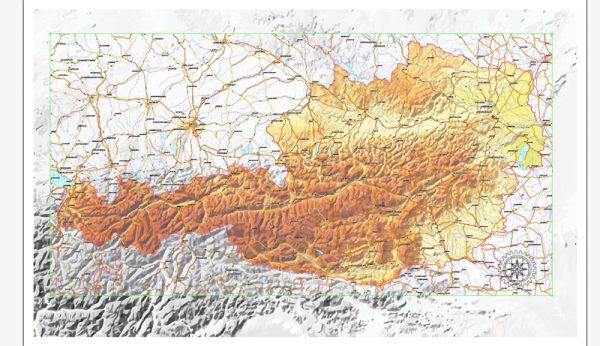
About this vectorial map Ver.2 of Austria (Europe) in (.CDR) format
Archive size: 1.3 Mb, zipped .CDR
DPI: 300
Vector Map Data: 2016
License: Royalty Free
Austria vector Relief road map Ver.2 in Corel Draw format [.CDR] are full editable maps, which can be printed in all sizes needed, no matter what big it is. With no quality loss, because it`s vector format.
All maps in VectorMap portal has a Royalty Free license. You don`t pay for each use, you can change all the content you want, including line thickness, font design, or add the objects you want.
We provide very precise Relief road map of Austria, perfect for large size printing, like office walls or billboards.
Also available in other formats at the same price: DWG, DXF AutoCAD, AI, EPS, PDF.
This Austria vector map features:
Highways, major roads
Relief road map
Big and small Rivers, small streams also,
Lake, ponds and other water bodies,
Landmark fill.
Need more data, or something special? Please, feel free to contact our friendly team.
Austria.
This vector map of Austria is used as a basis for design, editing, and further printing.
This is the most detailed, exact map of Austria for high-quality printing and polygraphy. You can always clarify the map development date by contacting us.
For your convenience, all objects on Austria vector map are divided into layers. And the editing is very easy – colors, lines, etc.
You can easily add any objects needed (e.g. shops, salons, sale points, gas station or attraction) on any layer of Austria vector map.
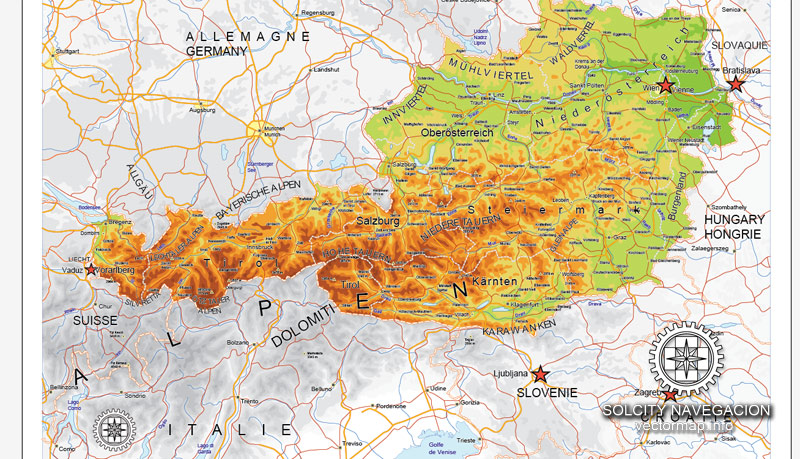
Austria is a country of nearly 9 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Hungary and Slovakia to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The territory of Austria covers 83,879 km2 (32,386 sq mi). The terrain is highly mountainous, lying within the Alps; only 32% of the country is below 500 m (1,640 ft), and its highest point is 3,798 m (12,461 ft). The majority of the population speaks local Bavarian dialects of German as their native language, and German in its standard form is the country’s official language. Other local official languages are Hungarian, Burgenland Croatian, and Slovene.
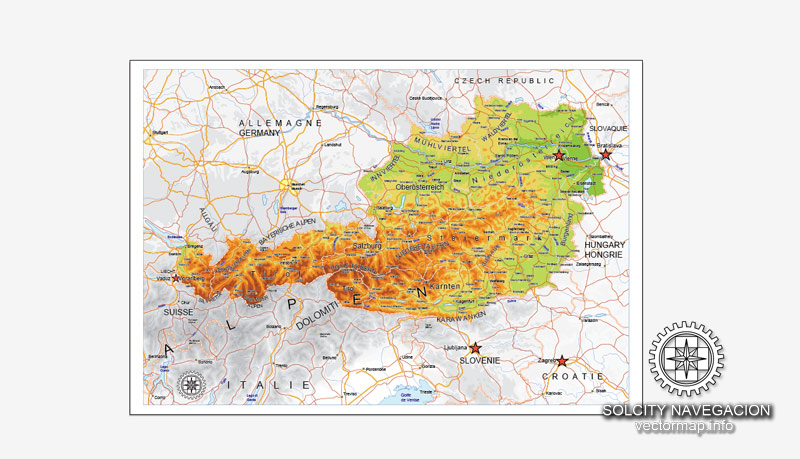
One of the advantages of Austria vector maps of our production is the relevance of cartographic data, we constantly update all our products.
This vector map of Austria is used by:
designers, layout designers, printers, advertisers and architects. Our product – vector maps – is designed for further editing and printing in large formats – from @Wall format (a few meters) to A-0 and A-1, A-2, A-3.
The Austria map in vector format is used for design, urban planning, presentations and media visualizations.
The advertising and presentation map of Austria (usually the final designer marks the routes, and puts the client’s objects (shops, saloons, gas stations etc.)
The undoubted advantage is that people will NEVER throw out this advertising product – the map. In fact, as an advertising medium, a map is the most “long-playing” of the well-known polygraphic advertising media, with the longest lifespan, and the maximum number of interactions with the customer.
For travelers, maps are sold at the airports and gas stations around the world. Often the source is our vector maps.
Take a look, who purchases our vector maps of Austria in “Our Clients and Friends” page – these are large and small companies, from super-brands like Volvo and Starbucks, to small design studios and printing houses.
It’s very easy to work with vector maps of Austria city, even for a not very experienced designer who can turn on and off the map layers, add new objects, change the colors of fill and lines according to customer requirements.
The undoubted advantage of Austria vector maps in printing is an excellent and detailed visualization, when customer can expand a large paper map and instantly define his location, find a landmark, an object or address on map, unlike using the popular electronic formats of Google and Yandex maps for example.
Printable vector maps of Austria are much more convenient and efficient than any electronic maps on your smartphone, because ALL DETAILS are displayed in the entire space of Austria map.
Useful tips on working with vector maps of cities and countries in Adobe Illustrator.
«V» – launches the Selection tool (cursor, black arrow), which makes active any vector line.
«А» – launches the Direct Selection tool (white cursor), allows you to select curve elements and drag them to the desired place.
«R» – activates the Rotate tool, which helps you rotating selected objects around the center point by 360 degrees.
«E» – gives you the opportunity to use the Eraser tool and erase unnecessary parts.
«X» – switches between Fill and Stroke in the Tools section. Try to get used to this hot key and
you will quickly understand that you can’t live and work without it.
Guides are not limited to vertical and horizontal in Adobe Illustrator. You can also create a diagonal guide for example. Moreover, you can turn any contours into guides. Select the outline and go to View > Guides > Make Guides (Create Guides), or simply press Cmd/Ctrl + 5. You can also turn the guides back into an editable object. Go to menu, View > Guides > Unlock Guides (Release Guides), select the guide you want to edit and select View > Guides > Release Guides (Reset Guides), or just press Cmd/Ctrl + Option / Alt + 5).
You will probably want to change the color scheme used on our Austria vector map.
To quickly and effectively play with colors.
Of course, you can do it manually, all objects in our Austria vector map are divided according to types and layers, and you can easily change the color gamma of vector objects in groups and layers.
But there is more effective way of working with the whole VECTOR MAP of Austria and all layers:
The overview dialog «Edit colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» (this dialog box name can change depending on the context):
If you have selected a part or a layer of Austria vector map and open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or the Color Catalog, or if you choose Edit > Edit Colors> Repaint Graphic Object, then the «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box appears, and you get access to «Assign» and «Edit» tabs.
If a picture or a map fragment is not selected, and you open the dialog box by clicking the icon in the Control panel, on the Samples palette or in the Color Catalog, the «Edit Colors» dialog box appears and you can only access the «Edit» tab.
Regardless of the name at the top of the dialog box, the right-hand side always displays the color group of the current document, as well as two default color groups: Print Color and Grayscale. These color groups can be selected and used any time.
Create and edit color groups of Austria vector map, and also assign colors using the «Edit Colors»/ а «Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
A. Creating and editing of a color group on the «Edit» tab
B. Assigning colors on the «Assign» tab
C. Select a group of colors from the «Color groups» list
The option «Repaint a graphic object» in the lower part of the dialog box allows you to preview the colors on a selected layer of Vector map, or a group of elements, and specify whether its colors will be redefined when the dialog box is closed.
The main areas of the dialog box are:
«Edit»
The «Edit» tab is designed to create a new or edit the existing color groups.
The harmony rules Menu and the Color Wheel are used to conduct experiments with color harmonies. The color wheel shows how colors are related in color harmony, and the color bars allow you to view and manipulate an individual color values. In addition, you can adjust the brightness, add and remove colors, save color groups and view colors on the selected Vector Map of Austria or a separated layers.
«Assign»
The «Assign» tab is used to view and control on how the original colors are replaced with colors from the color group like your corporate colors in the Vector Map of Austria city.
The assign color ability is provided only if the entire map, layer or fragment is selected in the document. You can specify which of new colors replace the current colors, whether the spot colors should be preserved and how colors are replaced (for example, you can replace colors completely or changing the color tone while maintaining the brightness). The «Assign» tab allows you to redefine colors in the Vector Map of Austria city, or in separate layers and fragments using the current color group or reducing the number of colors in the current Vector Map.
Color groups
Is a list of all saved color groups for current document (the same groups appear in the «Samples» palette). You can edit and delete the existing color groups, as well as creating a new ones using the list of “Color Groups” in the dialog box. All changes appear in the «Samples» palette.
The highlighted color group shows, which color group is currently edited.
Any color group can be selected and edited, or used to redefine the colors in the selected vector map of Austria city, its fragments or elements.
Saving a color group adds this group to the specified list.
Opening the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box.
Open the «Edit Colors»/«Repaint Graphic Object» dialog box using one of the following methods:
«Edit»> «Edit Colors»> «Repaint Graphic object» or «Repaint With Style».
Use these commands if you need to edit the colors in the selected vector map of Austria city.
«Repaint Graphic object» button on the «Control» panel.
Use this button if you need to adjust colors of Austria vector map using the а «Repaint graphic object» dialog box.
The specified button is available if the selected vector map or its fragment contains two or more colors.
Note. This color editing method is convenient for global color adjustment in a vector map, if global colors were not used when creating a Map of Austria.
The «Edit colors» button or «Edit or apply colors» on the «Color Catalog» palette
Click this button if you need to edit colors on the «Color Catalog» palette or edit and then apply them to the selected Vector Map of Austria or its fragment.
The «Edit color group» button or «Edit or apply color group» on the «Samples» palette.
Click this button if you need to edit the colors in the specific color group or edit and apply them to the selected Vector Map of Austria or a group of its elements, for example, the whole layer “Streets and lines”. You can also double-click the color group in the Samples panel to open the dialog box.
If the map file is too large and your computer freezes or even can’t open it quickly:
1. Try to reduce the color resolution of the video card (display) to 256 colors while working with a large map.
2. Using Windows Task Manager, select all the application you don’t need, while working with map, just turn them off.
3. Launch Adobe Illustrator. (DO NOT OPEN the vector map file)
4. Start the Windows Task Manager using administrator rights > Find the “Illustrator” process > set the «real time» priority,
5. Open the file. When you see the LEGACY FONT popup window – click “OK” (do not update). You can restore the TEXT later.
6. Can also be useful: When file is opened – Edit > Settings > Basic Settings > disable smoothing. /// It looks scary, but works quickly)))
We recommend saving the file in Adobe Illustrator 10 version. It’s much more stable when working with VERY BIG size files.
Austria is a federal republic with a parliamentary representative democracy comprising nine federated states. The capital and largest city, with a population exceeding 1.8 million, is Vienna. Other major urban areas of Austria include Graz, Linz, Salzburg and Innsbruck. Austria is consistently ranked as one of the richest countries in the world by per capita GDP terms. The country has developed a high standard of living and in 2018 was ranked 20th in the world for its Human Development Index. The republic declared its perpetual neutrality in foreign political affairs in 1955. Austria has been a member of the United Nations since 1955, joined the European Union in 1995, and is a founder of the OECD. Austria also signed the Schengen Agreement in 1995, and adopted the euro currency in 1999.
Geography
Austria is a largely mountainous country due to its location in the Alps. The Central Eastern Alps, Northern Limestone Alps and Southern Limestone Alps are all partly in Austria. Of the total area of Austria (84,000 km2 or 32,433 sq mi), only about a quarter can be considered low lying, and only 32% of the country is below 500 metres (1,640 ft). The Alps of western Austria give way somewhat into low lands and plains in the eastern part of the country.
Austria lies between latitudes 46° and 49° N, and longitudes 9° and 18° E.
It can be divided into five areas, the biggest being the Eastern Alps, which constitute 62% of the nation’s total area. The Austrian foothills at the base of the Alps and the Carpathians account for around 12% and the foothills in the east and areas surrounding the periphery of the Pannoni low country amount to about 12% of the total landmass. The second greater mountain area (much lower than the Alps) is situated in the north. Known as the Austrian granite plateau, it is located in the central area of the Bohemian Mass and accounts for 10% of Austria. The Austrian portion of the Vienna basin comprises the remaining 4%.
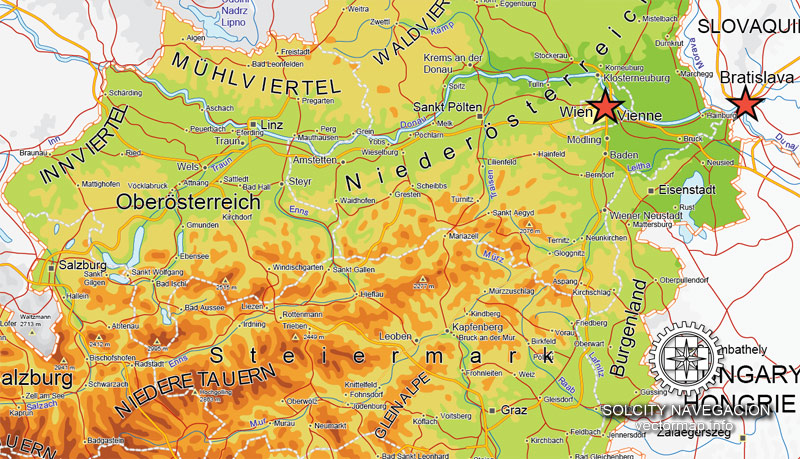
Austria is a small, predominantly mountainous country in Central Europe, approximately between Germany, Italy and Hungary. It has a total area of 83,879 km² (32,385 mi²), about twice the size of Switzerland.
The landlocked country shares national borders with Switzerland (a non-European Union member state, which it borders for 158 km, or 98 mi) and the principality of Liechtenstein (also a non-EU member state, of which it borders for 34 km or 21 mi) to the west, Germany (801 km or 497 mi) and the Czech Republic (402 km or 249 mi) and Slovakia (105 km or 65 mi) to the north, Hungary to the east (331 km or 205 mi), and Slovenia (299 km or 185 mi) and Italy (404 km or 251 mi) to the south (total: 2,534 km or 1,574 mi).
The westernmost third of the somewhat pear-shaped country consists of a narrow corridor between Germany and Italy that is between 32 km (19 mi) and 60 km (37 mi) wide. The rest of Austria lies to the east and has a maximum north–south width of 280 km (173 mi). The country measures almost 600 km (372 mi) in length, extending from Lake Constance (German Bodensee) on the Austrian-Swiss-German border in the west to the Neusiedler See on the Austrian-Hungarian border in the east. The contrast between these two lakes – one in the Alps and the other a typical steppe lake on the westernmost fringe of the Hungarian Plain – illustrates the diversity of Austria’s landscape.
Seven of Austria’s nine provinces have long historical traditions predating the establishment of the Republic of Austria in 1918: Upper Austria, Lower Austria, Styria, Carinthia, Salzburg, Tyrol, and Vorarlberg. The provinces of Burgenland and Vienna were established after World War I. Most of Burgenland had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary, but it had a predominantly German-speaking population and hence became Austrian. Administrative and ideological reasons played a role in the establishment of Vienna as an independent province. Vienna, historically the capital of Lower Austria, was a socialist stronghold, whereas Lower Austria was conservative, and both socialists and conservatives wanted to consolidate their influence in their respective provinces. Each province has a provincial capital with the exception of Vienna, which is a province in its own right in addition to being the federal capital. In Vienna, the City Council and the mayor function as a provincial parliament and provincial governor, respectively.
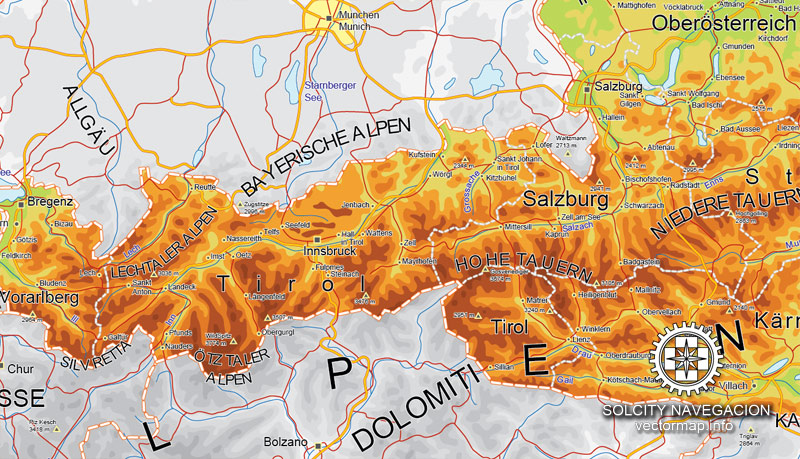
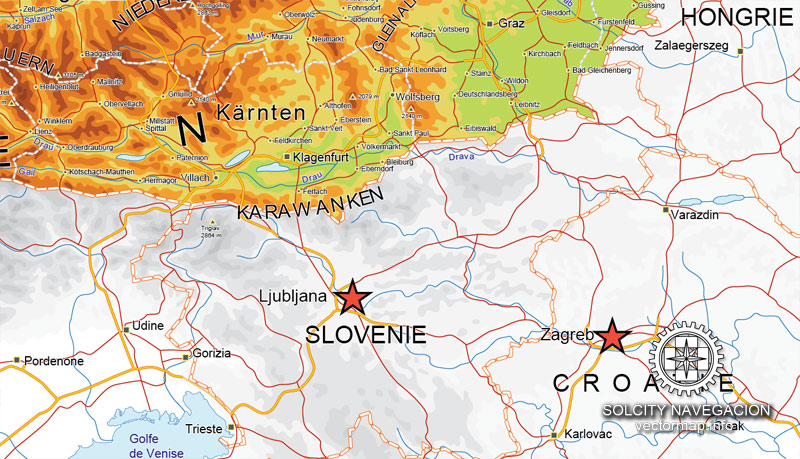
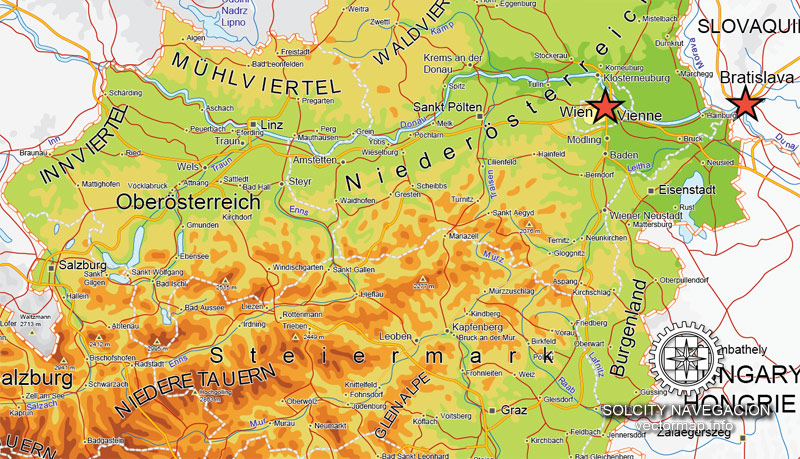
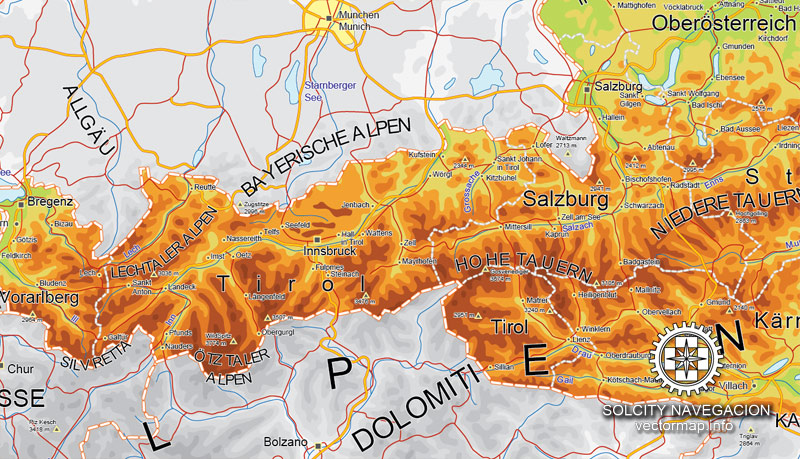
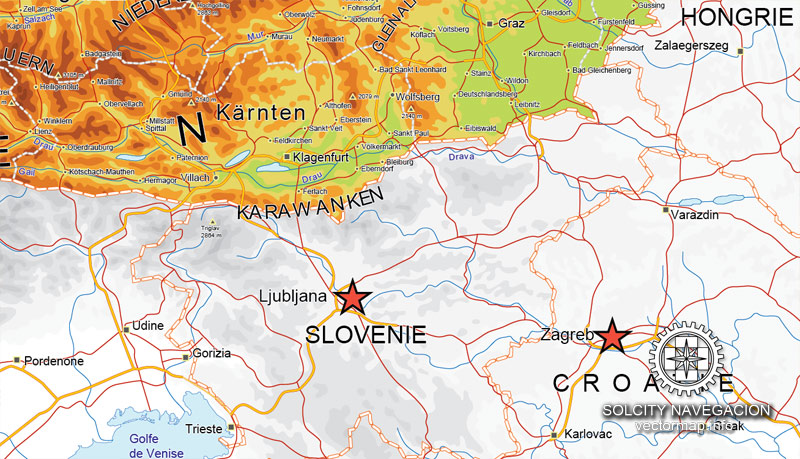
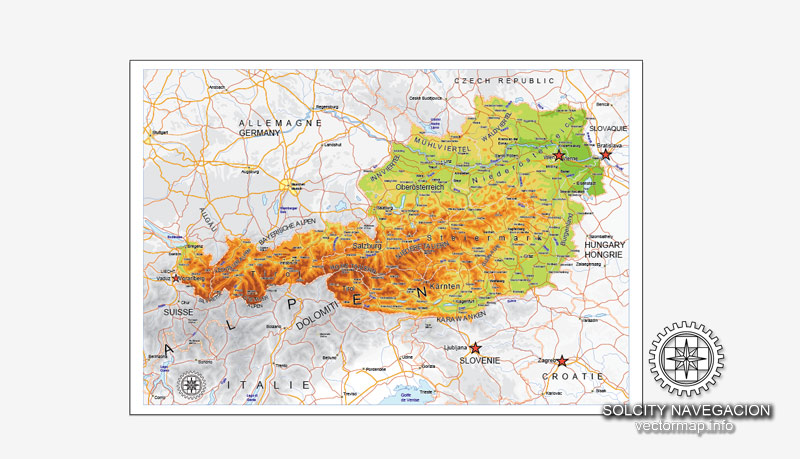
Cities and counties near or inside Austria vectorial map Ver.2, Europe
Looking for more Austria vector maps?
Purchasing and downloading of CorelDraw Austria (Europe) vectorial Relief road map Ver.2
We accept PayPal and Credit Card payment. After the payment you will be redirected to the download page. We guarantee 100% satisfaction. Royalty Free license.
De:
Über diese vectorial Relief Karte Ver.2 von Österreich (Europa) in (.CDR) Format
Archivgröße: 1,3 MB, Reißverschluss .CDR
DPI: 300
Vektor-Karte Daten: 2016
Lizenz: Royalty Free
Österreich Relief Vektorkarten Ver.2 in CorelDraw-Format [.CDR] sind voll editierbar Karten, die in allen Größen benötigt werden, egal was groß es ist gedruckt werden kann. Ohne Qualitätsverlust, weil es `s Vektor-Format.
Alle Karten im Vektorkarte-Portal hat eine Royalty Free Lizenz. Sie don `t für jeden Einsatz zu bezahlen, können Sie alle Inhalte, die Sie möchten, einschließlich Linienstärke, Schriftdesign zu ändern, oder fügen Sie die Objekte, die Sie wollen.
Wir bieten Ihnen eine sehr genaue Relief Karten von Österreich, ideal für Großformatdruck, wie Bürowänden oder Werbetafeln.
Auch in andere Formate zum gleichen Preis: DWG, DXF AutoCAD, Corel Draw, EPS, PDF.
Das Österreich-Vektor-Karte verfügt über:
Autobahnen, Hauptstraßen
Große und kleine Flüsse, kleine Bäche auch,
See, Teichen und anderen Gewässern,
Landmark Füllung.
Sie benötigen weitere Daten oder etwas Besonderes? Bitte, zögern Sie unser freundliches Team zu kontaktieren.
Städte und Landkreise in der Nähe oder in Österreich vectorial Karte, Europa
Auf der Suche nach mehr Österreich Vektorkarten?
Kaufen und Herunterladen von CorelDraw Österreich (Europa) vectorial Karte
Wir akzeptieren PayPal und Kreditkarten-Zahlung. Nach der Bezahlung werden Sie zur Download-Seite umgeleitet werden. Wir garantieren 100% Zufriedenheit. Lizenzfreie Lizenz.
Austria German: Österreich, officially the Republic of Austria (German: Republik Österreich, About this sound listen (help·info)), is a federal republic and a landlocked country of over 8.7 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Hungary and Slovakia to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The territory of Austria covers 83,879 square kilometres (32,386 sq mi). The terrain is highly mountainous, lying within the Alps; only 32% of the country is below 500 metres (1,640 ft), and its highest point is 3,798 metres (12,461 ft). The majority of the population speak local Bavarian dialects of German as their native language, and Austrian German in its standard form is the country’s official language. Other local official languages are Hungarian, Burgenland Croatian, and Slovene.
The origins of modern-day Austria date back to the time of the Habsburg dynasty when the vast majority of the country was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. From the time of the Reformation, many Northern German princes, resenting the authority of the Emperor, used Protestantism as a flag of rebellion. The Thirty Years War, the influence of the Kingdom of Sweden and Kingdom of France, the rise of the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Napoleonic invasions all weakened the power of the Emperor in the north of Germany, but in the south, and in non-German areas of the Empire, the Emperor and Catholicism maintained control. During the 17th and 18th centuries, Austria retained its position as one of the great powers of Europe and, in response to the coronation of Napoleon as the Emperor of the French, the Austrian Empire was officially proclaimed in 1804. Following Napoleon’s defeat, Prussia emerged as Austria’s chief competitor for rule of a greater Germany. Austria’s defeat by Prussia at the Battle of Königgrätz, during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, cleared the way for Prussia to assert control over the rest of Germany. In 1867, the empire was reformed into Austria-Hungary. After the defeat of France in the 1870-1 Franco-Prussian War, Austria was excluded from the new German Empire, although in the following decades its politics, and its foreign policy, increasingly converged with those of the Prussian-led Empire. During the 1914 July Crisis that followed the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria vector maps, Germany guided Austria in issuing the ultimatum to Serbia that led to the declaration of World War I.
After the collapse of the Habsburg (Austro-Hungarian) Empire in 1918 at the end of World War I, Austria adopted and used the name the Republic of German-Austria (Deutschösterreich), later changed to Österreich, in an attempt at union with Germany, but this was forbidden under the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919). The First Austrian Republic was established in 1919. In the 1938 Anschluss, Austria was annexed to Nazi Germany. This lasted until the end of World War II in 1945, after which Germany was occupied by the Allies and Austria’s printable map former democratic constitution was restored. In 1955, the Austrian State Treaty re-established Austria as a sovereign state, ending the occupation. In the same year, the Austrian Parliament created the Declaration of Neutrality which declared that the Second Austrian Republic would become permanently neutral.
Today, Austria is a parliamentary representative democracy comprising nine federal states. The capital and largest city, with a population exceeding 1.7 million, is Vienna. Austria is one of the richest countries in the world, with a nominal per capita GDP of $43,724[when?]. The country has developed a high standard of living and in 2014 was ranked 21st in the world for its Human Development Index. Austria editable map has been a member of the United Nations since 1955, joined the European Union in 1995, and is a founder of the OECD. Austria also signed the Schengen Agreement in 1995, and adopted the euro currency in 1999.
Geography of Austria
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Geography of Austria
Austria
Continent Europe
Region Central Europe
Coordinates 47°20′N 13°20′ECoordinates: 47°20′N 13°20′E
Area Ranked 114th
83,879 km2 (32,385 mi²)
Coastline 0 km (0 mi; landlocked)
Borders 2,534 km (1,574 mi)
Czech Republic 402 km (249 mi)
Germany 801 km (497 mi)
Hungary 331 km (205 mi)
Italy 404 km (251 mi)
Liechtenstein (non-EU) 34 km (21 mi)
Slovakia 105 km (65 mi)
Slovenia 299 km (185 mi)
Switzerland (non-EU) 158 km (98 mi)[citation needed]
Highest point Grossglockner
3,797 m
Lowest point Neusiedler See
115 m
Longest river Danube River
2,857 km
Largest lake Neusiedler See
320 km2
Austria is a small, predominantly mountainous country in Central Europe, approximately between Germany, Italy and Hungary. It has a total area of 83,879 km² (32,385 mi²), about twice the size of Switzerland and slightly smaller than the state of Maine.
The landlocked country shares national borders with Switzerland (a non-European Union member state, which it borders for 158 km, or 98 mi) and the principality of Liechtenstein (also a non-EU member state, of which it borders for 34 km or 21 mi) to the west, Germany (801 km or 497 mi) and the Czech Republic (402 km or 249 mi) and Slovakia (105 km or 65 mi) to the north, Hungary to the east (331 km or 205 mi), and Slovenia (299 km or 185 mi) and Italy (404 km or 251 mi) to the south (total: 2,534 km or 1,574 mi).
The westernmost third of the somewhat pear-shaped country consists of a narrow corridor between Germany and Italy that is between 32 km (19 mi) and 60 km (37 mi) wide. The rest of Austria map for Illustrator lies to the east and has a maximum north–south width of 280 km (173 mi). The country measures almost 600 km (372 mi) in length, extending from Lake Constance (German Bodensee) on the Austrian-Swiss-German border in the west to the Neusiedler See on the Austrian-Hungarian border in the east. The contrast between these two lakes – one in the Alps and the other a typical steppe lake on the westernmost fringe of the Hungarian Plain – illustrates the diversity of Austria’s landscape.
Seven of Austria’s nine provinces have long historical traditions predating the establishment of the Republic of Austria in 1918: Upper Austria, Lower Austria, Styria, Carinthia, Salzburg, Tyrol, and Vorarlberg. The provinces of Burgenland and Vienna were established after World War I. Most of Burgenland had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary, but it had a predominantly German-speaking population and hence became Austrian. Administrative and ideological reasons played a role in the establishment of Vienna as an independent province. Vienna, historically the capital of Lower Austria, was a socialist stronghold, whereas Lower Austria was conservative, and both socialists and conservatives wanted to consolidate their influence in their respective provinces. Each province has a provincial capital with the exception of Vienna, which is a province in its own right in addition to being the federal capital. In Vienna, the City Council and the mayor function as a provincial parliament and provincial governor, respectively.[citation needed]
Landform regions of Austria
Geographic coordinates: 47°20′N 13°20′E
Austria may be divided into three unequal geographical areas. The largest part of Austria (62%) is occupied by the relatively young mountains of the Alps, but in the east, these give way to a part of the Pannonian plain, and north of the Danube Riverlies the Bohemian Forest, an older, but lower, granite mountain range.
River Danube
The Danube has its source near Donaueschingen in southwestern Germany and flows through Austria scalable map before emptying into the Black Sea. It is the only major European river that flows eastwards, and its importance as an inland waterway has been enhanced by the completion in 1992 of the Rhine-Main-Danube Canal in Bavaria, which connects the Rhine and Main rivers with the Danube and makes barge traffic from the North Sea to the Black Sea possible.
The major rivers north of the watershed of the Austrian Alps (the Inn in Tyrol, the Salzach in Salzburg, and the Enns in Styria and Upper Austria) are direct tributaries of the Danube and flow north into the Danube valley, whereas the rivers south of the watershed in central and eastern Austria (the Gail and Drau rivers in Carinthia and the Mürz and Mur rivers in Styria) flow south into the drainage system of the Drau, which eventually empties into the Danube in Serbia. Consequently, central and eastern Austria are geographically oriented away from the watershed of the Alps: the provinces of Upper Austria and Lower Austria toward the Danube and the provinces of Carinthia and Styria toward the Drau.
The Alps
Three major ranges of the Alps – the Northern Calcareous Alps, Central Alps, and Southern Calcareous Alps – run west to east through Austria. The Central Alps, which consist largely of a granite base, are the largest and highest ranges in Austria. The Central Alps run from Tyrol to approximately the Styria-Lower Austria border and include areas that are permanently glaciated in the Ötztal Alps on the Tyrolean–Italian border and the High Tauern in East Tyrol and Carinthia. The Northern Calcareous Alps, which run from Vorarlberg through Tyrol into Salzburg along the German border and through Upper Austria and Lower Austria toward Vienna, and the Southern Calcareous Alps, on the Carinthia-Slovenia border, are predominantly limestone and dolomite. At 3,797 m, Großglockner is the highest mountain in Austria. As a general rule, the farther east the Northern and Central Alps run, the lower they become. The altitude of the mountains also drops north and south of the central ranges.
As a geographic feature, the Alps literally overshadow other landform regions. Just over 28% of Austria is moderately hilly or flat: the Northern Alpine Foreland, which includes the Danube Valley; the lowlands and hilly regions in northeastern and eastern Austria, which include the Danube Basin; and the rolling hills and lowlands of the Southeastern Alpine Foreland. The parts of Austria that are most suitable for settlement – that is, arable and climatically favorable – run north of the Alps through the provinces of Upper Austria and Lower Austria in the Danube Valley and then curve east and south of the Alps through Lower Austria, Vienna, Burgenland, and Styria. Austria’s least mountainous landscape is southeast of the low Leithagebirge, which forms the southern lip of the Viennese Basin, where the steppe of the Hungarian Plain begins.
Bohemian Forest (mountain range)
The granite massif of the Bohemian Forest (known in German as the Böhmerwald), a low mountain range with bare and windswept plateaus and a harsh climate, is located north of the Danube Valley and covers the remaining 10% of Austria’s area. Notable is the Manhartsberg a granite ridge which separates Waldviertel from Weinviertel.
Mountains
Großglockner
Wildspitze
Großvenediger
Similaun
Großes Wiesbachhorn
The 35 highest mountains in Austria:
Name Height Range
1 Großglockner 3,797 m High Tauern
2 Wildspitze 3,772 m Ötztal Alps
3 Kleinglockner 3,770 m High Tauern
4 Weißkugel 3,739 m Ötztal Alps
5 Pöschlturm 3,721 m High Tauern
6 Hörtnagelturm 3,719 m High Tauern
7 Hofmannspitze 3,711 m High Tauern
8 Weitzenböckturm 3,702 m High Tauern
9 Draschturm 3,701 m High Tauern
10 Gerinturm 3,700 m High Tauern
11 Glocknerhorn 3,680 m High Tauern
12 Teufelshorn 3,677 m High Tauern
13 Großvenediger 3,674 m High Tauern
14 Hinterer Brochkogel 3,628 m Ötztal Alps
15 Hintere Schwärze 3,628 m Ötztal Alps
16 Similaun 3,606 m Ötztal Alps
17 Großes Wiesbachhorn 3,564 m High Tauern
18 Rainerhorn 3,560 m High Tauern
19 Ötztaler Urkund 3,556 m Ötztal Alps
20 Marzellspitze 3,555 m Ötztal Alps
21 Ramolkogel 3,550 m Ötztal Alps
22 Schalfkogel 3,540 m Ötztal Alps
23 Watzespitze 3,533 m Ötztal Alps
24 Hochvernagtspitze 3,530 m Ötztal Alps
25 Langtaufererspitze 3,529 m Ötztal Alps
26 Weißseespitze 3,526 m Ötztal Alps
27 Mutmalspitze 3,522 m Ötztal Alps
28 Fineilspitze 3,516 m Ötztal Alps
29 Innere Querspitze 3,515 m Ötztal Alps
30 Hochfeiler 3,510 m Zillertal Alps
31 Teufelskamp 3,509 m High Tauern
32 Romariswandkopf 3,508 m High Tauern
33 Zuckerhütl 3,505 m Stubai Alps
34 Hohes Aderl 3,504 m High Tauern
35 Fluchtkogel 3,500 m Ötztal Alps
(All heights are related to the 1875 Trieste tide gauge used in Austria – metres above the Adriatic)
Westernmost point: River Rhine (at tripoint border of Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein), Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, 47°16′16″N 9°31′51″E, but note that the international borders between Austria, Germany and Switzerland are not agreed for Lake Constance.
Westernmost settlement: Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, 47°15′56″N 9°32′42″E
Easternmost point: the corner of a field in Deutsch Jahrndorf, Burgenland, 48°0′24″N 17°9′38″E
Easternmost settlement: Deutsch Jahrndorf, Burgenland, 48°0′37″N 17°6′33″E
Northernmost point: the Neumühlbach stream, near Rottal, Haugschlag, Lower Austria, 49°1′14″N 15°1′16″E
Northernmost settlement: Haugschlag, Lower Austria, 48°59′51″N 15°3′32″E
Southernmost point: in the Steiner Alpen, Eisenkappel-Vellach, Carinthia, between the Seeländer Sattel and the Sanntaler Sattel, at an altitude of more than 2000 m, 46°22′21″N 14°33′55″E
Southernmost settlement: Eisenkappel-Vellach, Carinthia, 46°25′37″N 14°32′58″E
Source
See more Austria cities maps in vector
For example: Austria map in Adobe Illustrator vector format
Vienna vector street map, Austria
Linz city street map printable, Austria










 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS