South Africa has an extensive road network that spans the entire country, making it one of the most developed road systems in Africa. The road infrastructure in South Africa is essential for transportation, trade, and connecting various regions within the country. Here’s a general description of South Africa’s road system:
- Road Types:
- National Roads: South Africa’s national road network is managed by the South African National Roads Agency (SANRAL). These roads are typically well-maintained and are major routes connecting different regions of the country. They are identified with the prefix “N” followed by a number (e.g., N1, N2).
- Provincial Roads: Provincial governments are responsible for these roads. They connect major cities and towns within a province and are designated with the prefix “R” followed by a number (e.g., R24).
- Municipal Roads: These roads are managed by local municipalities and are typically within city or town boundaries.
- Road Quality:
- South Africa’s major national and provincial roads are generally of good quality, with multiple lanes, smooth surfaces, and modern infrastructure.
- Some rural and municipal roads may not be as well-maintained and could have potholes, uneven surfaces, and other issues, especially in less developed areas.
- Toll Roads:
- South Africa has an extensive network of tolled roads, particularly on major national routes. Toll fees vary depending on the distance traveled, and electronic toll collection systems are in place on some routes.
- Road Safety:
- South Africa has a relatively high rate of road accidents and fatalities. Drivers are advised to exercise caution, obey speed limits, and be vigilant while driving, especially in rural areas.
- Road Signage:
- Road signage in South Africa is generally in English, with some signs in other official languages like Afrikaans. Signs follow international standards, and important information is often presented in pictograms to accommodate non-English speakers.
- Public Transportation:
- South Africa has an extensive public transportation system, including buses, minibus taxis, and commuter trains, which play a significant role in urban and intercity travel.
- Infrastructure Projects:
- South Africa has ongoing infrastructure development projects to improve and expand its road network. These projects aim to reduce congestion, improve safety, and enhance connectivity.
- Border Crossings:
- South Africa shares land borders with several neighboring countries, and there are border crossings with customs and immigration facilities for international travel.
- Scenic Routes:
- South Africa is known for its beautiful scenic routes, including the Garden Route along the southern coast, the Panorama Route in Mpumalanga, and the Drakensberg Mountain passes.
- Vehicle Requirements:
- Vehicles in South Africa drive on the left side of the road. It is essential to have a valid driver’s license and proper documentation when driving in the country.
- Traffic Rules:
- South Africa follows standard international traffic rules, including obeying speed limits, wearing seat belts, and not using mobile phones while driving.
Please note that road conditions and regulations may change over time, so it’s essential to check for the latest information and travel advisories before planning a trip or driving in South Africa.

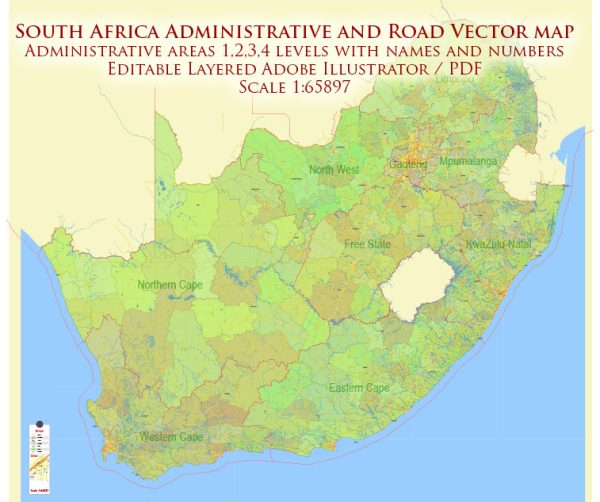
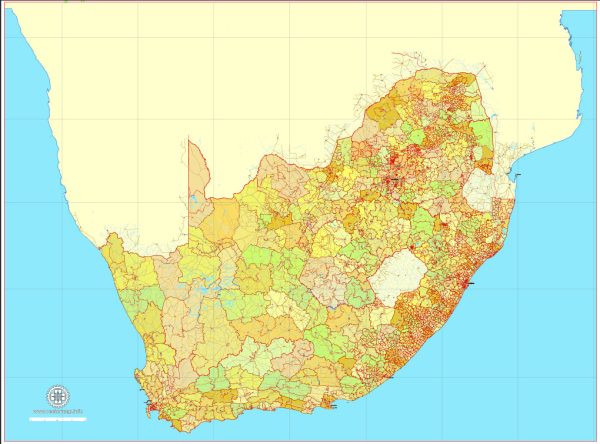
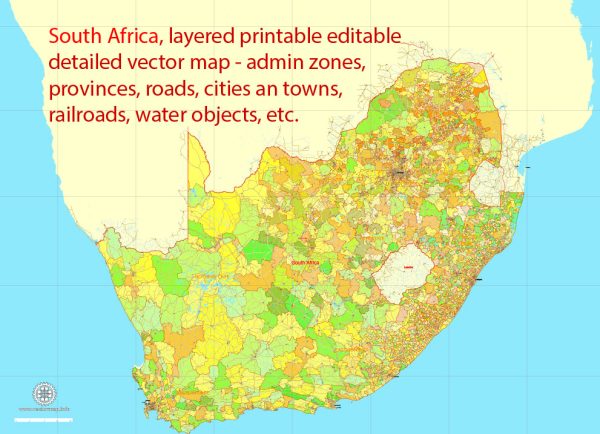
 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS