Railroad history in Finland dates back to the 19th century, and the development of railways played a crucial role in the economic and social transformation of the country.
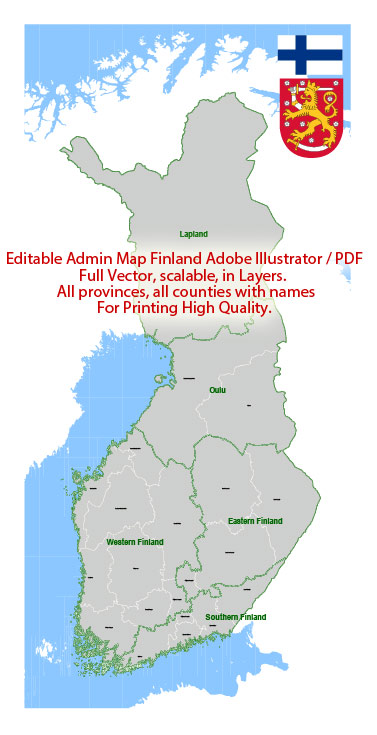
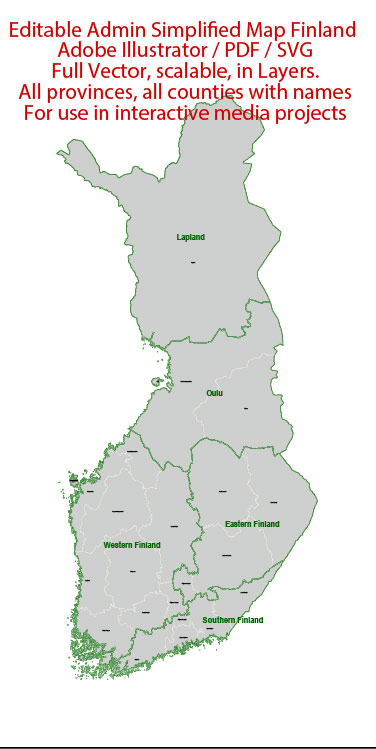
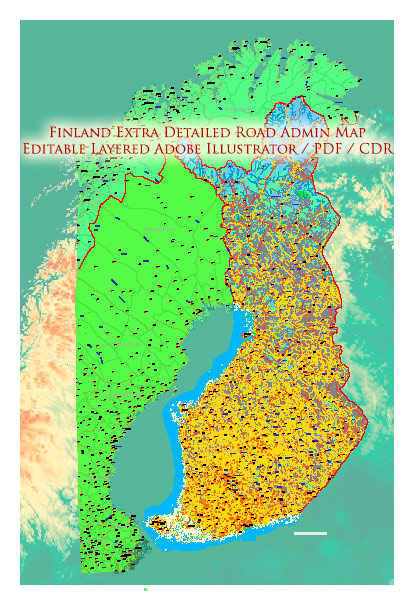
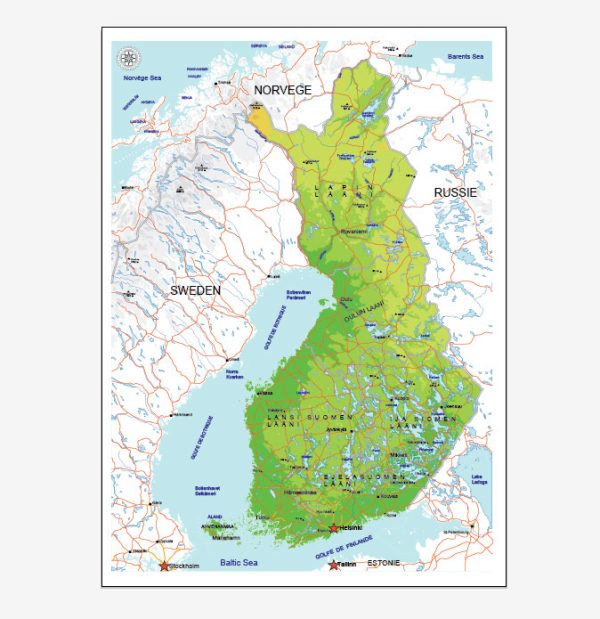
Vectormap.Net provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date vector maps in Adobe Illustrator, PDF and other formats, designed for editing and printing. Please read the vector map descriptions carefully.
Here’s a detailed overview of the railroad history in Finland:
- Early Plans and Proposals (19th Century):
- The idea of constructing railways in Finland emerged during the 19th century when the country was still under Russian rule.
- In 1860, the Finnish Senate appointed a committee to explore the feasibility of building railways to enhance transportation and boost economic development.
- First Railways and the Private Sector (1860s-1870s):
- The first railway line in Finland was the Helsinki-Hämeenlinna railway, inaugurated in 1862. This line connected the capital city, Helsinki, to Hämeenlinna.
- The private sector played a significant role in the early development of Finnish railways. Private companies, both domestic and foreign, were involved in the construction and operation of rail lines.
- Expansion and Nationalization (1880s-1910s):
- The government started to take a more active role in railway development in the late 19th century. The Finnish State Railways (Valtionrautatiet or VR) was founded in 1862 and gradually took over the ownership and operation of various private railway lines.
- The railway network expanded, connecting major cities and industrial centers. New lines were built to enhance connectivity and support economic activities.
- During this period, the railway infrastructure also played a crucial role in facilitating the transportation of goods, especially timber and other natural resources.
- Electrification and Modernization (1920s-1930s):
- In the 1920s and 1930s, Finland underwent electrification of its rail network. The Helsinki–Hämeenlinna line was the first to be electrified in 1933.
- Electrification improved the efficiency and reliability of train services, especially in densely populated and industrialized areas.
- Impact of World Wars (1939-1945):
- The Winter War (1939-1940) and the Continuation War (1941-1944) had a significant impact on the Finnish railways. The network was used for military transportation, and some damage occurred during the conflicts.
- Post-war reconstruction efforts focused on repairing and modernizing the rail infrastructure.
- Post-War Development and Technological Advancements (1950s-1980s):
- The post-war period saw continued development of the rail network, with new lines and improvements in technology.
- Diesel and electric locomotives replaced steam locomotives, contributing to more efficient and environmentally friendly rail transport.
- Liberalization and Restructuring (1990s-Present):
- In the 1990s, Finland, like many other European countries, began to liberalize its railway sector. This involved separating infrastructure management from train operations, allowing for more competition and efficiency.
- The Finnish Transport Agency (now part of the Finnish Transport and Communications Agency Traficom) was established to oversee the rail infrastructure.
- High-Speed Rail and Future Developments:
- Finland has explored the possibility of high-speed rail connections, particularly between major cities and neighboring countries.
- Ongoing investments and improvements continue to enhance the efficiency and capacity of the rail network, supporting sustainable and reliable transportation.
In summary, the railroad history of Finland reflects a trajectory of early private initiatives, followed by increased government involvement, electrification, modernization, and adaptation to changing technologies. The rail network continues to play a vital role in the country’s transportation infrastructure and economic development.

 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS