Finland’s history of urban development is characterized by a combination of traditional rural settlements and modern urban planning. Here is a brief overview:
- Medieval and Early Modern Periods (800-1809):
- Finland was part of the Kingdom of Sweden for several centuries, and during this time, urban centers like Turku and Vyborg (Viipuri) emerged as important trade and administrative hubs.
- The medieval street patterns and architectural styles reflected the influence of Swedish and European trends.
- Russian Rule (1809-1917):
- Finland became an autonomous Grand Duchy under Russian rule in 1809. During this period, Helsinki was chosen as the new capital in 1812, and significant urban development took place under the direction of German architect Carl Ludwig Engel.
- The architectural style of this era is often referred to as neoclassical, with wide boulevards and monumental buildings.
- Early 20th Century:
- After gaining independence from Russia in 1917, Finland experienced economic growth and industrialization. Urbanization increased as people moved from rural areas to cities in search of employment.
- The urban landscape began to reflect modernist influences, with functionalist architecture gaining popularity.
- Post-World War II Reconstruction:
- The Winter War (1939-1940) and Continuation War (1941-1944) with the Soviet Union led to significant damage in many Finnish cities. The post-war period saw extensive reconstruction efforts, with an emphasis on modern, efficient city planning.
- New housing projects and infrastructure developments were undertaken to accommodate the growing population.
- Late 20th Century:
- The latter half of the 20th century witnessed continued urbanization and the growth of metropolitan areas such as Helsinki, Espoo, and Vantaa. These cities became centers of commerce, education, and culture.
- Modernist urban planning principles were prevalent, with an emphasis on functional zoning and the separation of residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
- 21st Century:
- Finland has continued to prioritize sustainable and innovative urban development in the 21st century. The focus has shifted towards creating more livable cities, with an emphasis on green spaces, public transportation, and mixed-use developments.
- Helsinki, in particular, has gained recognition for its commitment to smart city initiatives, promoting technology and data-driven solutions for urban challenges.
- Regional Development:
- While the capital region has experienced significant urbanization, efforts have also been made to promote balanced regional development. Other cities and towns have seen infrastructure improvements and investments to attract businesses and residents.
Finland’s urban development history reflects a transition from medieval influences to modernist planning, with a contemporary focus on sustainability and technology in the 21st century. The country’s approach to urban planning has evolved to address changing societal needs and global trends.

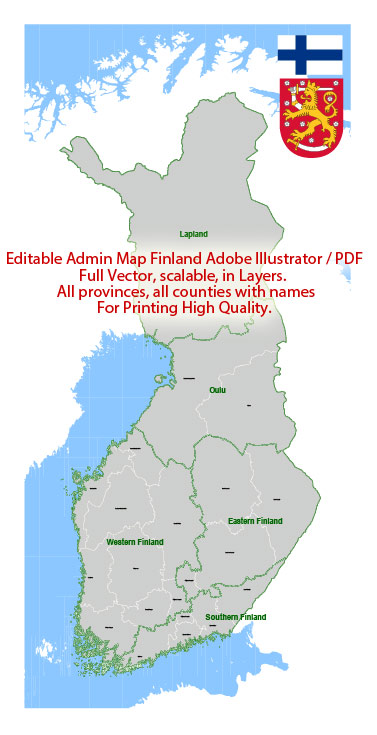
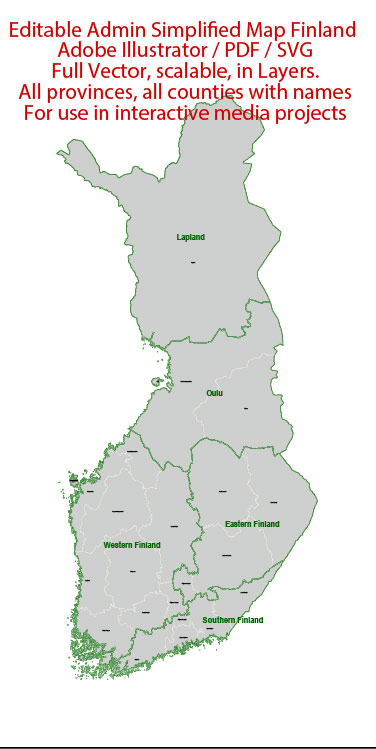
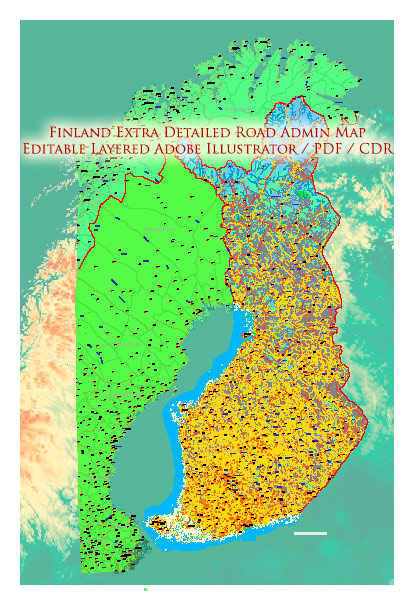
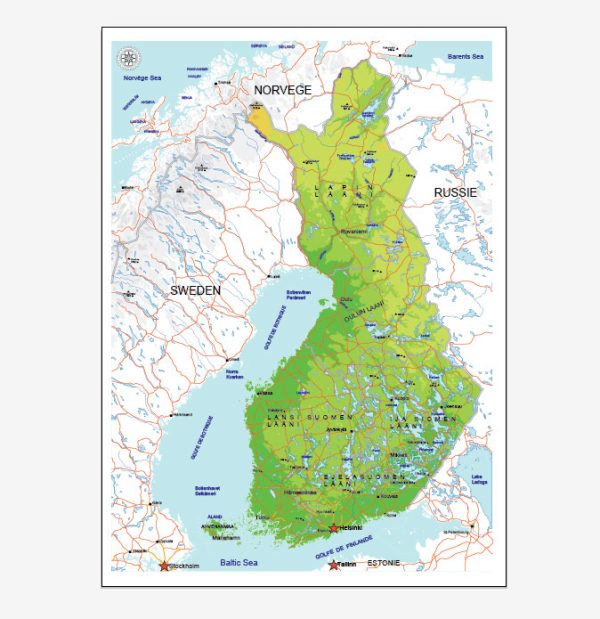
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D.
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D.