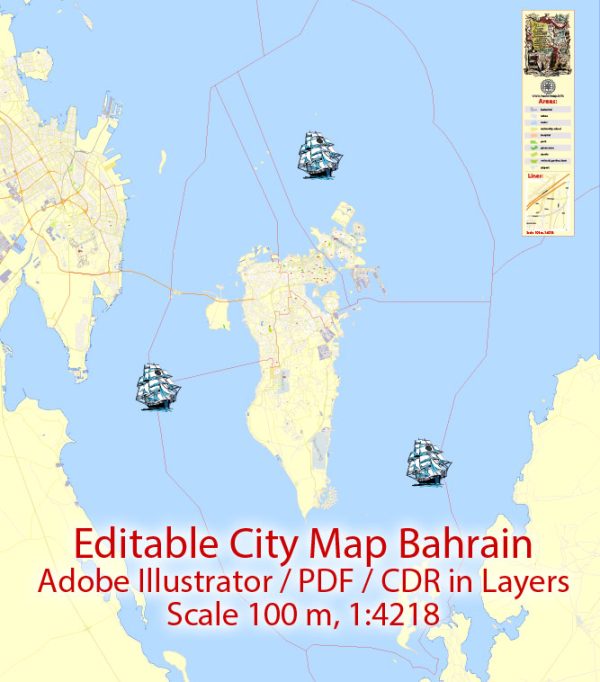
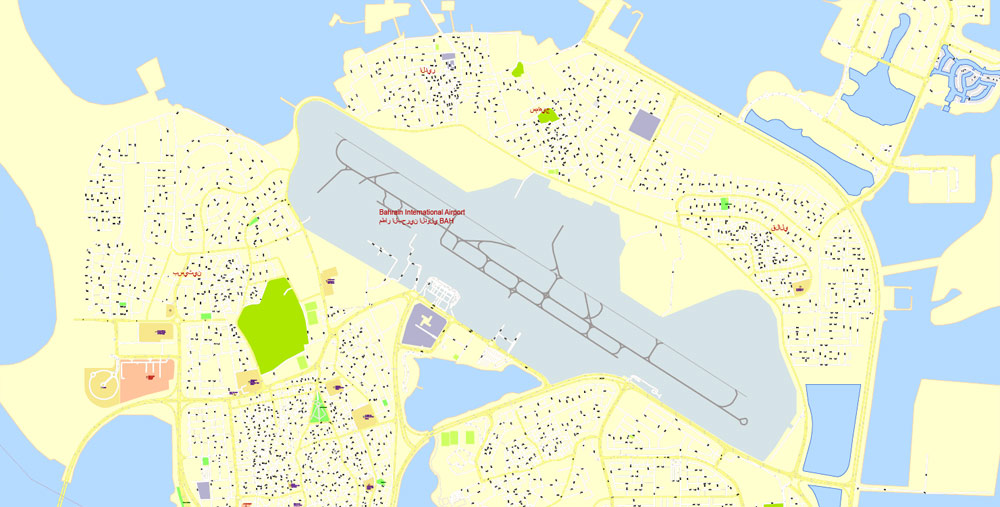
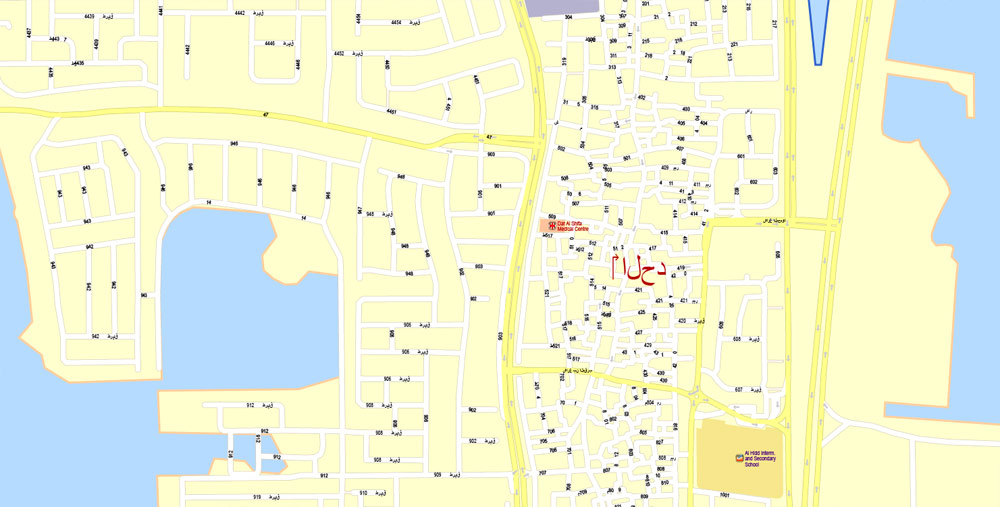
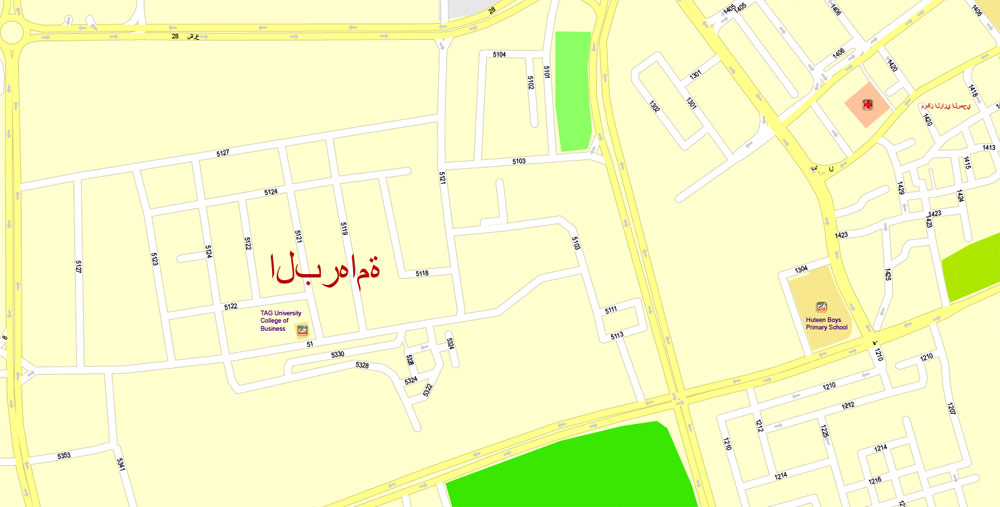
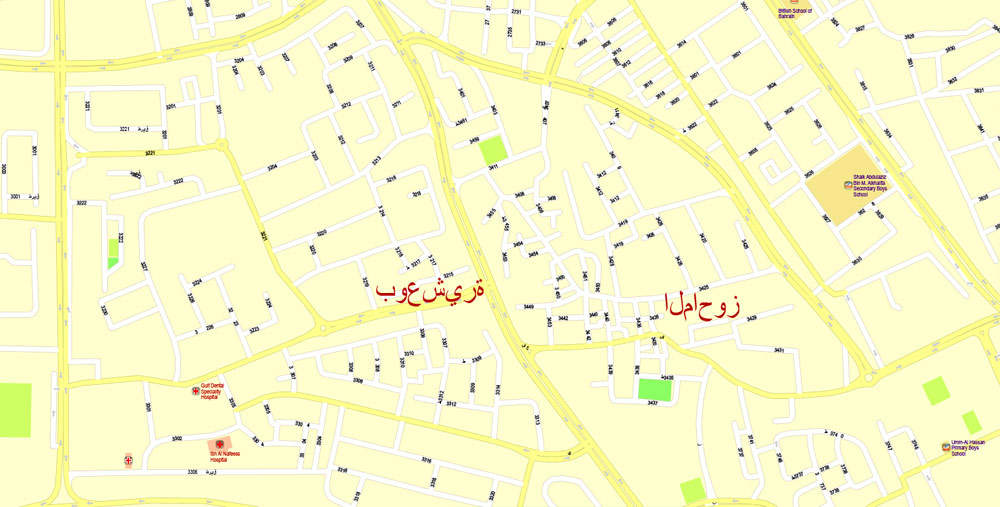
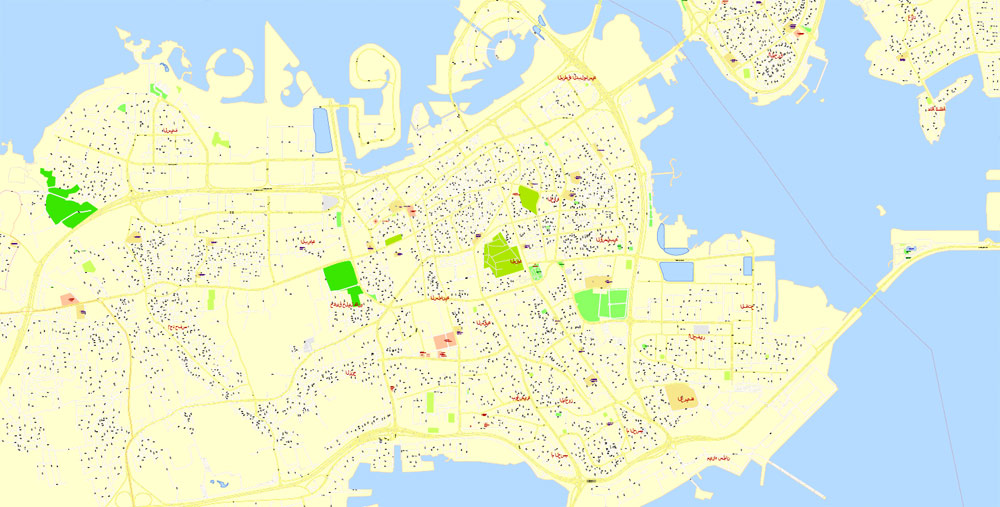
Printable Vector Map Bahrain, exact detailed City Plan, Scale 1:4218, editable Layered Adobe Illustrator Street Map, 16 Mb ZIP.
All streets named, main objects, all Buildings. Map for publishing, design, printing, publications, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers and builders, business, logistics. The most exact and detailed map of the city.
Layers: legend, grids, labels_roads, names_places, names_streets, names_objects, objects, arrows_streets, streets_roads, color_fills, etc.
DWG, DXF, CDR, ESRI Shapes, and other formats – by request, same price, please contact.
Bahrain.
This vector map of Bahrain is used as a basis for design, editing, and further printing.
This is the most detailed, exact map of Bahrain for high-quality printing and polygraphy. You can always clarify the map development date by contacting us.
For your convenience, all objects on Bahrain vector map are divided into layers. And the editing is very easy – colors, lines, etc.
You can easily add any objects needed (e.g. shops, salons, sale points, gas station or attraction) on any layer of Bahrain vector map.
Bahrain is an island country in the Persian Gulf. The sovereign state comprises a small archipelago centered around Bahrain Island, situated between the Qatar peninsula and the north eastern coast of Saudi Arabia, to which it is connected by the 25-kilometre (16 mi) King Fahd Causeway. Bahrain’s population is 1,234,571 (c. 2010), including 666,172 non-nationals. It is 765.3 square kilometres (295.5 sq mi) in size, making it the third-smallest nation in Asia after the Maldives and Singapore.
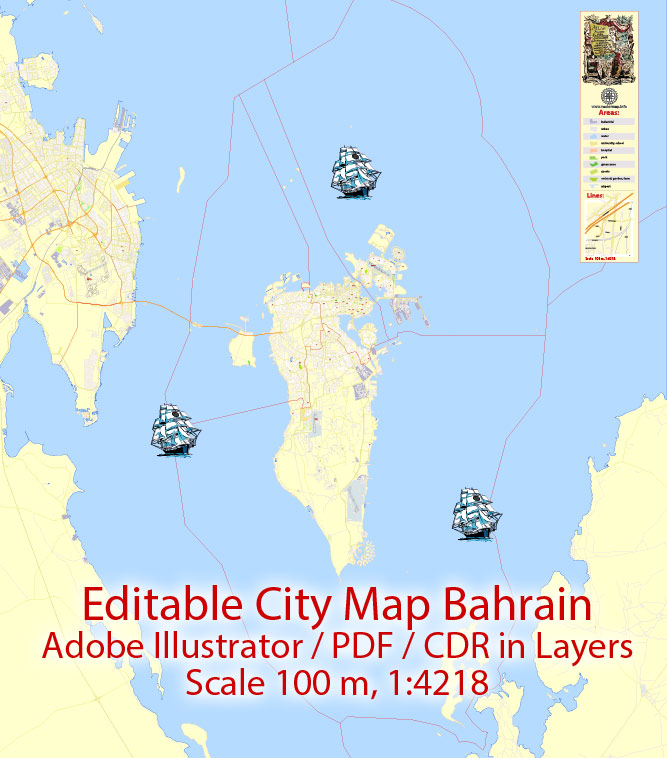
One of the advantages of Bahrain vector maps of our production is the relevance of cartographic data, we constantly update all our products.
This vector map of Bahrain is used by:
designers, layout designers, printers, advertisers and architects. Our product – vector maps – is designed for further editing and printing in large formats – from @Wall format (a few meters) to A-0 and A-1, A-2, A-3.
The Bahrain map in vector format is used for design, urban planning, presentations and media visualizations.
The advertising and presentation map of Bahrain (usually the final designer marks the routes, and puts the client’s objects (shops, saloons, gas stations etc.)
The undoubted advantage is that people will NEVER throw out this advertising product – the map. In fact, as an advertising medium, a map is the most “long-playing” of the well-known polygraphic advertising media, with the longest lifespan, and the maximum number of interactions with the customer.
Bahrain is the site of the ancient Dilmun civilisation. It has been famed since antiquity for its pearl fisheries, which were considered the best in the world into the 19th century. Bahrain was one of the earliest areas to convert to Islam, in 628 CE. Following a period of Arab rule, Bahrain was occupied by the Portuguese in 1521, who in turn were expelled in 1602 by Shah Abbas I of the Safavid dynasty under the Persian Empire. In 1783, the Bani Utbah clan captured Bahrain from Nasr Al-Madhkur and it has since been ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family, with Ahmed al Fateh as Bahrain’s first hakim.
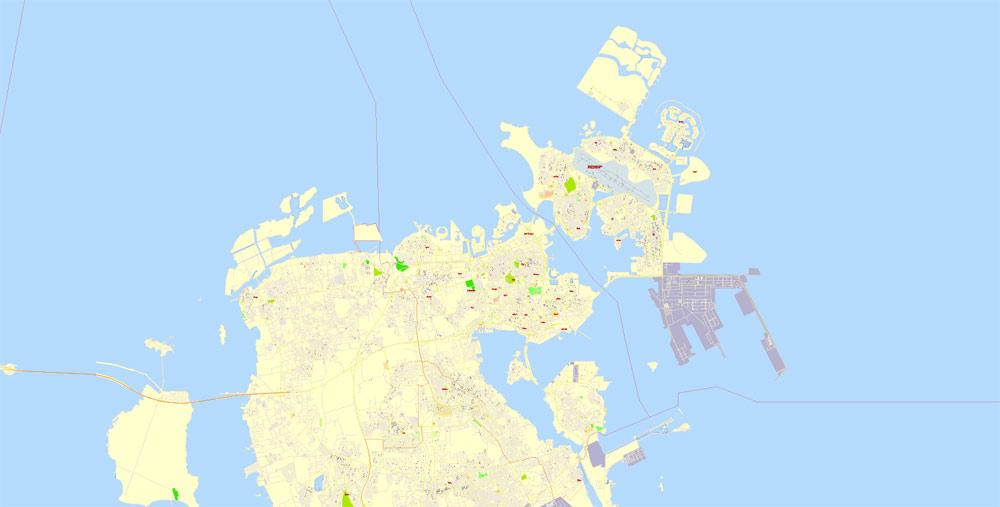
For travelers, maps are sold at the airports and gas stations around the world. Often the source is our vector maps.
Take a look, who purchases our vector maps of Bahrain in “Our Clients and Friends” page – these are large and small companies, from super-brands like Volvo and Starbucks, to small design studios and printing houses.
It’s very easy to work with vector maps of Bahrain city, even for a not very experienced designer who can turn on and off the map layers, add new objects, change the colors of fill and lines according to customer requirements.
The undoubted advantage of Bahrain vector maps in printing is an excellent and detailed visualization, when customer can expand a large paper map and instantly define his location, find a landmark, an object or address on map, unlike using the popular electronic formats of Google and Yandex maps for example.
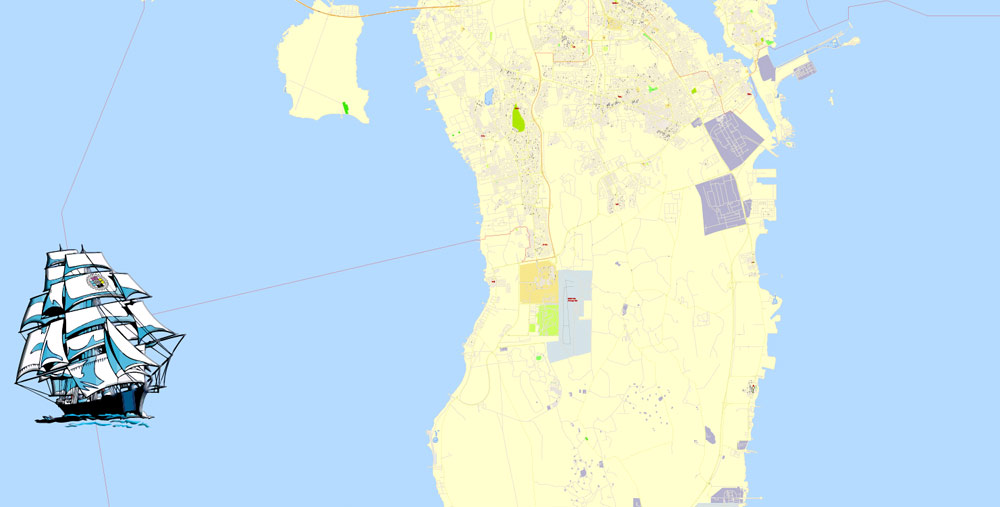
Printable vector maps of Bahrain are much more convenient and efficient than any electronic maps on your smartphone, because ALL DETAILS are displayed in the entire space of Bahrain map.
Useful tips on working with vector maps of cities and countries in Adobe Illustrator.
«V» – launches the Selection tool (cursor, black arrow), which makes active any vector line.
«А» – launches the Direct Selection tool (white cursor), allows you to select curve elements and drag them to the desired place.
«R» – activates the Rotate tool, which helps you rotating selected objects around the center point by 360 degrees.
«E» – gives you the opportunity to use the Eraser tool and erase unnecessary parts.
«X» – switches between Fill and Stroke in the Tools section. Try to get used to this hot key and
you will quickly understand that you can’t live and work without it.
Guides are not limited to vertical and horizontal in Adobe Illustrator. You can also create a diagonal guide for example. Moreover, you can turn any contours into guides. Select the outline and go to View > Guides > Make Guides (Create Guides), or simply press Cmd/Ctrl + 5. You can also turn the guides back into an editable object. Go to menu, View > Guides > Unlock Guides (Release Guides), select the guide you want to edit and select View > Guides > Release Guides (Reset Guides), or just press Cmd/Ctrl + Option / Alt + 5).
In the late 1800s, following successive treaties with the British, Bahrain became a protectorate of the United Kingdom. In 1971, Bahrain declared independence. Formerly an emirate, the Arab constitutional monarchy of Bahrain was declared a kingdom in 2002. In 2011, the country experienced protests inspired by the regional Arab Spring. Bahrain’s ruling al-Khalifa royal family has been accused and criticized for human rights abuses, including imprisonment, torture and execution of dissidents, political opposition figures and its Shia Muslim population.
You will probably want to change the color scheme used on our Bahrain vector map.
To quickly and effectively play with colors.
Of course, you can do it manually, all objects in our Bahrain vector map are divided according to types and layers, and you can easily change the color gamma of vector objects in groups and layers.
But there is more effective way of working with the whole VECTOR MAP of Bahrain and all layers:
The overview dialog «Edit colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» (this dialog box name can change depending on the context):
If you have selected a part or a layer of Bahrain vector map and open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or the Color Catalog, or if you choose Edit > Edit Colors> Repaint Graphic Object, then the «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box appears, and you get access to «Assign» and «Edit» tabs.
If a picture or a map fragment is not selected, and you open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or in the Color Catalog, the «Edit Colors» dialog box appears and you can only access the «Edit» tab.
Bahrain had the first post-oil economy in the Persian Gulf. Since the late 20th century, Bahrain has invested in the banking and tourism sectors. Many large financial institutions have a presence in Manama, the country’s capital. It has a high Human Development Index and is recognised by the World Bank as a high-income economy. Bahrain is a member of the United Nations, Non-Aligned Movement, Arab League, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
Regardless of the name at the top of the dialog box, the right-hand side always displays the color group of the current document, as well as two default color groups: Print Color and Grayscale. These color groups can be selected and used any time.
Create and edit color groups of Bahrain vector map, and also assign colors using the «Edit Colors»/ а «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
A. Creating and editing of a color group on the «Edit» tab
B. Assigning colors on the «Assign» tab
C. Select a group of colors from the «Color groups» list
The option «Repaint a graphic object» in the lower part of the dialog box allows you to preview the colors on a selected layer of Vector map, or a group of elements, and specify whether its colors will be redefined when the dialog box is closed.
Geography
Bahrain is a generally flat and arid archipelago in the Persian Gulf. It consists of a low desert plain rising gently to a low central escarpment with the highest point the 134 m (440 ft) Mountain of Smoke (Jabal ad Dukhan). Bahrain had a total area of 665 km2 (257 sq mi) but due to land reclamation, the area increased to 765 km2 (295 sq mi), which is slightly larger than Hamburg or the Isle of Man.
The main areas of the dialog box are:
«Edit»
The «Edit» tab is designed to create a new or edit the existing color groups.
The harmony rules Menu and the Color Wheel are used to conduct experiments with color harmonies. The color wheel shows how colors are related in color harmony, and the color bars allow you to view and manipulate an individual color values. In addition, you can adjust the brightness, add and remove colors, save color groups and view colors on the selected Vector Map of Bahrain or a separated layers.
«Assign»
The «Assign» tab is used to view and control on how the original colors are replaced with colors from the color group like your corporate colors in the Vector Map of Bahrain city.
The assign color ability is provided only if the entire map, layer or fragment is selected in the document. You can specify which of new colors replace the current colors, whether the spot colors should be preserved and how colors are replaced (for example, you can replace colors completely or changing the color tone while maintaining the brightness). The «Assign» tab allows you to redefine colors in the Vector Map of Bahrain city, or in separate layers and fragments using the current color group or reducing the number of colors in the current Vector Map.
Often described as an archipelago of 33 islands, extensive land reclamation projects have changed this; by August 2008 the number of islands and island groups had increased to 84. Bahrain does not share a land boundary with another country but does have a 161 km (100 mi) coastline. The country also claims a further 22 km (12 nmi) of territorial sea and a 44 km (24 nmi) contiguous zone. Bahrain’s largest islands are Bahrain Island, the Hawar Islands, Muharraq Island, Umm an Nasan, and Sitra. Bahrain has mild winters and very hot, humid summers. The country’s natural resources include large quantities of oil and natural gas as well as fish in the offshore waters. Arable land constitutes only 2.82% of the total area.
Color groups
Is a list of all saved color groups for current document (the same groups appear in the «Samples» palette). You can edit and delete the existing color groups, as well as creating a new ones using the list of “Color Groups” in the dialog box. All changes appear in the «Samples» palette.
The highlighted color group shows, which color group is currently edited.
Any color group can be selected and edited, or used to redefine the colors in the selected vector map of Bahrain city, its fragments or elements.
Saving a color group adds this group to the specified list.
Opening the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
Open the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box using one of the following methods:
«Edit»> «Edit Colors»> «Repaint Graphic object» or «Repaint With Style».
Use these commands if you need to edit the colors in the selected vector map of Bahrain city.
About 92% of Bahrain is desert with periodic droughts and dust storms, the main natural hazards for Bahrainis. Environmental issues facing Bahrain include desertification resulting from the degradation of limited arable land, coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, distribution stations, and illegal land reclamation at places such as Tubli Bay. The agricultural and domestic sectors’ over-utilisation of the Dammam Aquifer, the principal aquifer in Bahrain, has led to its salinisation by adjacent brackish and saline water bodies.
«Repaint Graphic object» button on the «Control» panel.
Use this button if you need to adjust colors of Bahrain vector map using the а «Repaint graphic object» dialog box.
The specified button is available if the selected vector map or its fragment contains two or more colors.
Note. This color editing method is convenient for global color adjustment in a vector map, if global colors were not used when creating a Map of Bahrain.
The «Edit colors» button or «Edit or apply colors» on the «Color Catalog» palette
Click this button if you need to edit colors on the «Color Catalog» palette or edit and then apply them to the selected Vector Map of Bahrain or its fragment.
The «Edit color group» button or «Edit or apply color group» on the «Samples» palette.
Click this button if you need to edit the colors in the specific color group or edit and apply them to the selected Vector Map of Bahrain or a group of its elements, for example, the whole layer “Streets and lines”. You can also double-click the color group in the Samples panel to open the dialog box.
A hydrochemical study identified the locations of the sources of aquifer salinisation and delineated their areas of influence. The investigation indicates that the aquifer water quality is significantly modified as groundwater flows from the northwestern parts of Bahrain, where the aquifer receives its water by lateral underflow from eastern Saudi Arabia, to the southern and southeastern parts. Four types of salinisation of the aquifer are identified: brackish-water up-flow from the underlying brackish-water zones in north-central, western, and eastern regions; seawater intrusion in the eastern region; intrusion of sabkha water in the southwestern region; and irrigation return flow in a local area in the western region. Four alternatives for the management of groundwater quality that are available to the water authorities in Bahrain are discussed and their priority areas are proposed, based on the type and extent of each salinisation source, in addition to groundwater use in that area.
If the map file is too large and your computer freezes or even can’t open it quickly:
1. Try to reduce the color resolution of the video card (display) to 256 colors while working with a large map.
2. Using Windows Task Manager, select all the application you don’t need, while working with map, just turn them off.
3. Launch Adobe Illustrator. (DO NOT OPEN the vector map file)
4. Start the Windows Task Manager using administrator rights > Find the “Illustrator” process > set the «real time» priority,
5. Open the file. When you see the LEGACY FONT popup window – click “OK” (do not update). You can restore the TEXT later.
6. Can also be useful: When file is opened – Edit > Settings > Basic Settings > disable smoothing. /// It looks scary, but works quickly)))
We recommend saving the file in Adobe Illustrator 10 version. It’s much more stable when working with VERY BIG size files.
Geography of Bahrain
The Kingdom of Bahrain consists of Bahrain Island and 33 of the 37 Bahrain Islands, lying in the Persian Gulf’s Gulf of Bahrain off the north shore of Asia’s Arabian Peninsula. Bahrain’s capital city is Manama. The islands are about 24 kilometers (15 mi) off the east coast of Saudi Arabia and 28 kilometers (17 mi) from Qatar. The total area of the country is about 780 square kilometers (301 sq mi), about 3.5 times the size of the District of Columbia.
Bahrain Island accounts for about 83% of the kingdom’s land area, comprising 590 square kilometers (228 sq mi). It is 48 kilometers (30 mi) long from north to south and at its widest point stretches 16 kilometers (10 mi) from east to west.
The island is surrounded by several of the Middle East’s large petroleum fields and commands a strategic position amid the Persian Gulf’s shipping lanes.
Geographical setting and islands
Following the return of Janan to Qatar in March 2001, that state of Bahrain consists of 33 natural islands in the Bahrain Islands archipelago.
Around most of Bahrain is a relatively shallow inlet of the Persian Gulf known as the Gulf of Bahrain. The seabed adjacent to Bahrain is rocky and, mainly off the northern part of the island, covered by extensive coral reefs. Most of the island is low-lying and barren desert. Outcroppings of limestone form low rolling hills, stubby cliffs, and shallow ravines. The limestone is covered by various densities of saline sand, capable of supporting only the hardiest desert vegetation – chiefly thorn trees and scrub. There is a fertile strip five kilometers wide along the northern coast on which date, almond, fig, and pomegranate trees grow. The interior contains an escarpment that rises to 134 meters, the highest point on the island, to form Jabal ad Dukhan (Mountain of Smoke), named for the mists that often wreathe the summit. Most of the country’s oil wells are situated in the vicinity of Jabal ad Dukhan.
One author writes about the geology of the nation: “Bahrein lies on a portion of the ancient Tethys Ocean geosynclinal belt represented today by the Persian Gulf. The formation of the principal island is the result of pressure from the mountain masses of Persia against the crystalline platform of central Asia, the thrust being absorbed by gentle folding in the geosynclines. The structure of Bahrein is that of a large, single, closed dome covering the entire faulting.
Rocks exposed at the surface consist of: 1) Recent sands and coquinas forming flat, raised beaches surrounding the island from which the surface rises gradually to an elevation 150 to 200 feet above sea level. At this point it breaks away into inward-facing cliffs eighty to one hundred feet high completely surrounding an oval central depression about twelve miles long and four wide. 2) Pleistocene sands, cross bedded and probably wind deposited, lying in the canyon. 3) Miocene silicious clay covering a very limited area. 4) Eocene limestone covering most of the island, the central region of which, known as “Jabal Dukhār “Mountain of Smoke”, rises to a point 439 feet above sea level. The limestone is very porous and is the source of most of the water in the northern half of the island.”
In addition to Bahrain Island, other islands of significance include Nabih Saleh, which is northwest of Sitrah; Jidda Island and Umm as Sabaan, to the north of Umm an Nasan; and a group of islands, the largest of which is Hawar, near the coast of Qatar. Nabih Saleh contains several freshwater springs that are used to irrigate the island’s extensive date palm groves. The rocky islet of Jiddah formerly housed the state prison but has now been converted to a holiday resort. Hawar and the fifteen small islands near it are the subject of a territorial dispute between Bahrain and Qatar. Hawar is nineteen kilometers long and about one and one half kilometers wide. The other islands (such as the Al Garum Islands) are uninhabited and are nesting sites for a variety of migratory birds.
Bahrain
Country in the Middle East
Bahrain, a nation comprising more than 30 islands in the Arabian Gulf, has been at the center of major trade routes since antiquity. In its modern capital, Manama, the acclaimed Bahrain National Museum showcases artifacts from the ancient Dilmun civilization that flourished in the region for millennia. The city’s thriving Bab al-Bahrain bazaar offers wares ranging from colorful handwoven fabrics and spices to pearls.
Capital: Manama
Free vector maps:
Free download printable map Europe vector Adobe Illustrator >>>
Free download printable PDF map Europe vector Adobe PDF >>>
Author Rating
Aggregate Rating
no rating based on 0 votes
City Map Street Map
Product Name City Map Bahrain Vector Urban Plan Adobe Illustrator Editable Street Map
Price
USD 59
Product Availability
Available in Stock


















 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS