Bremerhaven is a port city located in northern Germany, and its history of urban development is closely tied to its maritime and trading roots. Here’s a brief description of the city’s historical urban development:
- Early Settlement: Bremerhaven’s history dates back to the 19th century when it was established as a small fishing village. It was officially founded in 1827 as a subsidiary of the nearby city of Bremen, which sought to expand its access to the North Sea. The name “Bremerhaven” literally means “Bremen’s Harbor.”
- Port Development: The primary catalyst for Bremerhaven’s growth was its strategic location along the North Sea coast, which made it an ideal location for a deep-water harbor. As maritime trade expanded, the city’s port facilities grew to accommodate the increasing shipping traffic, transforming it into a bustling port city.
- Emigration Hub: In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Bremerhaven played a significant role in European emigration, serving as the main point of departure for millions of emigrants heading to the United States and other destinations. The city’s port facilities were crucial for this mass migration.
- Industrialization: The city’s development was further accelerated during the industrialization era. Bremerhaven’s port became a key hub for the import and export of goods, particularly for the transatlantic trade. This led to the growth of associated industries and infrastructure in the city.
- World War II and Reconstruction: Bremerhaven, like many other German cities, was heavily bombed during World War II. Much of the city was destroyed, including its historic center. After the war, extensive reconstruction efforts were undertaken, with an emphasis on modernizing the city’s infrastructure.
- Economic Revitalization: After the war, Bremerhaven continued to thrive as a major port city and an economic center. The city diversified its industries and developed as a center for shipbuilding, ship repair, and the automotive industry.
- Expansion and Modernization: In the latter half of the 20th century, Bremerhaven expanded its port facilities, incorporating advanced container handling technology. The city’s port remains a vital economic engine for the region and the country.
- Cultural and Tourist Development: Bremerhaven also invested in cultural and tourist infrastructure. The city boasts several museums, such as the German Emigration Center and the Klimahaus Bremerhaven 8° Ost, focusing on climate and environmental issues. These attractions have helped attract visitors to the city.
- Urban Redevelopment: In recent years, Bremerhaven has undergone urban redevelopment projects to revitalize the city center, making it more pedestrian-friendly and improving public spaces.
Overall, Bremerhaven’s history of urban development is closely tied to its maritime and industrial heritage. Today, it remains an important port city and a hub for various economic activities, while also offering cultural and tourist attractions to visitors.

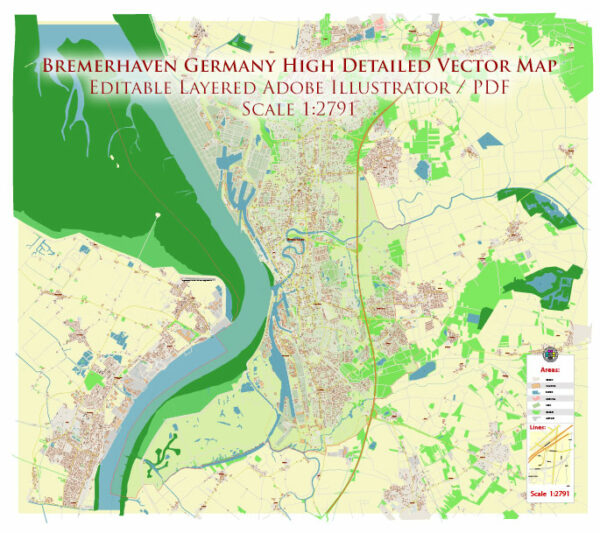
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS