Urban plan Toledo Spain pdf: Editable Maps
Gallery of Images "Urban plan Toledo Spain pdf" :
Video: Simple Manual for Vector Maps Work
Urban plan Toledo Spain pdf: Digital Cartography in Vector Formats
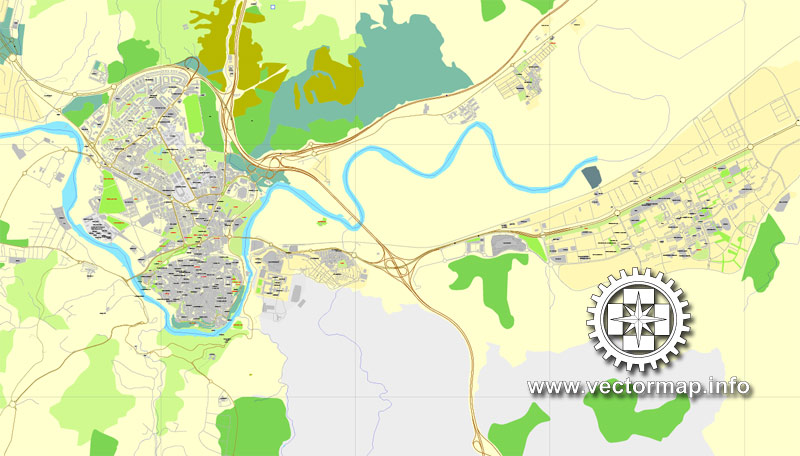
Toledo, a city in the central part of Spain, is the administrative center of the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha and the province of Toledo. Population: 60.3 thousand people (2020; the population of the municipality is 85.8 thousand people). Located in the central part of the Castilian plateau, on the Tagus River, 68 km southwest of Madrid. Junction of highways; railway station (high-speed railway connection with Madrid).
History
In ancient times, the settlement of the Celtic tribe of Carpetans, conquered in the 2nd century BC by the Romans. It was mentioned in 193 BC as the Roman city of Toletum. In 411 AD it was taken by the Alans, in 418 by the Visigoths, since the middle of the 6th century the capital of the Visigothic Kingdom, the center of the archbishopric (metropolis). In 711 it was captured by Muslim Arabs, and in 1085 it was recaptured by Alfonso VI the Brave. It developed as a center of crafts, primarily the manufacture of metal products. Until 1561, one of the residences of the Castilian (Spanish) kings. With the outbreak of the Civil War of 1936-39, the Republicans controlled the city, in July – September 1936 they unsuccessfully besieged the medieval fortress of Alcazar, in which about 1 thousand supporters of F. took refuge. Franco and several hundred civilians; in September 1936 Toledo was taken by the Francoists. Since 1982, the center of the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha.
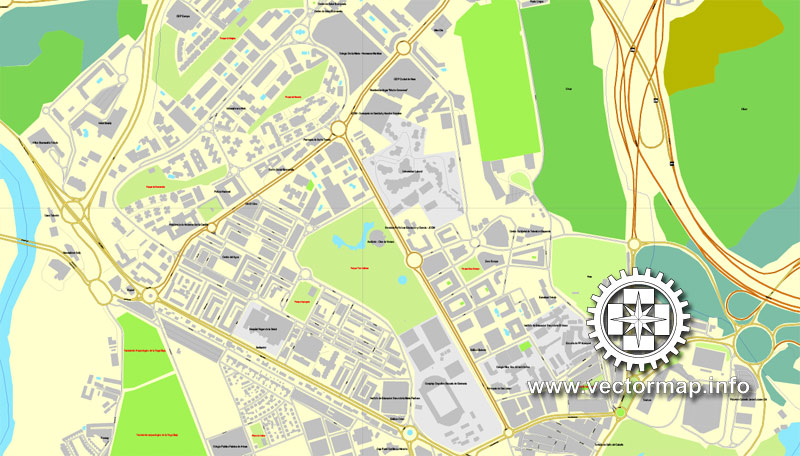
Architecture
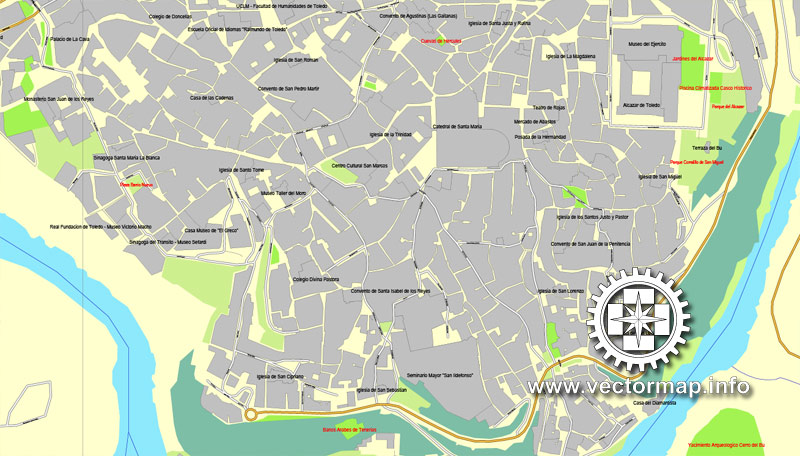
Ancient Roman structures: aqueduct, Puente de Alcantara Bridge (2nd century BC), ruins of circus, amphitheater. The city fortifications with entrance gates have been preserved - Puerta de Bisagra Antica (10th century), Puerta Bab al Mardum (10th century), Puerta del Sol (14th century), Puerta Nueva de Bisagra (1559, architect A. de Covarrubias), Puerta del Cambron (1576), etc. Among the medieval buildings: the former mosques of Cristo de la Luz (999) and Mesquita de las Tornerias (11th century), the fortress of San Servando (founded as a monastery in 1024, a fortress from 1088, reconstructed at the beginning of the 21st century), the monastery of Santo Domingo el Antiguo (1085), the bridge of San Martin (14th century).
In the Mudejar style: the churches of Santo Tome (12th century, in the interior painting "The Funeral of Count Orgas" by El Greco, 1586-88), San Roman (early 13th century, apse with dome, architect Covarrubias, now the Museum of the Church and Visigothic Culture, 1969) and Santiago del Arrabal (1245-48), Galiana Palace (13th century), monasteries of St. Ursula (14th century) and San Juan de los Reyes (1477-1526, in the style of Isabelino). Goth. Cathedral of Our Lady [1226-1493, architects - Master Martin, P. Perez, R. Alfonso, A. Martinez; in the interior there is a grandiose sculptural and picturesque retablo (1498-1504), a baroque altar of El Transparente (1729-1732, master N. Tome); works by El Greco]. In the former Jewish quarter of Huderia, one of the oldest synagogues in Europe is Santa Maria la Blanca (Ibn Shushan, 1180, an example of Almohad architecture, now a museum), the Synagogue del Transito (mid-14th century, in the interior – rich knock decor; now the Sephardic Museum, 1964).
Other architectural monuments include the Alcazar Fortress (the medieval building was rebuilt in the 1540s in the Renaissance style, then in the 16th-18th centuries, reconstructed in the 20th century), the Archbishop's Palace (13th century, rebuilt in 1541-43, arch. Covarrubias), hospitals "Santa Cruz" (16th century; now a museum, 1961) and "Tavera" (1541-1603, architects Covarrubias, B. Bustamante, now the museum of the Lerma Foundation and other institutions), the church of San Ildefonso (1629-1765) in the Baroque style, the building "Teatro de Rojas" (1866-78, architect L. A. Fenech). The historical center of the city is included in the World Heritage List.
Centers of Science and Culture
The campus of the University of Castile-La Mancha (Ciudad Real; dates back to the Royal University in 1520); Infantry Academy (1850).
Museums: the military (traces its history back to the Royal Military Museum in Madrid, 1803; originated as a result of the merger of several military museums), the Cathedral (1900), the Art Museum "Victorio Macho" (1967), Art Nouveau and Modern art (1977). El Greco House Museum (1911; collection of the artist's works). The multi-genre "Teatro de Rojas" (1878; named after the 17th century Toledo playwright V. F. de Rojas).
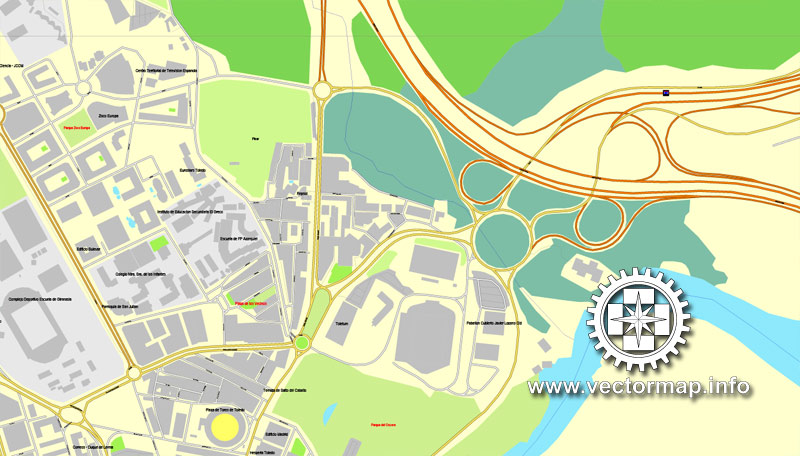
Sport
Toledo Football Club (founded in 1928), performs at the Salto del Caballo Stadium (opened in 1973; 5.5 thousand seats).
Toledo Economics
The basis of the economy is the service sector; its leading sectors are administrative services, tourism business, and healthcare. One of the most visited cities in Spain by tourists (598.9 thousand people, 2019). Important employers in the city include the San Ildefonso Medical Center, the National Hospital for the Paralyzed, and the General Hospital.
Aviation industry: Production of wing components, aft fuselage, including for Eurofighter combat aircraft (Airbus plant in Illescas northeast of Toledo). Food industry (processing of local horticulture and viticulture products). The historical center of metallurgical and weapons (sabers, knives, armor) production.
Gallery of Images "Urban plan Toledo Spain pdf":
Toledo Spain Editable Maps: For tourism, business, and logistics


Spain Editable Maps Collection: Digital Cartography
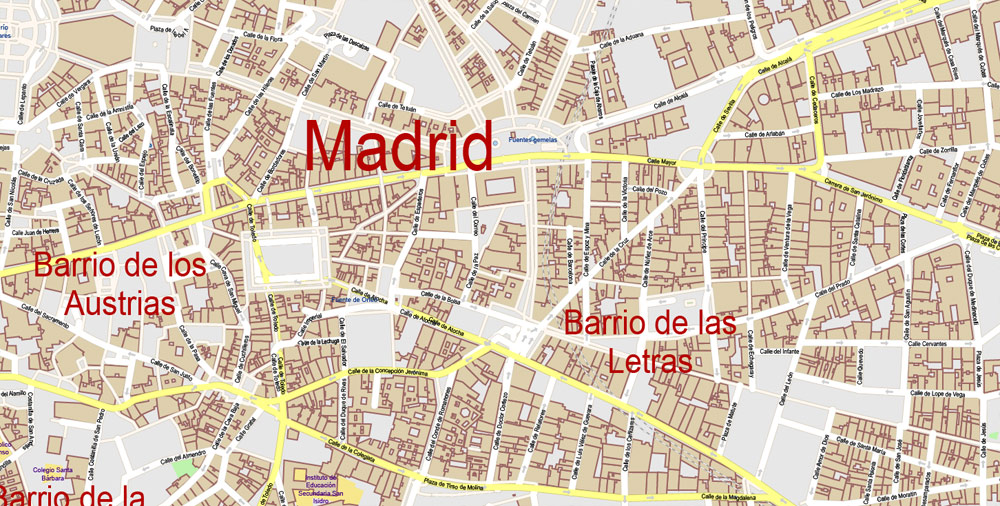
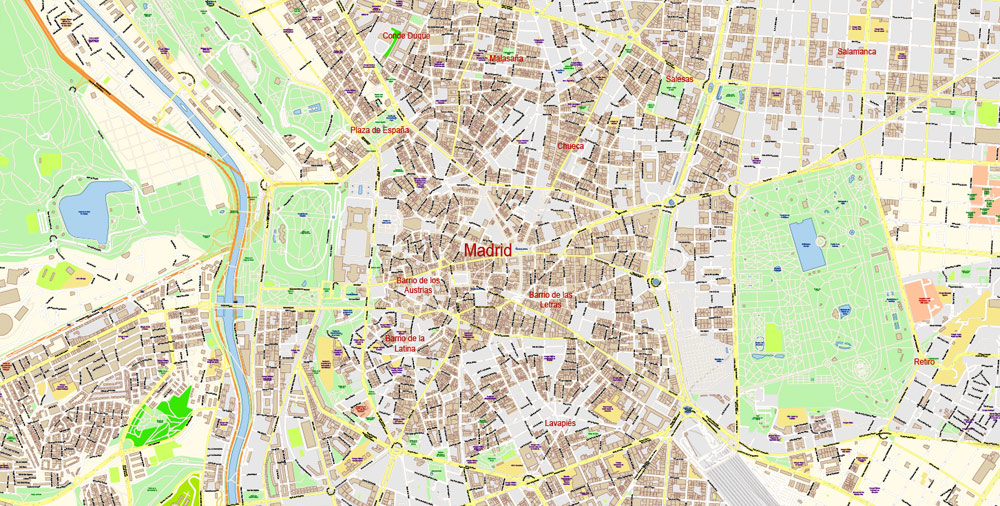
Printable maps of the SPAIN: City Plans for tourism, business and education
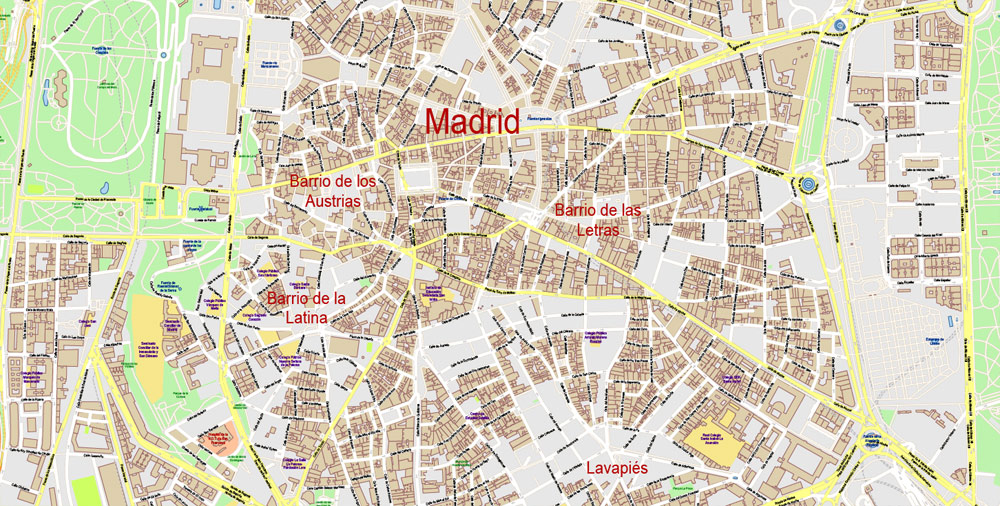
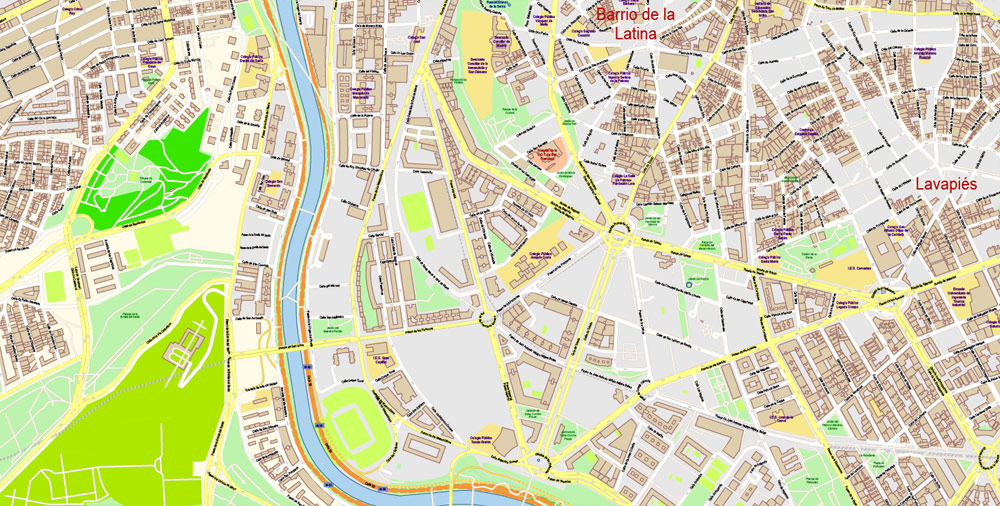
- Urban plan Harrisburg Pennsylvania
- Urban plan Wellington New Zealand 3 11 PDF
- Urban plan Baku Azerbaijan
- Urban plan Karlsruhe PDF
- Urban plan Lille France
- Urban plan South America Topo
- Urban plan Dover Delaware PDF
- Urban plan Linz Austria PDF
- Urban plan San Francisco Bay California
- Urban plan Gyumri Armenia autocad
- Urban plan Melbourn Australia
- Urban plan Orlando Florida ai
- Urban plan Norfolk Virginia Beach
- Urban plan San Antonio Texas ai
- Urban plan Canberra Australia 17
- Urban plan Onancock Virginia PDF
- Urban plan Charleston South Carolina
- Urban plan Oxford UK
- Urban plan grande Paris France 13 AI
- Urban plan Biertan Romania PDF
- Urban plan New York City 14 AI
- Urban plan Kazan PDF Russia
- Urban plan Genova Genoa Italy
- Urban plan Vienna
- Urban plan Liege Belgium pdf
- Urban plan Colorado State PDF
- Urban plan Los Angeles
- Urban plan Charleston South Carolina PDF
- Urban plan Sacramento California ai
- Urban plan Yaroslavl
- Urban plan Cardiff Newport Wales UK PDF
- Urban plan Geelong Australia
- Urban plan Birmingham Alabama
- Urban plan Macau China 125 PDF
- Urban plan Kalamazoo County Michigan
- Urban plan Reno Nevada PDF
- Urban plan Manhattan New York City
- Urban plan Terre Haute Indiana pdf
- Urban plan Cannes France
- Urban plan Cape Canaveral Florida
- Urban plan Murmansk PDF Russia
- Urban plan Belgium Administrative
- Urban plan Washington Baltimore PDF
- Urban plan Kansas City Missoury
- Urban plan Indianapolis
- Urban plan Raleigh Chapel Hill Durham North Carolina
- Urban plan Stockholm Sweden ai
- Urban plan Hamburg CDR
- Urban plan Rome Italy
- Urban plan Lyon France
- Urban plan Czech Republic Admin
- Urban plan Tulsa Oklahoma
- Urban plan Mcallen Texas PDF 3 10
- Urban plan Portland Oregon 25
- Urban plan Smolensk pdf
- Urban plan Cincinnati Ohio
- Urban plan Portland Oregon
- Urban plan Utrecht Netherlands pdf
- Urban plan New York City 15 AI
- Urban plan Basel Switzerland CDR
- Urban plan Charleston South Carolina 3 10 CDR
- Urban plan Mykonos Island PDF
- Urban plan Detroit Michigan