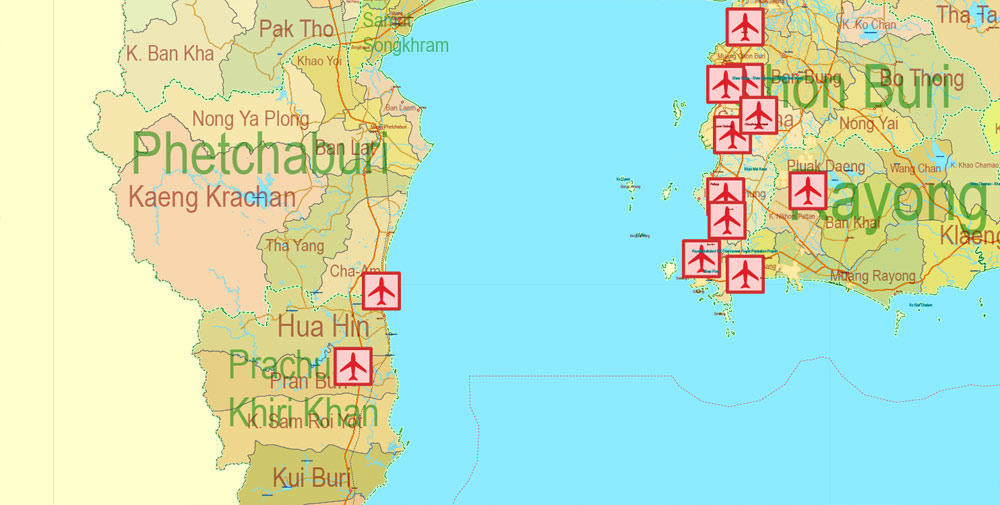
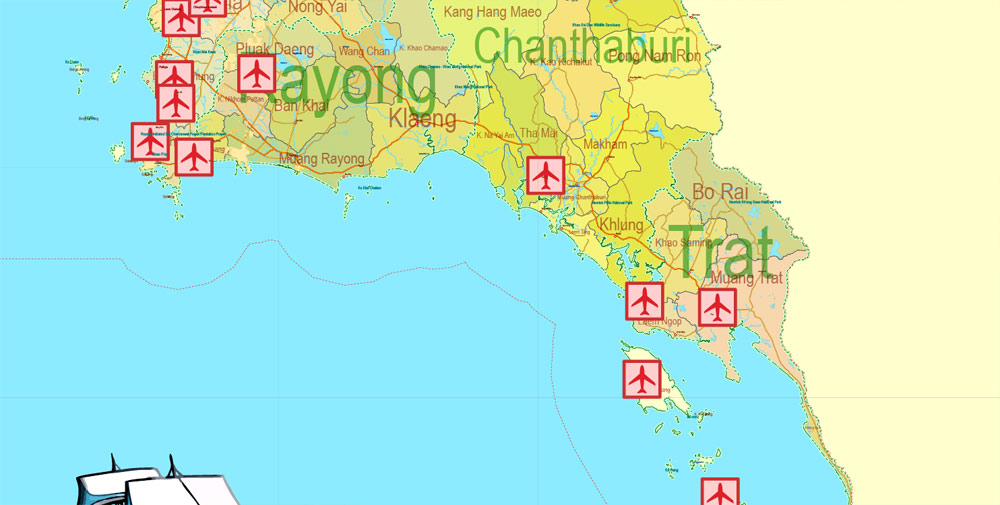
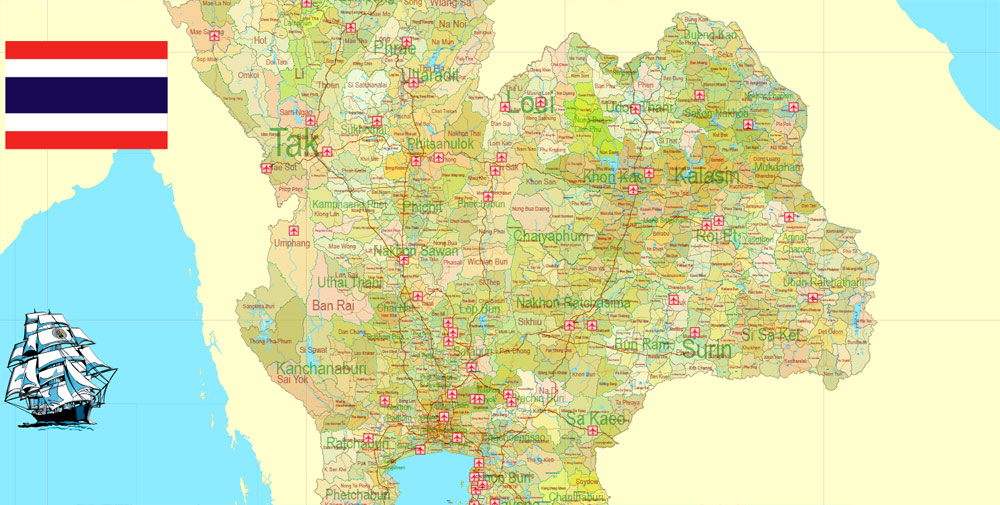
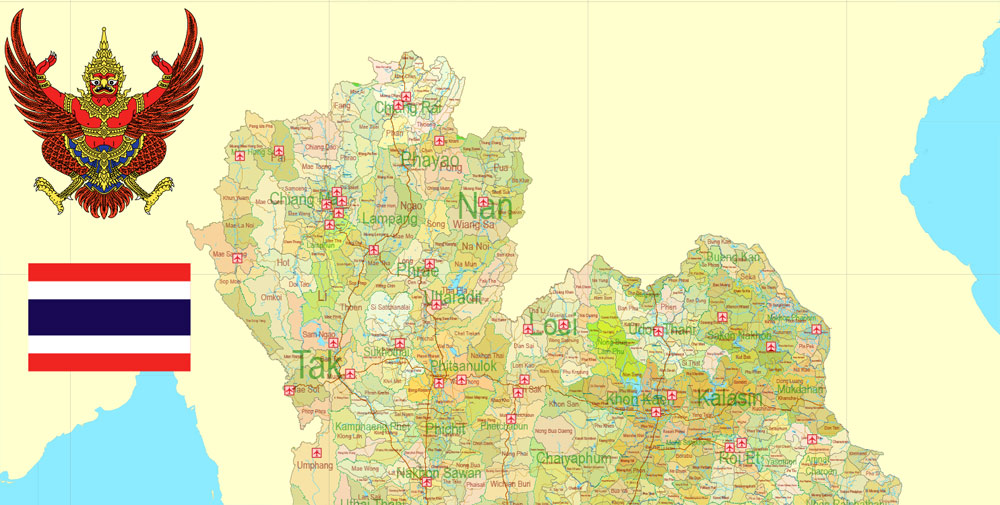
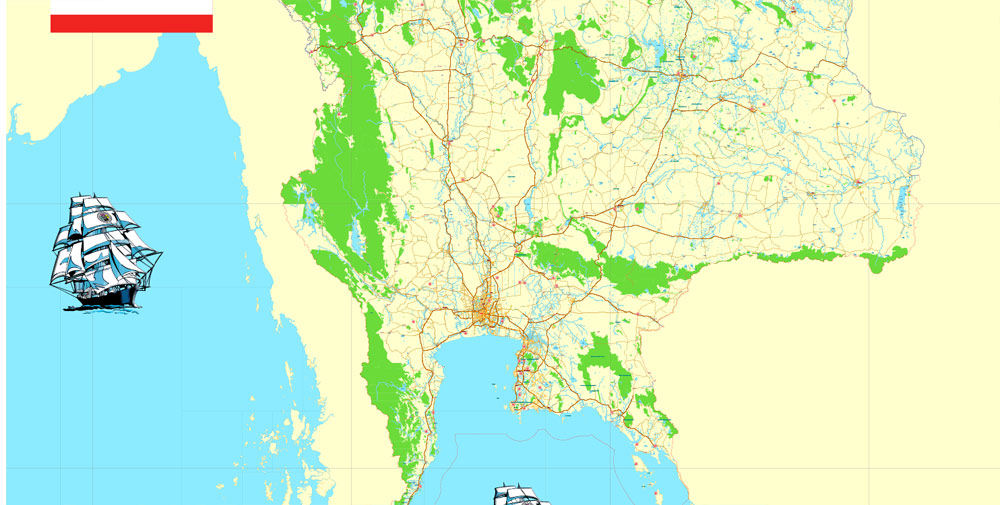
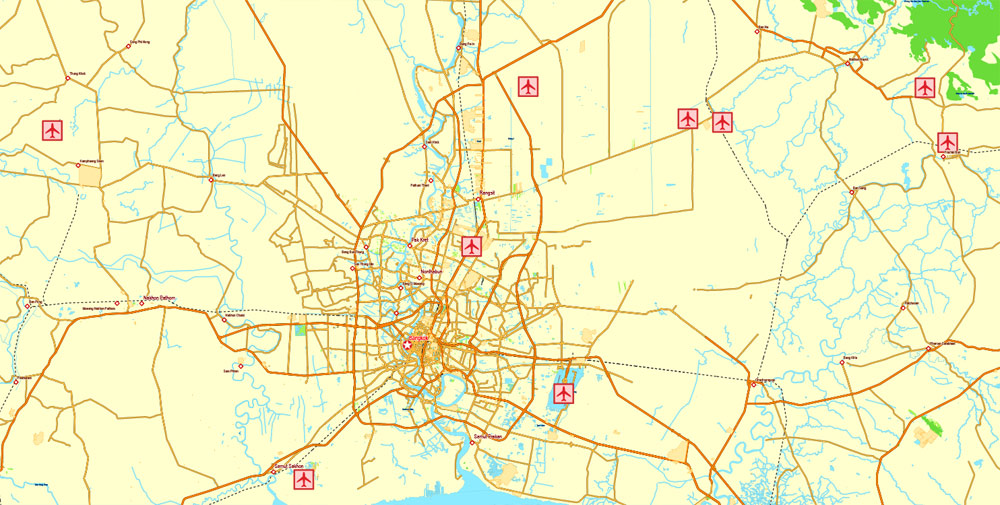
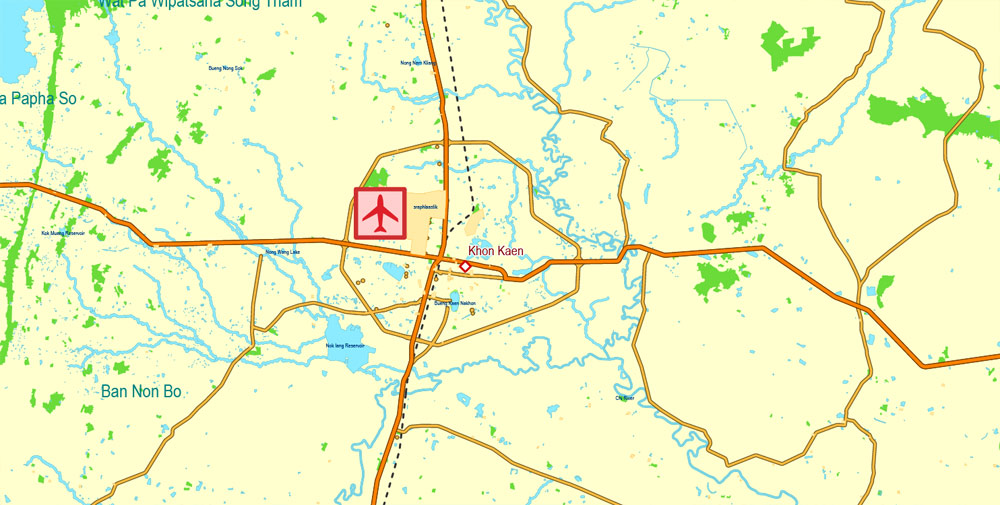
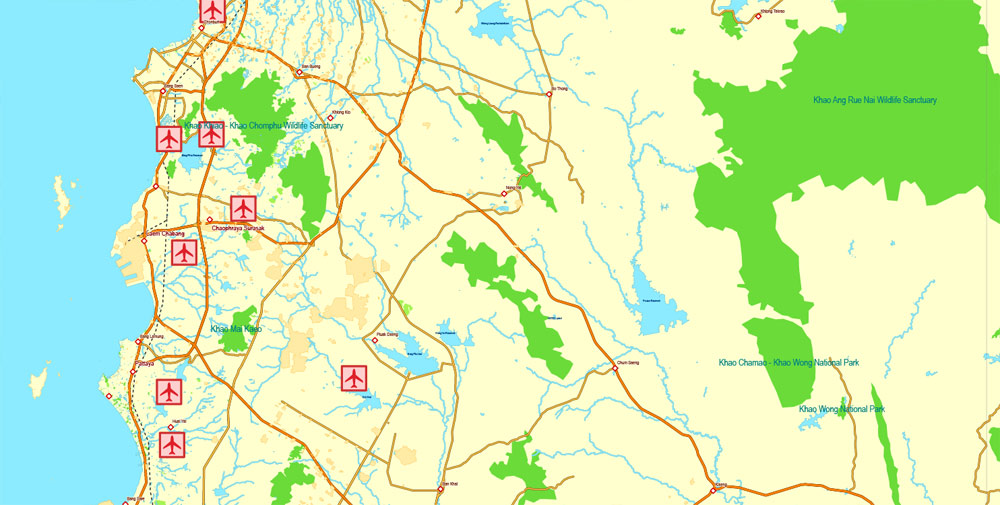
Printable Exact Detailed Map Thailand Admin, Roads, Cities, Towns, Railroads, Water, Airports in Adobe Illustrator, 94 mb ZIP
Map for publishing, design, printing, publications, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers and builders, business, logistics. The most exact and detailed map of the country.
Layers: legend + coat of arms + flag, grids, waterways and water objects, names_water, districts and names_districts, provinces and names provinces, main_roads, railroads, cities, airports, airports runways, etc. (more than 25 layers)
Text format names
DWG, DXF, EPS, ESRI Shapes, and other formats – by request, same price, please contact.
Thailand.
This vector map of Thailand is used as a basis for design, editing, and further printing.
This is the most detailed, exact map of Thailand for high-quality printing and polygraphy. You can always clarify the map development date by contacting us.
For your convenience, all objects on Thailand vector map are divided into layers. And the editing is very easy – colors, lines, etc.
You can easily add any objects needed (e.g. shops, salons, sale points, gas station or attraction) on any layer of Thailand vector map.
One of the advantages of Thailand vector maps of our production is the relevance of cartographic data, we constantly update all our products.
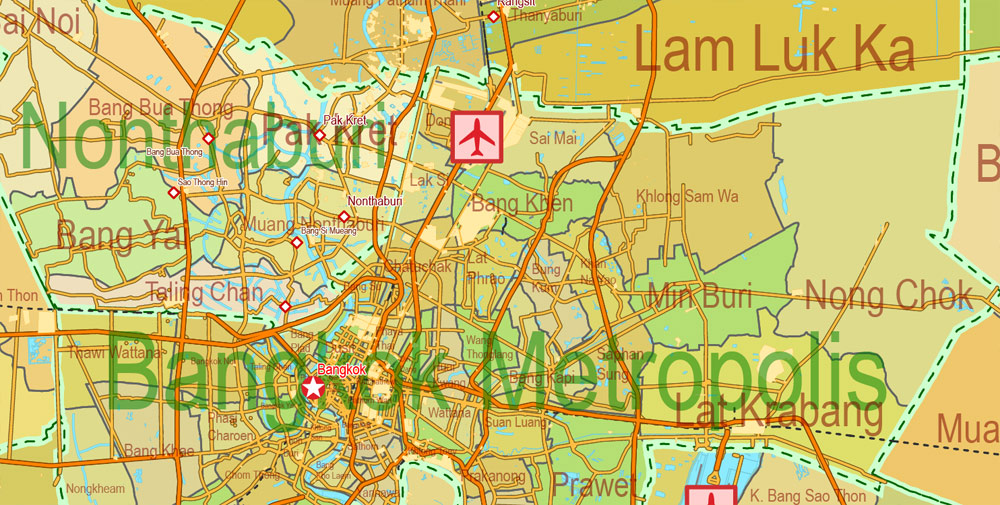
Thailand is a country at the center of the Southeast Asian Indochinese peninsula composed of 76 provinces. At 513,120 km2 (198,120 sq mi) and over 68 million people, Thailand is the world’s 50th largest country by total area and the 21st-most-populous country. The capital and largest city is Bangkok, a special administrative area.

This vector map of Thailand is used by:
designers, layout designers, printers, advertisers and architects. Our product – vector maps – is designed for further editing and printing in large formats – from @Wall format (a few meters) to A-0 and A-1, A-2, A-3.
The Thailand map in vector format is used for design, urban planning, presentations and media visualizations.
The advertising and presentation map of Thailand (usually the final designer marks the routes, and puts the client’s objects (shops, saloons, gas stations etc.)
The undoubted advantage is that people will NEVER throw out this advertising product – the map. In fact, as an advertising medium, a map is the most “long-playing” of the well-known polygraphic advertising media, with the longest lifespan, and the maximum number of interactions with the customer.
For travelers, maps are sold at the airports and gas stations around the world. Often the source is our vector maps.
Take a look, who purchases our vector maps of Thailand in “Our Clients and Friends” page – these are large and small companies, from super-brands like Volvo and Starbucks, to small design studios and printing houses.
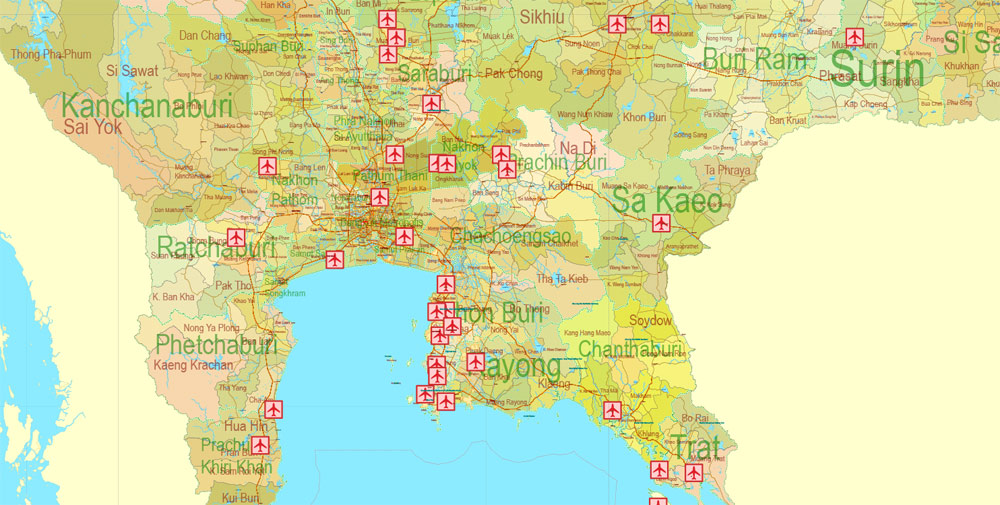
It’s very easy to work with vector maps of Thailand city, even for a not very experienced designer who can turn on and off the map layers, add new objects, change the colors of fill and lines according to customer requirements.
The undoubted advantage of Thailand vector maps in printing is an excellent and detailed visualization, when customer can expand a large paper map and instantly define his location, find a landmark, an object or address on map, unlike using the popular electronic formats of Google and Yandex maps for example.
Printable vector maps of Thailand are much more convenient and efficient than any electronic maps on your smartphone, because ALL DETAILS are displayed in the entire space of Thailand map.
Useful tips on working with vector maps of cities and countries in Adobe Illustrator.
«V» – launches the Selection tool (cursor, black arrow), which makes active any vector line.
«А» – launches the Direct Selection tool (white cursor), allows you to select curve elements and drag them to the desired place.
«R» – activates the Rotate tool, which helps you rotating selected objects around the center point by 360 degrees.
«E» – gives you the opportunity to use the Eraser tool and erase unnecessary parts.
«X» – switches between Fill and Stroke in the Tools section. Try to get used to this hot key and
you will quickly understand that you can’t live and work without it.
Guides are not limited to vertical and horizontal in Adobe Illustrator. You can also create a diagonal guide for example. Moreover, you can turn any contours into guides. Select the outline and go to View > Guides > Make Guides (Create Guides), or simply press Cmd/Ctrl + 5. You can also turn the guides back into an editable object. Go to menu, View > Guides > Unlock Guides (Release Guides), select the guide you want to edit and select View > Guides > Release Guides (Reset Guides), or just press Cmd/Ctrl + Option / Alt + 5).
You will probably want to change the color scheme used on our Thailand vector map.
To quickly and effectively play with colors.
Of course, you can do it manually, all objects in our Thailand vector map are divided according to types and layers, and you can easily change the color gamma of vector objects in groups and layers.
Thailand is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the southern extremity of Myanmar. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the southwest. Although nominally a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy, the most recent coup in 2014 established a de facto military dictatorship.
But there is more effective way of working with the whole VECTOR MAP of Thailand and all layers:
The overview dialog «Edit colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» (this dialog box name can change depending on the context):
If you have selected a part or a layer of Thailand vector map and open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or the Color Catalog, or if you choose Edit > Edit Colors> Repaint Graphic Object, then the «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box appears, and you get access to «Assign» and «Edit» tabs.
If a picture or a map fragment is not selected, and you open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or in the Color Catalog, the «Edit Colors» dialog box appears and you can only access the «Edit» tab.
Regardless of the name at the top of the dialog box, the right-hand side always displays the color group of the current document, as well as two default color groups: Print Color and Grayscale. These color groups can be selected and used any time.
Create and edit color groups of Thailand vector map, and also assign colors using the «Edit Colors»/ а «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
A. Creating and editing of a color group on the «Edit» tab
B. Assigning colors on the «Assign» tab
C. Select a group of colors from the «Color groups» list
The option «Repaint a graphic object» in the lower part of the dialog box allows you to preview the colors on a selected layer of Vector map, or a group of elements, and specify whether its colors will be redefined when the dialog box is closed.
The main areas of the dialog box are:
«Edit»
The «Edit» tab is designed to create a new or edit the existing color groups.
The harmony rules Menu and the Color Wheel are used to conduct experiments with color harmonies. The color wheel shows how colors are related in color harmony, and the color bars allow you to view and manipulate an individual color values. In addition, you can adjust the brightness, add and remove colors, save color groups and view colors on the selected Vector Map of Thailand or a separated layers.
«Assign»
The «Assign» tab is used to view and control on how the original colors are replaced with colors from the color group like your corporate colors in the Vector Map of Thailand city.
The assign color ability is provided only if the entire map, layer or fragment is selected in the document. You can specify which of new colors replace the current colors, whether the spot colors should be preserved and how colors are replaced (for example, you can replace colors completely or changing the color tone while maintaining the brightness). The «Assign» tab allows you to redefine colors in the Vector Map of Thailand city, or in separate layers and fragments using the current color group or reducing the number of colors in the current Vector Map.
Color groups
Is a list of all saved color groups for current document (the same groups appear in the «Samples» palette). You can edit and delete the existing color groups, as well as creating a new ones using the list of “Color Groups” in the dialog box. All changes appear in the «Samples» palette.
The highlighted color group shows, which color group is currently edited.
Any color group can be selected and edited, or used to redefine the colors in the selected vector map of Thailand city, its fragments or elements.
Saving a color group adds this group to the specified list.
Opening the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
Open the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box using one of the following methods:
«Edit»> «Edit Colors»> «Repaint Graphic object» or «Repaint With Style».
Use these commands if you need to edit the colors in the selected vector map of Thailand city.
«Repaint Graphic object» button on the «Control» panel.
Use this button if you need to adjust colors of Thailand vector map using the а «Repaint graphic object» dialog box.
The specified button is available if the selected vector map or its fragment contains two or more colors.
Note. This color editing method is convenient for global color adjustment in a vector map, if global colors were not used when creating a Map of Thailand.
The «Edit colors» button or «Edit or apply colors» on the «Color Catalog» palette
Click this button if you need to edit colors on the «Color Catalog» palette or edit and then apply them to the selected Vector Map of Thailand or its fragment.
The «Edit color group» button or «Edit or apply color group» on the «Samples» palette.
Click this button if you need to edit the colors in the specific color group or edit and apply them to the selected Vector Map of Thailand or a group of its elements, for example, the whole layer “Streets and lines”. You can also double-click the color group in the Samples panel to open the dialog box.
If the map file is too large and your computer freezes or even can’t open it quickly:
1. Try to reduce the color resolution of the video card (display) to 256 colors while working with a large map.
2. Using Windows Task Manager, select all the application you don’t need, while working with map, just turn them off.
3. Launch Adobe Illustrator. (DO NOT OPEN the vector map file)
4. Start the Windows Task Manager using administrator rights > Find the “Illustrator” process > set the «real time» priority,
5. Open the file. When you see the LEGACY FONT popup window – click “OK” (do not update). You can restore the TEXT later.
6. Can also be useful: When file is opened – Edit > Settings > Basic Settings > disable smoothing. /// It looks scary, but works quickly)))
We recommend saving the file in Adobe Illustrator 10 version. It’s much more stable when working with VERY BIG size files.
Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 11th century; the oldest known mention of their presence in the region by the exonym Siamese dates to the 12th century. Various Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon, the Khmer Empire and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as Ngoenyang, the Sukhothai Kingdom, Lan Na and the Ayutthaya Kingdom, which rivaled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, one of the great powers in the region. Ayutthaya reached its peak during cosmopolitan Narai’s reign (1656–88), gradually declining thereafter until being ultimately destroyed in 1767 in a war with Burma. Taksin quickly reunified the fragmented territory and established the short-lived Thonburi Kingdom. He was succeeded in 1782 by Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke, the first monarch of the Chakri dynasty and founder of the Rattanakosin Kingdom, which lasted into the early 20th century.
Through the 18th and 19th centuries, Siam faced pressure from France and the United Kingdom, including forced concessions of territory, but nevertheless it remained the only Southeast Asian country to avoid direct Western rule. Following a bloodless revolution in 1932, Siam became a constitutional monarchy and changed its official name to “Thailand”. While it joined the Allies in World War I, Thailand was an Axis satellite in World War II. In the late 1950s, a military coup revived the monarchy’s historically influential role in politics. Thailand became a major ally of the United States and played a key anti-communist role in the region.

Apart from a brief period of parliamentary democracy in the mid 1970s, Thailand has periodically alternated between democracy and military rule. In the 21st century, Thailand endured a political crisis that culminated in two coups and the establishment of its current and 20th constitution by the military junta.
Thailand is a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy under a military junta. Thailand is a founding member of Association of Southeast Asian Nations and remains a major ally of the US. Despite its comparatively sporadic changes in leadership, it is considered a regional power in Southeast Asia and a middle power in global affairs. With a high level of human development, the second largest economy in Southeast Asia, and the 20th largest by PPP, Thailand is classified as a newly industrialized economy; manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy.
Geography
Totalling 513,120 square kilometres (198,120 sq mi), Thailand is the 50th-largest country by total area. It is slightly smaller than Yemen and slightly larger than Spain.
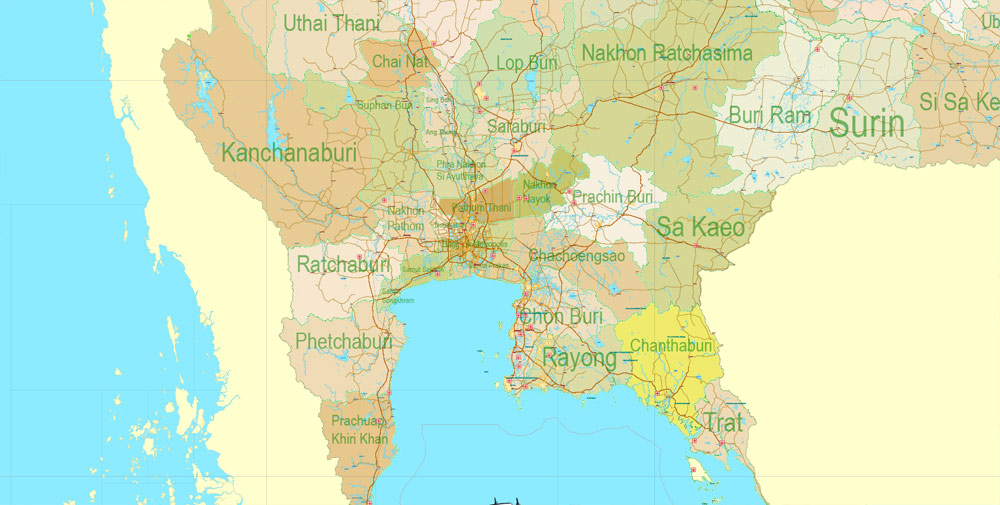
Thailand comprises several distinct geographic regions, partly corresponding to the provincial groups. The north of the country is the mountainous area of the Thai highlands, with the highest point being Doi Inthanon in the Thanon Thong Chai Range at 2,565 metres (8,415 ft) above sea level. The northeast, Isan, consists of the Khorat Plateau, bordered to the east by the Mekong River. The centre of the country is dominated by the predominantly flat Chao Phraya river valley, which runs into the Gulf of Thailand.
Southern Thailand consists of the narrow Kra Isthmus that widens into the Malay Peninsula. Politically, there are six geographical regions which differ from the others in population, basic resources, natural features, and level of social and economic development. The diversity of the regions is the most pronounced attribute of Thailand’s physical setting.
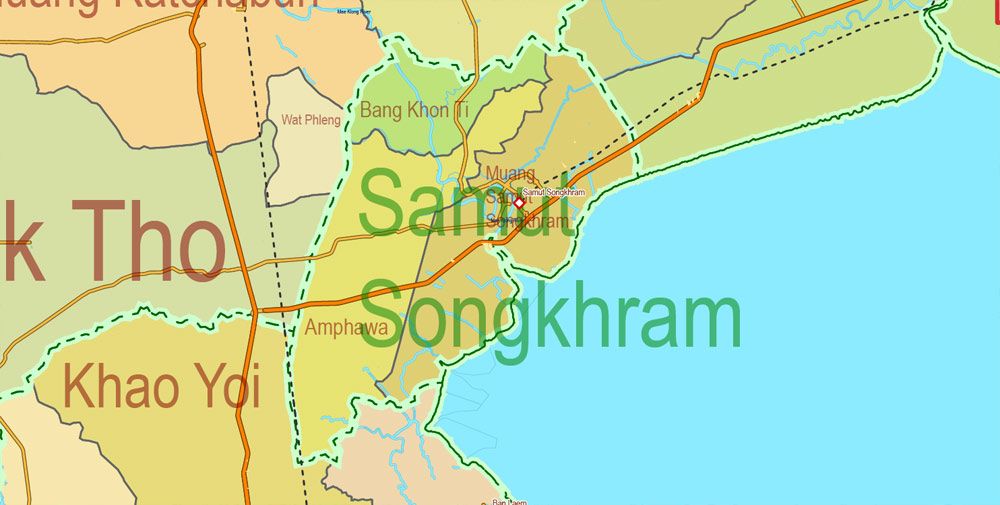
The Chao Phraya and the Mekong River are the indispensable water courses of rural Thailand. Industrial scale production of crops use both rivers and their tributaries. The Gulf of Thailand covers 320,000 square kilometres (124,000 sq mi) and is fed by the Chao Phraya, Mae Klong, Bang Pakong, and Tapi Rivers. It contributes to the tourism sector owing to its clear shallow waters along the coasts in the southern region and the Kra Isthmus. The eastern shore of the Gulf of Thailand is an industrial centre of Thailand with the kingdom’s premier deepwater port in Sattahip and its busiest commercial port, Laem Chabang.
The Andaman Sea is a precious natural resource as it hosts the most popular and luxurious resorts in Asia. Phuket, Krabi, Ranong, Phang Nga and Trang, and their islands, all lay along the coasts of the Andaman Sea and, despite the 2004 tsunami, they remain a tourist magnet for visitors from around the world.
Plans have resurfaced for a canal which would connect the Andaman Sea to the Gulf of Thailand, analogous to the Suez and the Panama Canals. The idea has been greeted positively by Thai politicians as it would cut fees charged by the Ports of Singapore, improve ties with China and India, lower shipping times, and eliminate pirate attacks in the Strait of Malacca, and support the Thai government’s policy of being the logistical hub for Southeast Asia. The canal, it is claimed, would improve economic conditions in the south of Thailand, which relies heavily on tourism income, and it would also change the structure of the Thai economy by making it an Asia logistical hub. The canal would be a major engineering project and has an expected cost of US$20–30 billion.
Administrative divisions
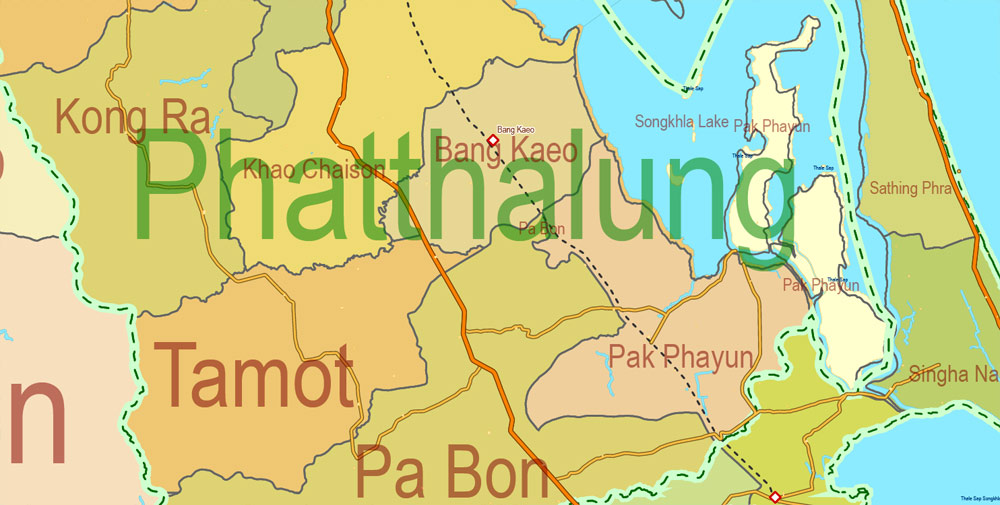
Thailand is divided into 76 provinces, which are gathered into five groups of provinces by location. There are also two specially-governed districts: the capital Bangkok (Krung Thep Maha Nakhon) and Pattaya. Bangkok is at provincial level and thus often counted as a province.
Each province is divided into districts and the districts are further divided into sub-districts (tambons). As of 2017 there were 878 districts and the 50 districts of Bangkok, which is further divided into 7,255 subdistricts in the 76 provinces or Bangkok’s subdistricts. Some parts of the provinces bordering Bangkok are also referred to as Greater Bangkok. These provinces include Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Nakhon Pathom and Samut Sakhon. The name of each province’s capital city is the same as that of the province. For example, the capital of Chiang Mai Province (Changwat Chiang Mai) is Mueang Chiang Mai or Chiang Mai.
Regions
Thai provinces are administrated by regions. The regions that Thailand uses to divide the provinces is the four-region division system. It divides the country into the four regions: Northern Thailand, Northeastern Thailand, Central Thailand and Southern Thailand. Each region has its own different historical background, culture, language and people.
In contrast to the administrative divisions of the Provinces of Thailand, Thailand is a Unitary state, the provincial Governors, district chiefs, and district clerks are appointed by the central government. The regions themselves do not have an administrative character, but are used for geographical, statistical, geological, meteorological or touristic purposes.
Geographic coordinates
15°00′N 100°00′E
The fertile floodplain and tropical monsoon climate, ideally suited to wet-rice (tham na) cultivation, attracted settlers to this central area over to the marginal uplands and the highlands of the northern region or the Khorat Plateau to the northeast.
By the 11th century AD, a number of loosely connected rice-growing and trading states flourished in the upper Chao Phraya Valley. They broke free from domination of the Khmer Empire, but from the middle of the 14th century gradually came under the control of the Ayutthaya kingdom at the southern extremity of the floodplain.
Successive capitals, built at various points along the river, became centers of great Thai kingdoms based on rice cultivation and foreign commerce. Unlike the neighboring Khmer and Burmese, the Thai continued to look outward across the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman Sea toward foreign ports of trade.
When European imperialism brought a new phase in Southeast Asian commerce in the late 1800s, Thailand (known then as Siam) was able to maintain its independence as a buffer zone between British-controlled Burma to the west and French-dominated Indochina to the east, but losing over 50% of its territory in the process. Most of the areas lost contained a non-Thai population (Khmer, Lao or Shan). The Thai-speaking heartland remains intact.
Thailand
Country in Asia
Thailand is a Southeast Asian country. It’s known for tropical beaches, opulent royal palaces, ancient ruins and ornate temples displaying figures of Buddha. In Bangkok, the capital, an ultramodern cityscape rises next to quiet canalside communities and the iconic temples of Wat Arun, Wat Pho and the Emerald Buddha Temple (Wat Phra Kaew). Nearby beach resorts include bustling Pattaya and fashionable Hua Hin.
Capital: Bangkok
Spoken languages: Isan; Kam Mueang; Pak Tai
Currency: Thai baht
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and formerly known as Siam, is a country at the centre of the Indochinese peninsula in Southeast Asia. With a total area of approximately 513,000 km2 (198,000 sq mi), Thailand is the world’s 50th-largest country. It is the 20th-most-populous country in the world, with around 69 million people.
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy and has switched between parliamentary democracy and military junta for decades, the latest coup being in May 2014 by the National Council for Peace and Order. Its capital and most populous city is Bangkok. It is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the southern extremity of Myanmar. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the southwest.
The Thai economy is the world’s 20th largest by GDP at PPP and the 27th largest by nominal GDP. It became a newly industrialised country and a major exporter in the 1990s. Manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy. It is considered a middle power in the region and around the world.
Area
• Total
513,120 km2 (198,120 sq mi)
• Water (%)
0.4 (2,230 km2)
Population
• 2016 estimate
68,863,514
• 2010 census
64,785,909
• Density
132.1/km2 (342.1/sq mi)




















 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS