Nigeria is a country located in West Africa and is divided into several administrative territories. Nigeria is organized into six geopolitical zones, 36 states, and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT). Here’s a general description of these administrative territories:
- Geopolitical Zones: Nigeria is divided into six geopolitical zones. These zones were created to help in the administration and organization of the country. Each zone is a cluster of several states with similar cultural, geographical, and historical characteristics. The six geopolitical zones are:
- North-West
- North-East
- North-Central
- South-West
- South-East
- South-South
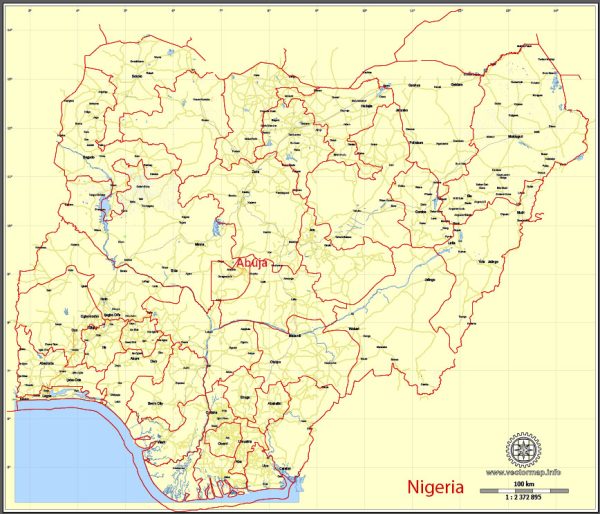
- States: Nigeria is comprised of 36 states, each with its own government and governor. Each state has a capital city and is further subdivided into local government areas (LGAs). These states are responsible for implementing policies, governance, and development at the state level. Some of the major states include Lagos, Kano, Rivers, and Enugu.
- Federal Capital Territory (FCT): The Federal Capital Territory, Abuja, serves as the capital of Nigeria. It is distinct from the states and is directly administered by the federal government. Abuja was chosen as the capital to replace Lagos, which was Nigeria’s former capital.
- Local Government Areas (LGAs): Each state in Nigeria is further divided into local government areas. These are the smallest administrative units in the country. As of my last knowledge update, Nigeria had 774 LGAs. Local governments play a vital role in the implementation of government policies and services at the grassroots level.
- Traditional Rulers: In addition to the formal administrative divisions, Nigeria also has a rich system of traditional rulers and chieftaincies. These traditional leaders hold significant influence within their respective communities and often play a key role in local governance and dispute resolution.
- Special Status Areas: Some areas in Nigeria, like the Federal Capital Territory and Lagos, are given special status due to their significance. Lagos, for example, is considered a special city due to its economic and commercial importance.
It’s important to note that Nigeria’s administrative divisions and political landscape may change over time due to government reorganizations, boundary adjustments, or other factors.

 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS