Dortmund, located in the North Rhine-Westphalia region of Germany, has a rich history of urban development that spans centuries. The city’s evolution reflects the broader historical and economic changes in the region.
- Medieval Period (circa 882-1803):
- Dortmund’s history can be traced back to the 9th century when it was first mentioned in records around 882 AD. It was initially a small village but grew in importance due to its location as a crossroads for trade routes.
- The city became a member of the Hanseatic League, a medieval trade association that facilitated commerce between cities in Northern Europe. This significantly boosted Dortmund’s economic and political influence.
- Industrialization (19th Century):
- The 19th century marked a significant turning point for Dortmund with the onset of industrialization. The city became a major center for coal and steel production, contributing to the growth of heavy industry.
- The expansion of industrial activities led to a rapid increase in population, and Dortmund transformed into a bustling urban center.
- World War II (1939-1945):
- Like many German cities, Dortmund suffered extensive damage during World War II due to bombings. The city’s industrial infrastructure was particularly targeted because of its importance to the war effort.
- Post-war reconstruction efforts were focused on rebuilding the city and its industries.
- Post-War Period and Economic Transformation:
- In the post-war period, Dortmund experienced an economic shift away from heavy industry towards a more diversified economy. The city embraced technology, services, and education sectors.
- The establishment of the Technical University of Dortmund in 1968 contributed to the city’s reputation as a center for education and research.
- Modern Urban Development:
- In recent decades, Dortmund has undergone urban renewal and redevelopment projects, transforming former industrial areas into residential, commercial, and recreational spaces.
- The Phoenix See, a large artificial lake created on the site of former steelworks, is an example of successful urban redevelopment, providing a waterfront area for leisure and residential development.
- Cultural and Sporting Hub:
- Dortmund is renowned for its vibrant cultural scene, with theaters, museums, and galleries contributing to its cultural richness.
- The city is also known for its passionate sports culture, particularly football. Borussia Dortmund, one of Germany’s most successful football clubs, has a significant impact on the city’s identity.
- Transportation and Infrastructure:
- Dortmund’s transportation infrastructure has evolved over the years. The city is a major railway hub, and the Dortmund Airport connects it to national and international destinations.
- Modern urban planning focuses on sustainable development, with an emphasis on public transportation and green spaces.
Dortmund’s history of urban development reflects the resilience of the city, adapting to economic and social changes while preserving elements of its rich heritage. The integration of modern amenities with historical landmarks contributes to Dortmund’s unique character as a dynamic and evolving urban center.


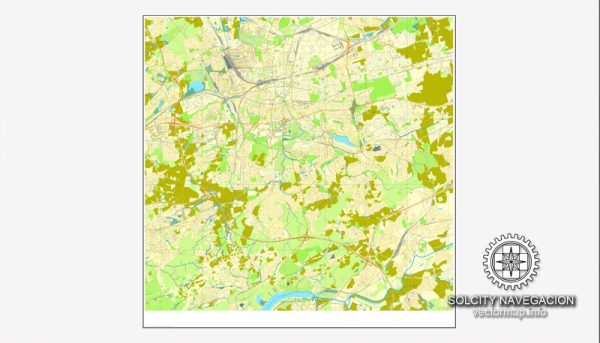
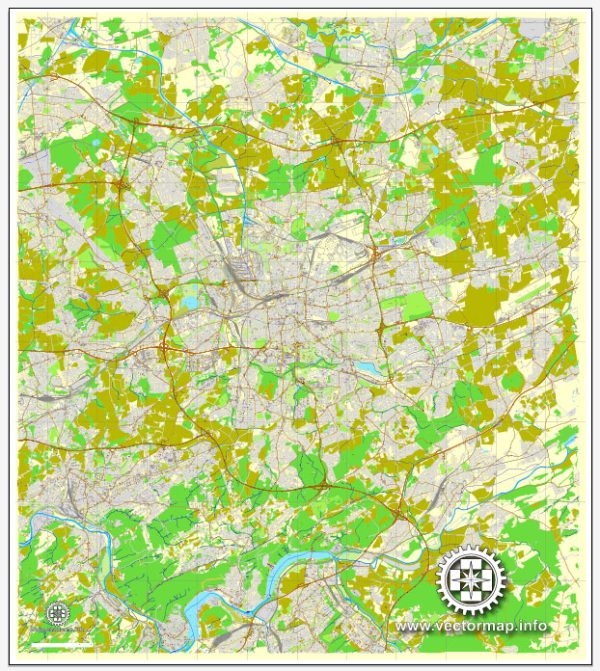
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D.
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D.