French wine agriculture, often referred to as viticulture, is renowned worldwide for its long history, diverse terroirs, and commitment to producing high-quality wines. France is one of the most prominent wine-producing countries in the world, and its viticultural practices are deeply rooted in tradition. Here is an overview of French wine agriculture:
- Terroir: Terroir is a fundamental concept in French winemaking. It refers to the combination of natural factors that influence a wine’s character, including the soil, climate, topography, and the grapevine’s interaction with these elements. French vineyards are known for their specific terroirs, which contribute to the unique flavors and qualities of their wines.
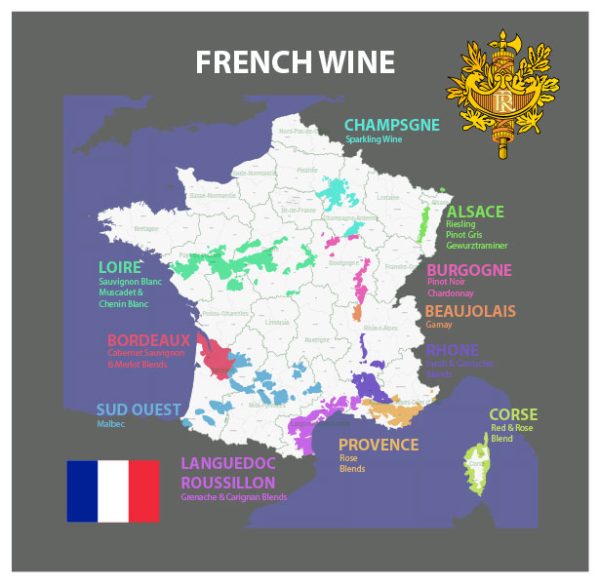
- Grape Varieties: France is home to a wide range of grape varieties, each associated with specific wine regions. Some of the most famous include Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in Bordeaux, Chardonnay and Pinot Noir in Burgundy, and Syrah in the Rhône Valley.
- Appellations: France has a highly regulated appellation system that categorizes wine based on its origin, grape varieties, and winemaking methods. The Appellation d’Origine Contrôlée (AOC) system ensures that wines produced in specific regions adhere to strict quality and production standards.
- Vineyard Management: French vineyard management practices vary depending on the region and terroir. Techniques include pruning, trellising, and canopy management to optimize grape quality and yield. Many vineyards are managed manually or with minimal mechanical intervention.
- Harvesting: The timing of the harvest is crucial in French wine agriculture. It is determined by factors such as grape ripeness and weather conditions. Grapes are often hand-picked to ensure that only the best fruit is selected for winemaking.
- Wine Production: Traditional winemaking methods are used in France. Red and white wines are typically fermented in stainless steel, concrete, or wooden vats. French oak barrels are widely used for aging, which can impart specific flavors and textures to the wine.
- Wine Classification: French wines are classified into different quality levels. The hierarchy starts with Vin de Table (table wine) and progresses through Vin de Pays (country wine), AOC, and higher-quality designations such as Premier Cru and Grand Cru in Burgundy.
- Wine Regions: France has many renowned wine regions, each with its own distinct characteristics. Some of the most famous include Bordeaux, Burgundy, Champagne, the Loire Valley, the Rhône Valley, and Provence. These regions produce a wide variety of wine styles.
- Sustainable Practices: In recent years, there has been a growing focus on sustainable and organic viticulture in France. Many winemakers are adopting environmentally friendly practices to protect their terroirs and promote biodiversity.
- Cultural Significance: French wine is deeply intertwined with the country’s culture, history, and cuisine. It plays a central role in French life, with wine often enjoyed at family gatherings, celebrations, and daily meals.
French wine agriculture is not just about producing wine; it’s about preserving tradition and respecting the unique qualities of each region’s terroir. This commitment to quality and authenticity has made French wines highly regarded and sought after around the world.

 Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS
Author: Kirill Shrayber, Ph.D. FRGS