Printable Vector Map China, exact high detailed editable layered Adobe Illustrator scalable, editable, text format all names, 55 MB ZIP
Names all provinces, cities and principal water objects, main airports
Map for design, printing, arts, projects, presentations, for architects, designers, and builders, business, logistics.
The most exact and detailed map of China
Map for editing and High-Quality Printing

Layers list:
- Legend
- Names Countries
- Names Provinces
- Names Places
- Names Airports
- Points Places and Capitals
- Points Airports
- Names Water Areas
- Main Roads
- Railroads
- Waterways
- Country Boundaries
- Provinces Areas (colored poygons)
- Islands
- Water objects (areas)
Geographical Description of China
China, officially known as the People’s Republic of China (PRC), is the world’s third-largest country by land area, covering approximately 9.6 million square kilometers (3.7 million square miles) . It spans a vast and diverse range of landscapes, from towering mountains and arid deserts to fertile plains and tropical forests. The country is located in East Asia, bordering 14 countries and stretching across five time zones, although it operates on a single time zone (China Standard Time).
1. Location and Borders
China is situated in Eastern Asia, with its eastern coast facing the Pacific Ocean. It shares borders with the following countries:
- North : Mongolia and Russia
- Northeast : North Korea
- East : Japan (across the East China Sea) and South Korea (across the Yellow Sea)
- South : Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Bhutan, Nepal, and India
- West : Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan
China also has maritime boundaries with several countries, including Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Indonesia.
2. Topography
China’s topography is incredibly diverse, featuring a variety of landscapes that include mountains, plateaus, basins, plains, and hills. The country can be divided into three major geographical regions:
a. Western China: Mountains and Plateaus
The western part of China is dominated by high-altitude terrain, including the Tibetan Plateau, often referred to as the “Roof of the World.” This region is characterized by:
- Tibetan Plateau : The highest and largest plateau in the world, with an average elevation of over 4,500 meters (14,800 feet). It is home to the Himalayas, which include Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak at 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet).
- Kunlun Mountains : Running east-west, these mountains form a natural boundary between the Tibetan Plateau and the Tarim Basin.
- Tian Shan Mountains : Located in the northwest, these mountains stretch into neighboring Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
- Tarim Basin : A large desert basin in Xinjiang Province, containing the Taklamakan Desert, one of the largest sandy deserts in the world.
- Qaidam Basin : A high-altitude basin in Qinghai Province, rich in mineral resources.
b. Central China: Hills and Basins
Central China consists of a mix of hills, basins, and river valleys. This region is more temperate and fertile compared to the west and includes:
- Sichuan Basin : A fertile basin surrounded by mountains, known for its agricultural productivity and mild climate.
- Loess Plateau : Located in northern China, this plateau is covered with loess soil, which is highly susceptible to erosion. The region is historically significant as the cradle of Chinese civilization.
- Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau : A mountainous area in southwestern China, known for its karst landscapes, limestone formations, and biodiversity.
c. Eastern China: Plains and Coastal Regions
The eastern part of China is dominated by low-lying plains and coastal areas, which are the most densely populated and economically developed regions of the country. Key features include:
- North China Plain : Also known as the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, this is one of the largest and most important agricultural regions in China, producing wheat, corn, and other crops.
- Yangtze River Delta : Located near the East China Sea, this region is one of China’s most prosperous areas, centered around Shanghai, and includes the Yangtze River, the longest river in Asia (6,300 km or 3,915 miles).
- Pearl River Delta : In southern China, this delta region includes Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong, and is a major hub for trade, manufacturing, and finance.
- Coastal Plains : Stretching along the eastern seaboard, these plains are home to many of China’s largest cities and ports, including Tianjin, Qingdao, and Ningbo.
3. Climate
China’s vast size and varied geography result in a wide range of climates, from subarctic in the north to tropical in the south. The country can be divided into several climatic zones:
a. Monsoon Climate
Much of eastern and southern China experiences a monsoon climate , characterized by hot, humid summers and cold, dry winters. The monsoon season typically occurs from June to September, bringing heavy rainfall to the southern and eastern regions.
b. Continental Climate
Northern and western China have a continental climate , with cold winters and warm summers. The northeastern provinces, such as Heilongjiang and Jilin, experience long, harsh winters with temperatures dropping below -30°C (-22°F).
c. Highland Climate
The Tibetan Plateau and other high-altitude regions have a highland climate , with cold temperatures year-round and limited vegetation due to the thin air and low oxygen levels.
d. Tropical Climate
Southernmost China, particularly Hainan Island and parts of Yunnan and Guangdong provinces, have a tropical climate with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year.
4. Major Rivers and Lakes
China is home to some of the longest and most important rivers in the world, as well as numerous lakes. These water bodies play a crucial role in agriculture, transportation, and energy production.
Rivers
- Yangtze River (Chang Jiang) : The longest river in Asia and the third-longest in the world, stretching 6,300 kilometers (3,915 miles). It flows through central China and empties into the East China Sea near Shanghai.
- Yellow River (Huang He) : Known as the “Mother River of China,” it is the second-longest river in China (5,464 km or 3,395 miles) and is considered the cradle of Chinese civilization.
- Pearl River (Zhu Jiang) : The third-longest river in China, flowing through Guangdong Province and forming the Pearl River Delta, one of the most economically dynamic regions in the country.
- Mekong River : Although it originates in Tibet, the Mekong flows through several Southeast Asian countries before emptying into the South China Sea.
Lakes
- Poyang Lake : The largest freshwater lake in China, located in Jiangxi Province. It is an important habitat for migratory birds and plays a key role in flood control.
- Dongting Lake : Located in Hunan Province, this is the second-largest freshwater lake in China and is known for its wetlands and biodiversity.
- Qinghai Lake : The largest inland saltwater lake in China, located on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
5. Natural Resources
China is rich in natural resources, including minerals, fossil fuels, and renewable energy sources. Some key resources include:
- Coal : China has the world’s largest coal reserves and is the largest producer and consumer of coal.
- Oil and Natural Gas : Significant oil and gas reserves are found in the Tarim Basin, the Bohai Bay, and offshore areas in the South China Sea.
- Rare Earth Elements : China holds the majority of the world’s rare earth element reserves, which are critical for electronics, renewable energy, and defense industries.
- Hydropower : With its extensive river systems, China has become a global leader in hydropower generation, with projects like the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River.
6. Biodiversity
China is one of the world’s most biodiverse countries, with a wide range of ecosystems and species. The country is home to several endangered species, including the giant panda, snow leopard, and red-crowned crane. Efforts to protect biodiversity have led to the establishment of numerous national parks and nature reserves, such as the Wolong National Nature Reserve for pandas.
7. Environmental Challenges
Despite its natural wealth, China faces significant environmental challenges, including:
- Air Pollution : Rapid industrialization has led to severe air pollution, particularly in urban areas like Beijing and Shanghai.
- Water Scarcity : Northern China suffers from water scarcity, exacerbated by overuse and pollution of rivers and lakes.
- Desertification : Overgrazing, deforestation, and climate change have contributed to the expansion of deserts, particularly in the north and west.
- Deforestation : Large-scale logging and agricultural expansion have reduced forest cover, though reforestation efforts are underway.
Conclusion
China’s geography is a complex tapestry of diverse landscapes, climates, and ecosystems. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the fertile plains of the Yangtze River Delta, the country’s natural environment has shaped its history, culture, and economy. However, rapid development and environmental degradation pose ongoing challenges that will require careful management in the years to come.

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator
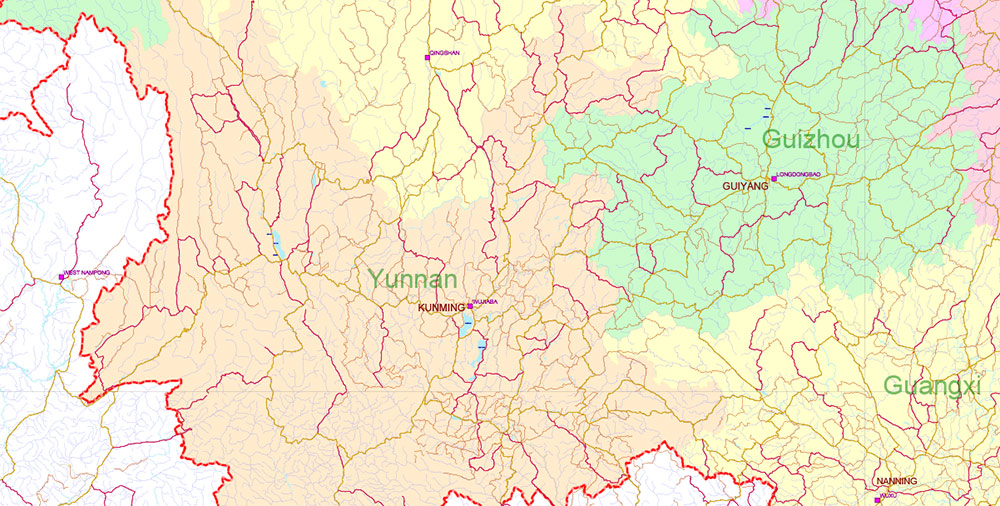
China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator

China High Detailed Vector Map: Admin, Roads, Cities and Water areas Editable Layered Adobe Illustrator























 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS