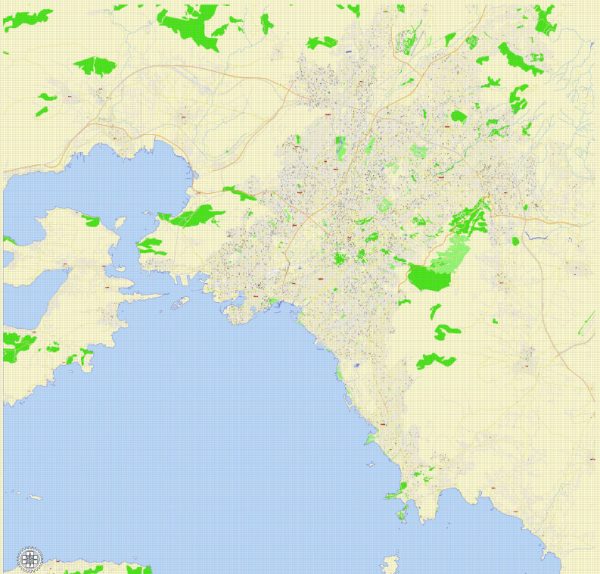
Athens and Piraeus are two interconnected urban areas located in Greece. Here’s a geographical description of both cities:
- Athens:
- Location: Athens is the capital city of Greece and is situated in the southern part of the country.
- Geography: Athens is characterized by a hilly terrain with several small mountains and hills, the most famous being Lycabettus and the Acropolis. These elevated areas offer panoramic views of the city. The city is also close to the Saronic Gulf, which provides a coastal area to the west of the city.
- Climate: Athens has a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Summers are typically very warm and dry, while winters are milder and wetter. This climate is ideal for tourism and outdoor activities.
- Piraeus:
- Location: Piraeus is a major port city and a suburb of Athens. It is located on the Saronic Gulf, making it an essential part of Athens’ maritime activities.
- Geography: Piraeus is primarily a coastal city, and its geography is dominated by its role as a major seaport. The city has a natural harbor, which has been of strategic importance throughout history. The port area is extensive and includes various docks, terminals, and marinas.
- Climate: Piraeus shares the same Mediterranean climate as Athens, with hot and dry summers and mild, wet winters. The proximity to the sea can moderate temperatures, making it a bit more pleasant during the summer months.
Athens and Piraeus are effectively part of the same urban area, with Piraeus serving as the main port for the capital city. They are well-connected by a network of roads and public transportation, including the Athens Metro. The geographical location of these cities has played a significant role in the historical and economic development of Greece, as they have been important centers of trade, culture, and transportation for centuries.





 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS