Geography of Alaska
Alaska occupies the northwestern portion of the North American continent and is bordered only by Canada on the east.
It is one of two U.S. states not bordered by another state; Hawaii is the other. Alaska has more ocean coastline
than all of the other U.S. states combined. About 500 miles (800 km) of Canadian territory separate Alaska
from Washington state. Alaska is thus an exclave of the United States that is part of the continental U.S. and the U.S. West Coast,
but is not part of the contiguous U.S. Alaska is also the only state, other than Hawaii, whose capital city is accessible
only via ship or air, because no roads connect Juneau to the rest of the continent.
The state is bordered by Yukon and British Columbia, Canada to the east, the Gulf of Alaska and the Pacific Ocean
to the south, Russia (Chukotka Autonomous Okrug), Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, and Chukchi Sea to the west,
and the Beaufort Sea and the Arctic Ocean to the north.
Because it extends into the Eastern Hemisphere, it is technically both the westernmost and easternmost state
in the United States, as well as also being the northernmost.
Alaska is the largest state in the United States in terms of land area at 570,380 square miles (1,477,300 km2),
over twice (roughly 2.47 times) as large as Texas, the next largest state, and is the seventh largest country
subdivision in the world, and the third largest in North America, about 20.4% smaller than Denmark’s autonomous
country of Greenland and 17.6% smaller than Canada’s largest territory of Nunavut. If the state’s westernmost
point were superimposed on San Francisco, California, its easternmost point would be in Jacksonville, Florida.
Alaska is larger than all but 18 sovereign nations (it is slightly larger than Iran but slightly smaller than Libya).
Alaska is home to 3.5 million lakes of 20 acres (8.1 ha) or larger. Marshlands and wetland permafrost
cover 188,320 square miles (487,700 km2) (mostly in northern, western and southwest flatlands).
Frozen water, in the form of glacier ice, covers some 16,000 square miles (41,000 km2) of
land and 1,200 square miles (3,100 km2) of tidal zone. The Bering Glacier complex near the southeastern
border with Yukon, Canada, covers 2,250 square miles (5,800 km2) alone.
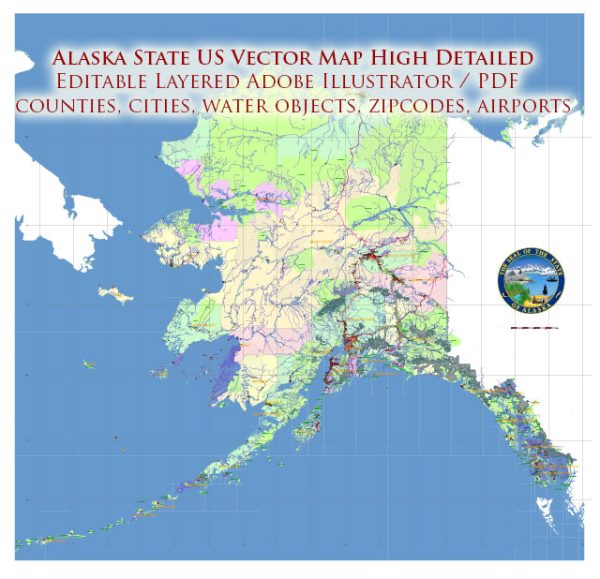
Alaska State US urban layout and transportation infrastructure.
Alaska is characterized by its vast, rugged landscapes and relatively low population density. The state has a few urban centers, with Anchorage being the largest city and economic hub.
Vectormap.Net provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date vector maps in Adobe Illustrator, PDF and other formats, designed for editing and printing. Please read the vector map descriptions carefully.
Here is a brief overview of the urban layout and transportation infrastructure in Alaska:
Anchorage:
- Urban Layout:
- Anchorage is the largest city in Alaska and is located in the south-central part of the state.
- The city is situated between the Chugach Mountains to the east and the Cook Inlet to the west.
- Downtown Anchorage serves as the central business district and cultural hub.
- Transportation Infrastructure:
- Roads and Highways: Anchorage has a network of roads and highways, including the Glenn Highway, Seward Highway, and the New Seward Highway, facilitating transportation within the city and connecting it to other parts of the state.
- Public Transit: The People Mover bus system provides public transportation services within Anchorage. While the city is relatively spread out, public transit is essential for many residents.
- Airport: Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport is a major hub for air travel, connecting Alaska to domestic and international destinations.
Fairbanks:
- Urban Layout:
- Fairbanks is another significant city in Alaska, located in the interior of the state.
- It is situated along the Chena River and is known for its cold winters.
- Transportation Infrastructure:
- Roads and Highways: The Richardson Highway connects Fairbanks to Anchorage and other parts of the state. Other local roads facilitate transportation within the city.
- Public Transit: Fairbanks also has a bus system to serve residents, though public transit options may be more limited compared to larger cities in the contiguous United States.
Other Urban Centers:
- Juneau:
- As the capital of Alaska, Juneau is located in the southeastern part of the state.
- Accessible primarily by air and water due to the mountainous terrain, Juneau has a small road system within the city.
- Ketchikan:
- Situated in the southeastern panhandle, Ketchikan is known for its connection to the Inside Passage.
- Transportation is primarily maritime, with ferries connecting Ketchikan to other coastal communities.
Challenges:
- Alaska’s challenging geography, extreme weather conditions, and vast distances present unique challenges for transportation infrastructure development and maintenance.
- In many rural and remote areas, transportation relies heavily on small aircraft and boats due to the lack of road access.
For the most current and detailed information on Alaska’s urban layout and transportation infrastructure, it is recommended to check with local authorities and official government sources in Alaska.

 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS