Extended Description of the Vector Map
Printable PDF Vector Map of Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China (English names) detailed map + admin areas + cities, roads, railroads and water objects, editable Adobe PDF, scalable, editable text/curves format of names, 4 Mb ZIP.
Fully editable map: Map for publishing, design, printing, publications, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers, and builders, business, logistics. The most exact and detailed map. GPS correct Mercator Projection.
For printing any format.
DWG, DXF, CDR, ESRI Shapes, and other formats – by request, the same price, please contact.

Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China PDF Vector Map Road and Railroad map + admin areas + Main cities, water objects editable Adobe PDF (English)
AO BRIEF (Statistical) — Chengdu–Chongqing–Xi’an Macro-Region, China
-
Inland western China growth belt linking Chengdu (Sichuan Basin west), Chongqing (upper Yangtze metropolis), and Xi’an (Guanzhong Plain).
-
Functional triangle distance scale: Chengdu–Chongqing ≈ 300 km; Chongqing–Xi’an ≈ 650 km; Chengdu–Xi’an ≈ 700 km (corridor routing dependent).
Administrative & Population Metrics (2020 census era)
| City / Municipality |
Admin Level |
Population (municipal) |
Urbanized Core Character |
| Chengdu |
Sub-provincial city |
~20.9 million |
Flat basin megacity, polycentric expansion |
| Chongqing |
Direct-admin municipality |
~32.0 million |
Mountain–river megaregion; large rural hinterland |
| Xi’an |
Sub-provincial city |
~13.0 million |
Plain-city on Guanzhong corridor |
Combined macro population: ~66 million+
Physical Geography & Elevation Bands
| Zone |
Elevation |
Terrain Type |
Mobility Impact |
| Sichuan Basin (Chengdu) |
450–750 m |
Alluvial plain, low relief |
High road/rail density, logistics-friendly |
| Chongqing Uplands |
200–900 m (urban core on terraces) |
Deeply dissected hills, river gorges |
Tunnel/bridge reliance, chokepoint risk |
| Qinling–Daba Approaches (to Xi’an) |
1,000–2,500 m passes |
Mountain corridors |
Limited parallel routes |
| Guanzhong Plain (Xi’an) |
350–600 m |
Broad basin/valley floor |
Strong surface mobility |
Transport Infrastructure (High-Level Counts)
Expressways (G-series + provincial)
-
Chengdu Basin network density: among the highest in western China; multiple ring roads (≥3) plus radial G-routes.
-
Chongqing: >20 major Yangtze/Jialing river bridges within metro area; complex stacked interchanges.
-
Northbound corridors toward Xi’an: 2–3 primary expressway axes through mountain tunnel systems (weather/landslide sensitive).
High-Speed Rail (HSR)
-
Chengdu–Chongqing HSR travel time ≈ 1–1.5 hrs.
-
Xi’an connected to both via national HSR grid; Xi’an–Chengdu HSR crosses Qinling tunnels.
-
Stations per metro: typically 4–8 major HSR nodes in wider municipal footprint.
Airports
| City |
Major Airport System |
Notes |
| Chengdu |
Dual-airport system |
Western aviation hub; intercontinental reach |
| Chongqing |
Major single hub |
Central-west air logistics pivot |
| Xi’an |
Primary northwest hub |
Strong military/civil aviation history |
Inland River Transport
-
Chongqing is the upper Yangtze’s largest inland port city.
-
River class supports 10,000-ton barge convoys downstream seasonally (water level dependent).
Economic Structure (Sector Weight)
| Sector |
Chengdu |
Chongqing |
Xi’an |
| Electronics / IT |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
| Automotive / Heavy Industry |
Moderate |
Very High |
Moderate |
| Aerospace / Defense Industry |
High |
Moderate |
High |
| Logistics & Trade |
High |
Very High |
High |
| Education & R&D |
High |
High |
Very High |
Urban Form Indicators
| Metric |
Chengdu |
Chongqing |
Xi’an |
| Terrain constraint |
Low |
Very High |
Low |
| River crossings (major urban) |
Few |
Dozens |
Few |
| Average urban density |
High |
High core / dispersed outskirts |
High historic core |
| Logistics park suitability |
Excellent |
Limited by topography |
Good |
Risk & Constraint Statistics (Qualitative Frequency)
-
Seismic exposure: Western Sichuan margin — moderate to high regional hazard.
-
Flood risk (river stage): Seasonal operational impacts in Chongqing riverfront zones.
-
Fog/haze days: Elevated winter frequency affecting aviation reliability.
-
Landslide corridors: Mountain expressways toward Xi’an — localized closure risk.
Strategic Transport Ratios
-
Intra-basin redundancy (Chengdu–Chongqing): High.
-
Inter-basin redundancy (to Xi’an): Moderate–low.
-
Multimodal diversity index: Chongqing highest (road+rail+river+air).
Command Takeaways (Data-Driven)
-
Population mass + industry density make this one of China’s largest inland economic clusters (~66M people).
-
Chongqing = multimodal freight pivot but highest terrain friction.
-
Chengdu = logistics geometry advantage (flat basin).
-
Xi’an = northern corridor anchor with strong rail/air orientation.
-
Mobility bottlenecks concentrate in mountain tunnel belts and major river bridges.
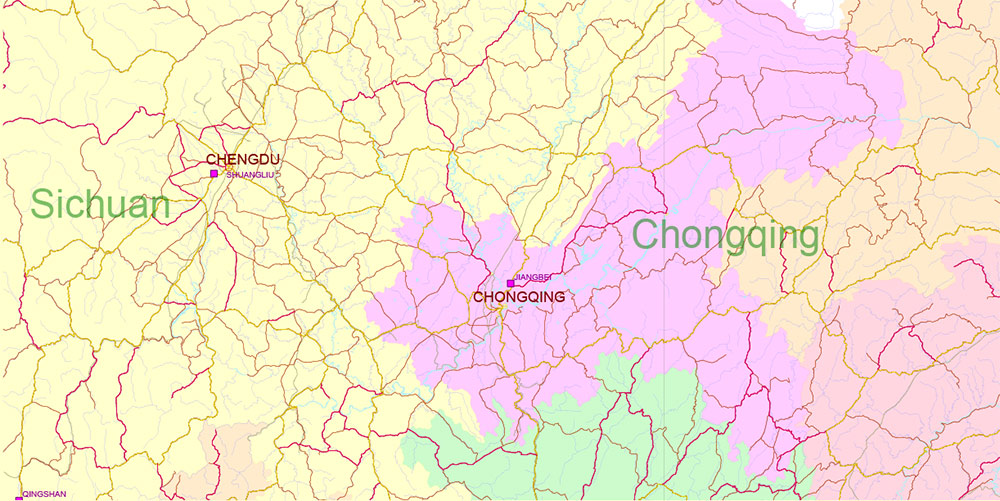
Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China PDF Vector Map Road and Railroad map + admin areas + Main cities, water objects editable Adobe PDF (English)
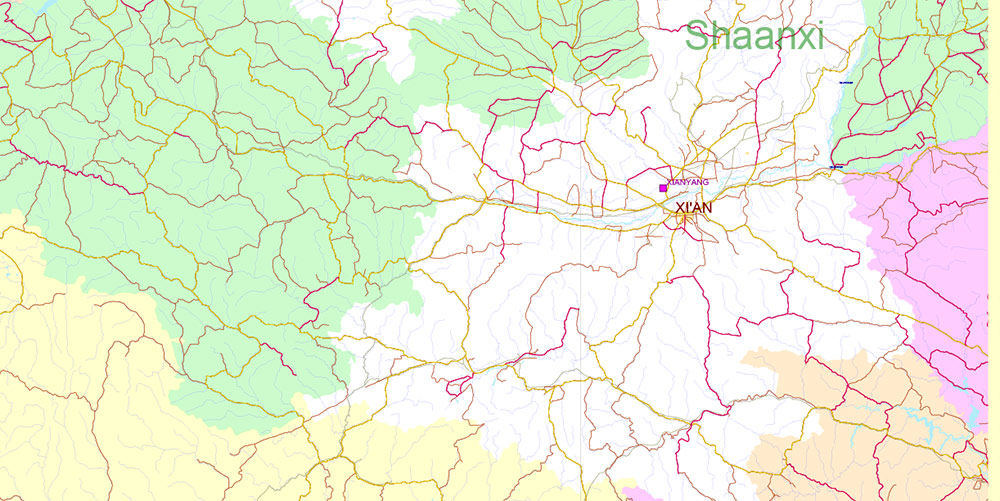
Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China PDF Vector Map Road and Railroad map + admin areas + Main cities, water objects editable Adobe PDF (English)
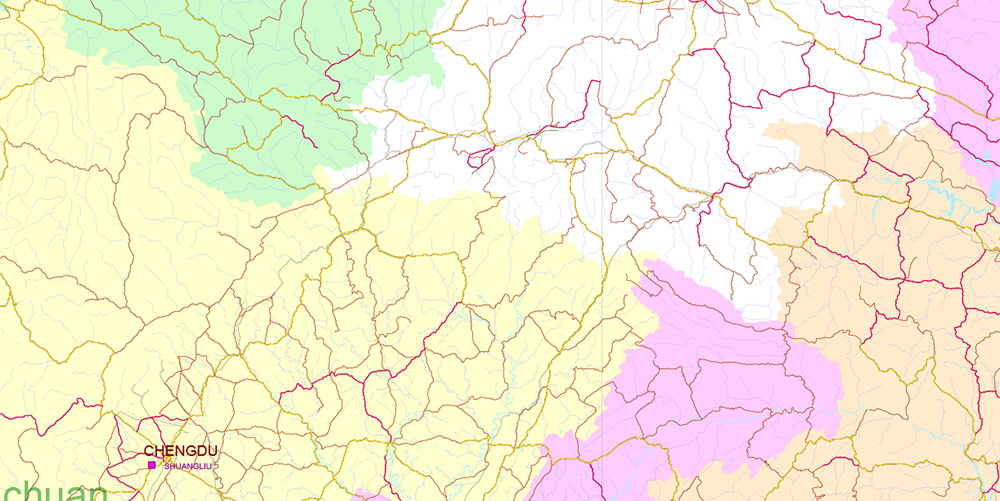
Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China PDF Vector Map Road and Railroad map + admin areas + Main cities, water objects editable Adobe PDF (English)
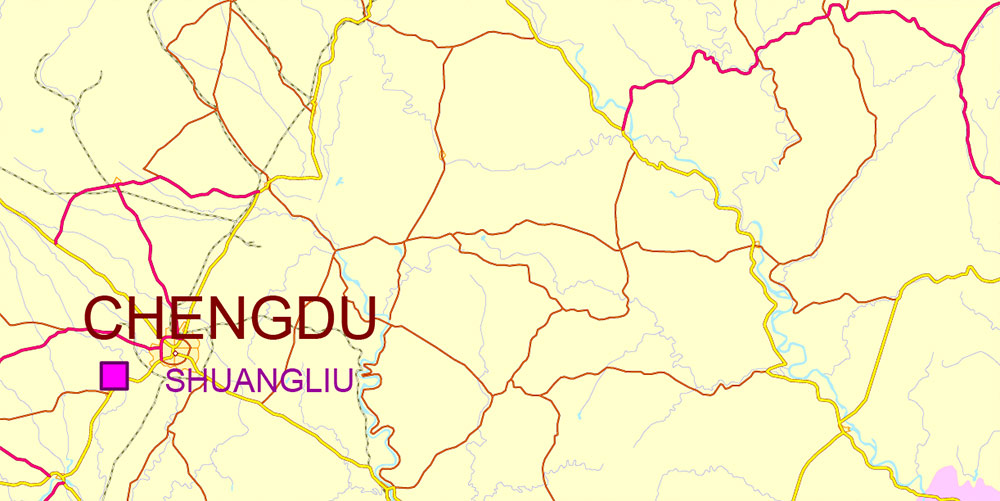
Chengdu, Xi’An and Chonquing China PDF Vector Map Road and Railroad map + admin areas + Main cities, water objects editable Adobe PDF (English)







 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS