Hungary has a rich and complex history that spans over a thousand years. Here is a brief overview of Hungary’s history:
- Early History: The history of Hungary can be traced back to the arrival of the Magyar tribes in the Carpathian Basin in the late 9th century. Under the leadership of Árpád, the Magyars established a principality in the region.
- Kingdom of Hungary: In the year 1000, King Stephen I was crowned as the first Christian king of Hungary. This marked the beginning of the Kingdom of Hungary, which lasted for centuries. The Kingdom of Hungary played a significant role in the medieval history of Central Europe.
- Mongol Invasion: In 1241-1242, Hungary faced a devastating invasion by the Mongols, which caused significant damage and loss of life. The country eventually recovered and rebuilt.
- Ottoman Rule: Hungary was invaded by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century, leading to a long period of Ottoman rule. The Ottomans controlled parts of Hungary for over 150 years, and it wasn’t until the late 17th century that the Habsburgs gradually reasserted control over the region.
- Habsburg Monarchy: In 1687, the Habsburgs fully incorporated Hungary into the Habsburg Monarchy, which later became the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Hungary retained a degree of autonomy, but it was largely under Habsburg control.
- 1848 Revolution: In 1848, Hungary experienced a revolution and war of independence against Habsburg rule, led by figures like Lajos Kossuth. The revolution was ultimately crushed by the Habsburgs with Russian assistance.
- Austro-Hungarian Empire: The Compromise of 1867, also known as the Austro-Hungarian Compromise, established the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy, which gave Hungary a high degree of autonomy within the empire. This period marked a cultural and economic flourishing for Hungary.
- World War I: Hungary was a key component of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, which collapsed at the end of World War I. The Treaty of Trianon in 1920 led to the dismemberment of Hungary, reducing its territory and population significantly.
- Interwar Period: Hungary became a kingdom without a king and later a republic during the interwar period. Miklós Horthy established a conservative regime that lasted until World War II.
- World War II: Hungary initially aligned with Nazi Germany during World War II, leading to its occupation by the Germans. However, in 1944, Hungary tried to exit the war, leading to a Soviet invasion and the establishment of a communist government.
- Communist Era: After World War II, Hungary came under Soviet influence and established a communist government. The Hungarian Revolution of 1956, a failed uprising against communist rule, was a significant event during this period.
- Transition to Democracy: In 1989, Hungary began a peaceful transition to democracy and a market economy, following the fall of the Berlin Wall and the end of communism in Eastern Europe.
- European Union and NATO: Hungary joined NATO in 1999 and became a member of the European Union in 2004. It has since become an integral part of the European community.
Today, Hungary is a democratic republic and a member of the European Union. Its history is marked by a blend of cultural influences, including Magyar, Ottoman, Austrian, and Soviet, and it continues to be a country with a unique and rich heritage.

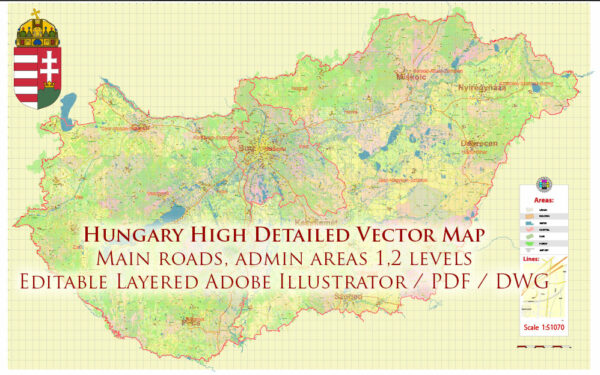
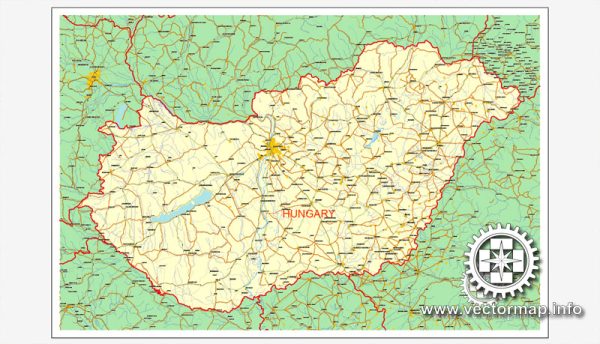
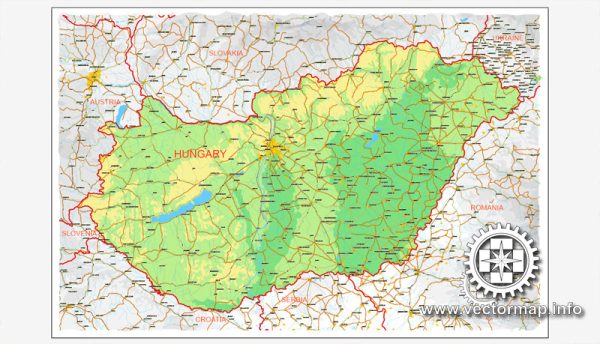
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS