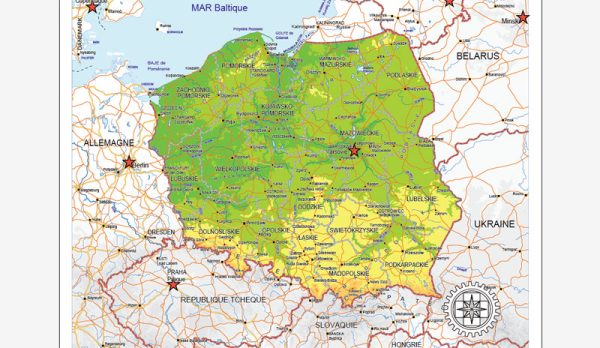
Poland is a country located in Central Europe, and its geology is characterized by a diverse range of geological features and formations. The geology of Poland can be divided into several distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics. Here is a brief description of Poland’s geology:
- Baltic Sea Coastal Plain: This region covers the northern and western parts of Poland and consists of relatively flat, low-lying terrain. It is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, including sand, clay, and glacial deposits. The area is known for its extensive sand dunes and coastal marshes.
- Pomeranian Plateau: Located to the north of the country, this region is characterized by gently rolling hills and is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, including sandstones and marls. It is a significant agricultural area.
- Masurian Lake District: In northeastern Poland, this region is characterized by numerous lakes, hills, and forests. It was shaped by glacial processes and is known for its scenic beauty.
- Polish Lowlands: This extensive plain covers much of central and western Poland. It is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, including limestone, marl, and sandstone. It is an important agricultural and industrial region.
- Carpathian Mountains: In the south of Poland, the Carpathian Mountains extend into the country. This mountain range is predominantly composed of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, including limestone, shale, and granite. It offers a diverse landscape, including rugged peaks and deep valleys, and is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts.
- Sudetes: In the southwestern part of Poland, the Sudetes are another mountain range. They are formed by a variety of rock types, including granite, gneiss, and schist. The Sudetes are known for their scenic beauty and are popular for hiking and winter sports.
- Silesian Upland: This region, in the southwest of Poland, is characterized by rolling hills and is rich in mineral resources, including coal and iron ore. It has played a significant role in the country’s industrial history.
- Tatra Mountains: Part of the Carpathian range, the Tatra Mountains are the highest peaks in Poland. They are known for their stunning alpine landscapes, with rocky crags, glacial lakes, and diverse flora and fauna.
Poland’s geology has been shaped by various geological processes, including glaciation, tectonic activity, and sedimentation. The country’s diverse geology not only contributes to its natural beauty but also influences its economy and land use, including agriculture, mining, and tourism.


 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS