched in its architecture, streets, and the enduring spirit of its people.

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

Kolkata India SVG Vector Map Exact Extra High Detailed Street Map in layers

















 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS